Table of Contents
GAGAN, which stands for GPS-Aided GEO Augmented Navigation, is a pioneering initiative by the Indian government aimed at enhancing satellite-based navigation services within India. In collaboration with the Airports Authority of India (AAI) and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), GAGAN has been developed as a regional Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) with the primary objective of ensuring precise and safe aircraft navigation in the Indian airspace and neighboring regions. Know All about GAGAN in this Article by Scrolling down.
GAGAN Overview
GAGAN, short for GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation, is a collaborative effort between ISRO and AAI, aimed at providing enhanced navigational services over the Indian Flight Information Region (FIR), with potential expansion to neighboring regions. It operates as a Space-Based Augmentation System (SBAS), utilizing a network of satellites and ground stations to improve the accuracy of GPS signals.
The GAGAN system is operational and utilizes payloads on satellites, including GSAT-8 and GSAT-10, with a third payload scheduled for launch in GSAT-15. This remarkable project has been implemented in three phases since 2008, with an estimated cost of Rs 7.74 billion (approximately $117 million).
Key Features of GAGAN
Unique Certification
GAGAN is the world’s first Satellite-Based Augmentation System certified for approach with vertical guidance, specifically tailored for the equatorial ionospheric region.
Wide Coverage
GAGAN extends its services from Africa to Australia and possesses the capacity for seamless navigation services across the entire region.
Enhanced Accuracy and Safety
GAGAN significantly improves navigation accuracy, availability, and integrity for all phases of flight, from en route to airport approach. This not only enhances air safety but also makes airline operations more efficient and cost-effective.
Reduction in Ground Aids
With the provision of vertical guidance at runways, GAGAN eliminates the need for certain ground-based navigation aids, resulting in cost savings and reduced workload for airline crew and air traffic controllers.
Ionospheric Studies
The GAGAN project includes the study of ionospheric behavior over the Indian region, with ISRO developing the GAGAN ionospheric algorithm. This capability places India among the select few countries in the world with precision approach capabilities.
Cross-Sector Benefits
While initially developed for aviation, GAGAN’s precision navigation services have the potential to benefit other sectors such as transportation, railways, surveying, maritime, highways, the telecom industry, and security agencies.
GAGAN’s Objectives
GAGAN aims to achieve the following key objectives:
- Deliver satellite-based navigation services.
- Enhance air traffic management within Indian airspace.
- Facilitate precise aircraft landings in Indian airspace and its vicinity.
- Elevate air safety standards and fuel efficiency.
- Provide accuracy comparable to ground-based landing systems, enabling aircraft to land safely at smaller and regional airports without costly ground-based equipment.
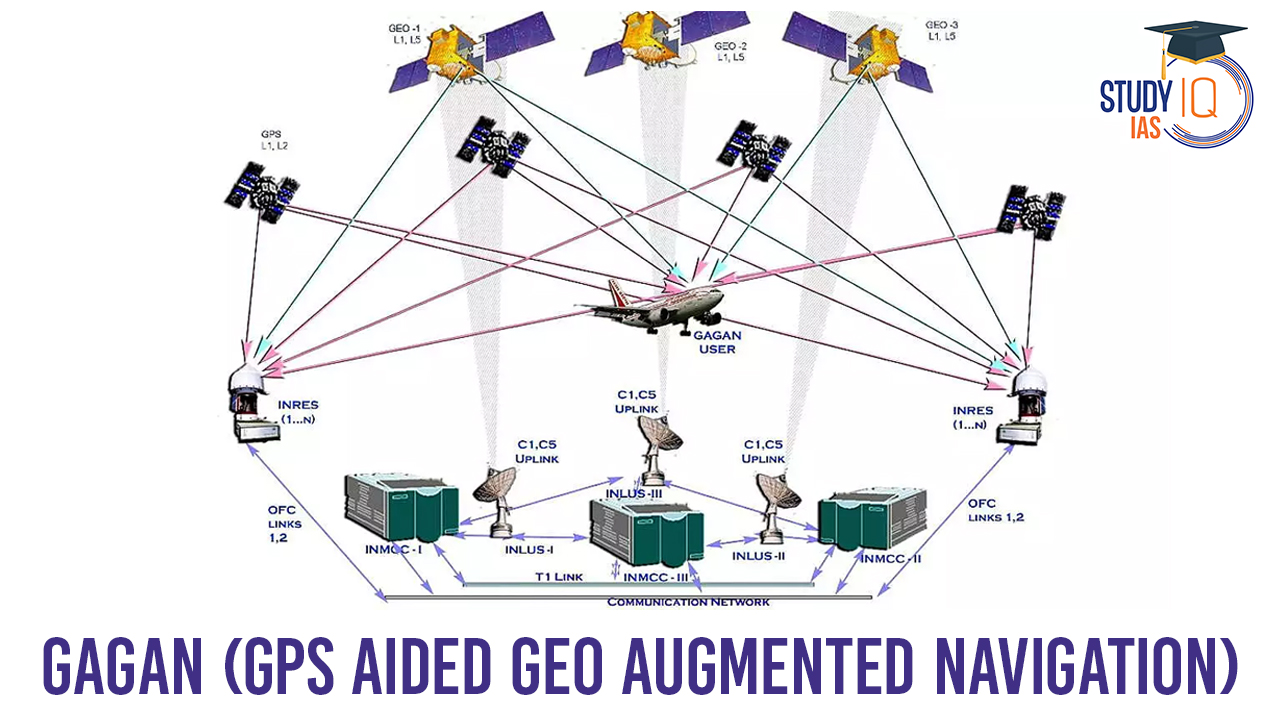
How does GAGAN work?
- It utilizes a network of ground reference stations across India known as Indian Reference Stations (INRES) to collect GPS satellite data.
- Data from these reference stations is gathered at the Indian Master Control Centre (INMCC), where GPS correction messages are generated.
- Corrected differential messages are transmitted via the Indian Uplink Station (INLUS) and broadcasted through three geostationary satellites (GSAT-8, GSAT-10, and GSAT-15).
- The information transmitted is compatible with the standard GPS signal structure, allowing any SBAS-enabled GPS receiver to interpret it.
GAGAN Coverage Area
GAGAN’s coverage extends across a vast region, from Africa to Australia, and has the capability to support up to 45 reference stations for expansion into neighboring countries.
GAGAN Navigation Accuracy
GAGAN provides a civil aeronautical navigation signal that complies with ICAO Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) established by the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Panel. It offers both non-precision approach (NPA) service accurate to within 1/10th of a nautical mile (Required Navigation Performance or RNP-0.1) over the Indian FIR and precision approach service of APV-1.0 (Approach with Vertical guidance) over the Indian landmass on nominal days.
GAGAN Interoperability
GAGAN is designed to be interoperable with other international SBAS systems, including the S. Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS), the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS), and the Japanese MTSAT Satellite Augmentation System (MSAS). This interoperability ensures seamless air navigation across regional boundaries.
GAGAN vs NavIC
| GAGAN (GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation) | NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) | |
| Purpose | Augments GPS signals for improved accuracy and integrity, primarily for aviation and civil operations. | Provides independent regional satellite navigation and positioning services, serving various sectors including transportation, agriculture, disaster management, and more. |
| Type | Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) | Regional Navigation Satellite System (RNSS) |
| Developed By | Collaboration between ISRO and AAI (Airports Authority of India) | Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) |
| Coverage Area | Primarily covers Indian airspace and neighboring regions. | Provides regional coverage extending up to approximately 1,500 kilometers from India’s borders. |
| Global Compatibility | Interoperable with other international SBAS systems. | Primarily designed to serve India and surrounding regions, not intended for global use. |
| User Applications | Mainly focused on civil aviation, but also benefits sectors like forestry, railways, scientific research, and more. | Has a wide range of applications, including transportation, agriculture, fishing, disaster management, and location-based services. |
| Satellite Constellation | Utilizes geostationary satellites for signal correction and broadcast. | Comprises a constellation of seven geosynchronous satellites, including one in geostationary orbit, to provide continuous regional coverage. |
| System Maturity | GAGAN is operational and in use. | NavIC is operational and available for public use. |
| Precision | Provides improved accuracy for GPS signals but is primarily focused on aviation. | Offers precise positioning and navigation services, suitable for various applications. |
| Independence | Relies on GPS for its core positioning, augmented with corrections by the Indian system. | Offers independent positioning and navigation services using its constellation of Indian satellites. |
| Expansion | Limited to the Indian FIR and neighboring regions. | Intended for regional use but has the potential for broader regional expansion. |
Importance of GAGAN
- GAGAN, or GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation, offers precise satellite-based navigation services.
- It boosts air traffic management by providing accurate guidance and routing within Indian airspace.
- The system ensures safer landings for aircraft in and around India, including smaller airports.
- It significantly improves aviation safety, reducing the risk of accidents during crucial flight phases.
- GAGAN’s versatility extends beyond aviation, benefiting forestry, agriculture, railways, maritime navigation, disaster management, and more.
- It reduces India’s reliance on foreign navigation systems, fostering national self-reliance.
- The system is compatible with other international SBAS, facilitating seamless cross-border air navigation.
- Cost savings are realized by eliminating the need for some expensive ground-based landing equipment at airports.
- GAGAN elevates India’s position in the global space technology and navigation landscape.
GAGAN UPSC
GAGAN, or GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation, is a collaborative initiative between the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and the Airports Authority of India (AAI). It is a regional Satellite-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) designed to improve satellite-based navigation services over the Indian Flight Information Region (FIR) and potentially extend its coverage to neighboring regions. GAGAN enhances navigation accuracy, promotes air safety, reduces dependence on ground-based systems, and has a wide range of applications beyond aviation, including forestry, railways, maritime navigation, and disaster management. It is a significant technological advancement in satellite-based navigation and positioning services.

 AI and its Regulation in India, Limitati...
AI and its Regulation in India, Limitati...
 Tuberculosis (TB), Symptoms, Causes and ...
Tuberculosis (TB), Symptoms, Causes and ...
 Silicon Photonics Enables Low-power AI A...
Silicon Photonics Enables Low-power AI A...





















