Table of Contents
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is heat stored inside the Earth’s crust. The centre of the Earth remains very hot due to nuclear fusion. This heat can melt rocks, causing them to rise and collect in “hot spots.” When underground water reaches a hot spot, it turns into steam, and sometimes this hot water flows to the surface, creating hot springs.
The Earth has a lot of thermal energy, but only a part of it used. Geothermal Energy is used in places where the geology allows water (either liquid or steam) to bring heat from deep hot areas to the surface. This creates geothermal resources. Other sources of geothermal energy include hot springs, geysers, and deep wells that are drilled 1 to 3 kilometers deep.
Read about: Nuclear Power Plants in India
Geothermal Energy Extraction Method
Wells that are 1.6 kilometres deep or more are drilled into the ground to tap into hot water and steam for making geothermal electricity. These hot water and steam power turbines are connected to generators that produce electricity. Geothermal electricity started in Larderello, Italy, in 1904. Here are the methods to extract geothermal heat.
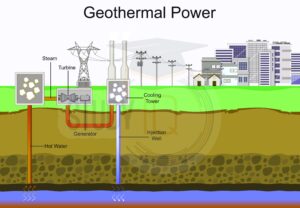
Hydrothermal Heat Source
Water seeps into the ground from rain or surface sources like rivers, lakes, or glaciers, and it gets heated by hot rocks below due to volcanic or seismic activity. This is why places like the Himalayas, the Alps, and Iceland have hot springs. For the water to move easily and bring hot water to the surface, the ground in the area needs to be porous.
Deep Geothermal System
Deep geothermal systems, include drilling a deep borehole to access hot basal rock and injecting water into the holes to generate steam. Using this method of resource extraction, a turbine is powered. Due to the high cost of accessing the deep base rock substrate, this method is rarely used.
Read about: Hydropower Plants in India
Geothermal Energy in India
Research and exploration for geothermal energy in India started in 1970. The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has identified 350 areas in the country where geothermal energy can be found. The Puga Valley in Ladakh is one of the most promising locations. According to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), India has a potential for about 10 gigawatts (GW) of geothermal energy, and these resources have been mapped out.
| Geothermal Facility | Place |
| Himalayas | J&K, Himachal Pradesh and Sikkim; PUGA hot spring in J&K and Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh. |
| Sohana | Haryana, Rajasthan. |
| Son-Narmada-Tapi (SONATA) | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand; Tattapani spring in Chhattisgarh. |
| Cambay | Mainly Gujarat and some parts of Rajasthan |
| Godavari | Andra Pradesh |
| Mahanadi | Odisha, Taptapani Spring in Odisha. |
| Major Geothermal Sites in India | |
| Geothermal Site in India | Location |
| Puga valley | Ladakh |
| Chummathang | Ladakh |
| Cambay | Gujarat |
| Tattapani | Chattisgarh |
| Khammam | Telangana |
| Ratnagiri | Maharashtra |
Read about: Nuclear Energy
Geothermal Energy Advantages
The benefits of using geothermal energy are listed below:
- Geothermal Energy emits only one-sixth as much CO2 as a natural gas plant, it is a cleaner fuel.
- Being unlimited and unending due to the constant flow of heat from the Earth, Geothermal energy is a renewable resource.
- Geothermal Energy is the only renewable energy source that is always available to humans, unaffected by day-night or seasonal fluctuations, and does not require storing.
- Geothermal Energy is essential to develop new energy sources, such as geothermal energy, given the need to replace power produced by coal with other energy sources.
- Geothermal energy can be used as a primary source of power as well as a replacement for electricity as a source of heat, depending on the geothermal characteristics and regional geographic conditions.
- Geothermal Energy is a site-specific renewable energy source that is great for supplying rural or interior populations’ energy demands.
- Geothermal heat pump systems use less room for equipment and consume 25% to 50% less electricity than conventional systems for heating or cooling.
- Hot spring mineral byproducts including silica, borax, and caesium may be employed.
Read More: Biomass Energy
Geothermal Energy Disadvantages
The following list contains the drawbacks of using geothermal energy.
- Geothermal has been associated with other pollutants like sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide despite producing minimal carbon dioxide.
- In the regions where they operate, geothermal generating facilities alter the topography and generate rifts and mild earthquakes. Building in a certain location is expensive upfront. It is sometimes referred to as “the most location-specific energy source known to man” due to its activity along the tectonic plates of the globe.
- Exploring and drilling for geothermal energy to set up power plants is more expensive than other energy sources like oil and gas.
- Most geothermal hotspots are located in remote areas, making it even more expensive to transport the energy.
- Building power plants to use geothermal heat can lead to pollution of groundwater around the plant.
Read about: Solar Energy
Examples of Geothermal Energy:
Below are some examples of Geothermal energy:
- Hot Springs: These occur when heated groundwater rises to the surface.
- Lava Fountains: Found in active volcanoes, these fountains shoot magma from the ground.
- Geysers: Similar to hot springs, geysers force heated water out of the ground in bursts.
- Mud Pots or Mud Pools: These are acidic hot springs with little water, where acid and tiny organisms break down rocks, creating bubbling mud.
- Hydrothermal Vents: These are openings on the ocean floor that release hot water. When this hot water meets cold seawater, it creates a large cloud of steam.
Geothermal Energy Government Initiatives
- The government plans to give a capital subsidy of up to 30% for industrial projects.
- Chhattisgarh’s first geothermal power plant is a joint effort between NTPC and the state’s renewable energy agency (CREDA) at the Tattapani geothermal field.
- For research and development of geothermal energy in India, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) provides important support and subsidies.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has found that India has the potential for 10,000 MW of geothermal energy.
Read about: Wind Energy
Geothermal Energy UPSC
Due to the high cost of geothermal discovery, financial incentives may be introduced to promote the investigation of geothermal resources. Funding for exploration will motivate exploration organisations to undertake geothermal energy projects for electricity production and direct heat use. Additionally, it will draw private financiers for the expansion of geothermal energy. To entice private companies to develop geothermal energy in India, it may be urged to use foreign financing, knowledge transfer, and appropriate financial incentives.
India’s research has thus far mainly been surface-level, leaving a data gap for the design of power projects. Deciphering the properties of deep reservoirs is crucial for figuring out whether certain resources are viable for use in the production of electricity. Geothermal energy can help developing nations combat climate change while also raising living standards if there is strong international cooperation and backing from wealthy nations.


 Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre, Date, History...
 Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
Important Lakes of India, State wise and...
 Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...
Buddhism History, Origin, Sect, Councils...





















