Table of Contents
The environment encompasses all the external conditions, resources, and stimuli that an organism interacts with, shaping both its habitat and the broader ecosystem. It includes physical elements (like air, water, and soil), biological components (like plants, animals, and microorganisms), and chemical processes (like the carbon and nitrogen cycles). The environment is essential for the survival and development of all life forms, as it provides the necessary resources for food, water, shelter, and energy. Understanding the environment and its various functions is crucial to maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the sustainability of life on Earth. However, human activities and natural changes have created numerous challenges, such as pollution, deforestation, climate change, and global warming, which threaten the health of the environment. In this article, we will explore the definition, functions, types, challenges, and possible solutions for protecting and preserving the environment.
What is the Environment?
The environment refers to the external conditions, resources, and stimuli that organisms interact with, shaping their habitat and ecosystem. It includes both living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components that influence the life processes and survival of organisms.
Organisms depend on the environment for their basic physical needs such as:
- Food
- Water
- Oxygen
- Energy
- Shelter
Definition of Environment
In a biological sense, the environment refers to the physical (nutrients, water, and air), biological (biomolecules, organisms), and chemical (chemical cycles like the carbon and nitrogen cycles) factors that impact organisms or groups of organisms.
Function of Environment
Environment performs various functions in day to day life of humans that directly or indirectly affects the living organisms:
Supply of Resources
- Production is the process of transforming raw materials into useful things. The environment provides natural resources that are used as inputs or raw materials in manufacturing. The environment provides two different sorts of resources: renewable and non-renewable.
- Renewable Resources: They are those that can be used for a lifetime without being depleted or exhausted. For example, oxygen, sunlight, etc.
- Non-renewable Resources: These are those that can be depleted over a period of time because of extraction and use. For example, coal, fossil energy, etc.
Natural Waste Management
Waste is a byproduct of consumption and production, and the majority of it is rubbish. The ecology takes up all of this trash by the process of decomposition. The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is in the Pacific Ocean between Hawaii and California is the biggest example of it.

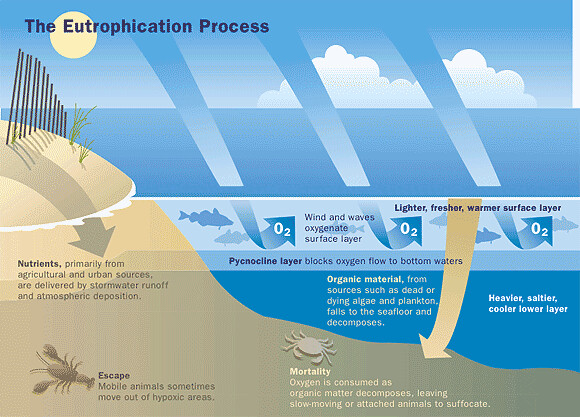
But the environment can only assimilate biodegradable wastes and non-biodegradable waste causes environmental pollution one such example is eutrophication
Sustains Life
Light, earth, oxygen, and water are all components of the environment that are essential for human existence to survive. Therefore, the environment supports life by offering these essential components. It also helps in sustaining life by providing biodiversity and genetics.
Improves Quality of Life
The environment is made up of things like soil, water, rain, mountains, deserts, and so forth. Each of these components helps to keep our surroundings beautiful and vibrant. The fact that these surroundings assist them raise their standard of living makes people respect them. These functions can be carried out without interruption as long as the demand falls within the environmental carrying capacity.
Types of Environment
The environment can be divided as – Natural, Anthropogenic or Built both have been discussed below in detail:
| Type of Environment | Description | Components | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Natural Environment | Refers to all naturally occurring elements and systems that support life. It includes both living and non-living components that interact with each other. | – Biotic: Plants, animals, microorganisms – Abiotic: Air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature |
– Forests, rivers, oceans – Mountains, deserts, glaciers – Coral reefs, grasslands |
| A. Terrestrial Environment | Land-based ecosystems that support various life forms and natural processes. | – Forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras – Soil, minerals, and rocks |
– Amazon Rainforest, Sahara Desert, Himalayan Mountains |
| B. Aquatic Environment | Water-based ecosystems include freshwater and marine systems. | – Oceans, seas, rivers, lakes, ponds – Marine life, coral reefs, plankton |
– Indian Ocean, Great Lakes, Ganga River |
| C. Atmospheric Environment | The layer of gases surrounding the Earth supports life and regulates climate. | – Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide – Weather patterns, winds, humidity |
– Earth’s atmosphere, ozone layer |
| D. Biological Environment | Interaction of living organisms with each other and their physical surroundings. | – Plants, animals, microorganisms – Ecosystem, food chain |
– Tropical forests, savannahs, wetlands |
| 2. Anthropogenic (Built) Environment | Human-made structures and systems that alter the natural environment. | – Urban areas, infrastructure, agriculture – Industrial zones, transportation networks |
– Cities, roads, factories – Farmlands, ports, dams |
| A. Urban Environment | Densely populated areas with advanced infrastructure and public services. | – Buildings, roads, transportation – Communication, utilities |
– New York City, Tokyo, Mumbai |
| B. Industrial Environment | Areas dedicated to manufacturing, production, and economic activity. | – Factories, warehouses, refineries – Heavy machinery, industrial zones |
– Steel plants, oil refineries |
| C. Agricultural Environment | Land used for farming and food production. | – Croplands, irrigation systems – Fertilizers, pesticides |
– Wheat fields, rice paddies |
| D. Recreational Environment | Human-created spaces for relaxation and leisure activities. | – Parks, sports facilities, gardens – Resorts, amusement parks |
– Central Park, Disneyland |
Natural Environment
- A habitat found in nature is referred to as a natural environment. All naturally existing objects, both living and nonliving, are included. As a result, it entails intricate interactions among weather, climate, living things, and natural resources.
- Based on the components, the Natural environment can also be classified into
- Aquatic environment (oceans and seas, lakes and rivers),
- Marine environments are the largest known environments as they are distinguished by the presence of water with a high salt content the 97% of the water on Earth is found in marine environments. Marine environments support communication between organisms and their physical surroundings.
- Because they serve as a significant supply of resources and sustenance, these habitats are very significant to humans. Threats posed by human activity to the marine environment include warming, acidification, and marine pollution.
- Terrestrial environment (land)
- Terrestrial environments are those that can only be found on land. It stands in for the land of continents, islands, and the creatures that inhabit them. The existence of water in terrestrial habitats is crucial since, unlike aquatic or marine environments, they do not contain large amounts of water.
- Terrestrial habitats experience daily and seasonal temperature changes as a result of the relative scarcity of water.
- Tropical, Temperate, Grasslands, Deserts, Taiga, and Tundra are the six types of terrestrial ecosystems.
- Atmospheric environment (air).
- An environment’s air component is referred to as its atmospheric environment. Numerous organisms depend heavily on the Earth’s atmosphere (air) for their survival and continued growth. Physicochemical characteristics such as solar radiation, air constituents, climate, and air pollution are just a few that might characterize an environment.
- Aquatic environment (oceans and seas, lakes and rivers),
Anthropogenic Environment
Unlike natural habitats, anthropogenic environments are those that humans have created, such as urban settings or agricultural conversions. Many natural settings now have some degree of being “built” due to the wide range of human interventions and conversions.
Modern tools have been created by humans to alter environmental elements to suit their purposes. Some animal species are also able to construct nests, mounds, dams, and homes utilizing raw materials as tools. Their tools are, however, quite rudimentary, and frequently, their impact is not as great as that of human tools and technology. Human technology spread rapidly around the globe, having an indirect or direct impact on every aspect of the environment.
Problems Faced by Environment
Environmental problems are the disruptions that are caused in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these problems may be the result of natural processes or human activity (human impact on the environment). When an ecosystem can no longer heal itself into normal conditions, then these problems are deemed critical, and catastrophic when an ecosystem collapse is projected. Some of the important Problems faced by the Environment are:
Deforestation
Another significant contributor to environmental problems is deforestation, which results from the alarming rate at which trees and forests are being destroyed. Because they give us oxygen, and a variety of basic materials, and help keep the earth’s temperature stable, trees are vital to our survival. However, there has been a significant change in the temperature of the planet as a result of humans destroying forests and trees for profit.
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of hazardous elements into the natural environment causing adverse changes. Pollutants are the name for these dangerous substances. Natural pollutants include volcanic ash, for example. They can also be brought about by human activities, such as factory runoff or waste. The quality of the air, water, and land is harmed by pollutants.
The term “pollution” generally implies that the contaminants have an anthropogenic source, which is a source produced by human activities such as manufacturing, extractive industries, poor waste management, transportation, or agriculture, although environmental pollution can also be caused by natural events.
Ozone Depletion
The planet is shielded from the sun’s deadly UV radiation by the ozone layer. An essential layer of the earth is the ozone layer. However, over time, CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), which are utilized in various businesses and aspects of daily life (such as aerosol cans), are destroying them.
These chemicals’ chlorine content destroys the ozone layer. The ozone layer is forming a hole, which exposes people and wildlife to dangerous UV rays and causes several skin conditions, including cancer.
Global Warming
The increase in temperature of the earth’s environment brought on by the combustion of fossil fuels, vehicle emissions, and atmospheric chlorofluorocarbons is known as global warming. This has hurt the environment and caused a rise in environmental changes. worldwide warming is the term used to describe this rise in atmospheric temperature on a worldwide scale.
Climate Change
In the current atmosphere of environmental concerns, climate change is one of the main worries. With the onset of habitat degradation, global warming, overcrowding, and pollution over the past few decades, climate change has accelerated. Climate change is mostly caused by greenhouse gases, which raise the temperature of the world. Destructive effects brought on by environmental changes include the melting of glaciers, seasonal shifts, epidemics, etc.
Solutions to the Environmental Problems
Here are a few of the most popular approaches to the environmental problem:
- Use of reusable things instead of disposal ones.
- Avoid using paper whenever possible.
- Conserve electricity and water.
- Encourage eco-friendly behaviors.
- To preserve natural resources, recycle garbage.


 NCERT Books for UPSC Preparation, Check ...
NCERT Books for UPSC Preparation, Check ...
 UPSC Syllabus 2025, Check UPSC CSE Sylla...
UPSC Syllabus 2025, Check UPSC CSE Sylla...
 UPSC Mains Syllabus 2025, Optional Sylla...
UPSC Mains Syllabus 2025, Optional Sylla...





















