Table of Contents
El Niño and La Niña are climatic phenomena that occur in the Pacific Ocean and significantly influence global weather patterns, including the Indian monsoon.
El-Nino and Its Impact on India in 2023-2024
El Nino and La Nina are phases of changing sea-surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean that influence global weather.
- Above-Normal Temperatures Forecast:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD) predicts above-normal temperatures until May.
- Both maximum and minimum temperatures expected to be higher than usual across most regions.
- Impact on Health and Well-being:
- Heightened risk of heat-related illnesses, especially among vulnerable populations.
- Urgent need for heat preparedness plans to mitigate health risks.
- Agricultural Implications:
- Heat stress poses challenges for crop yields, livestock health, and water availability.
- Adaptive strategies like crop diversification and irrigation optimization are crucial for agricultural resilience.
- Infrastructure Resilience and Adaptation:
- Infrastructure systems vulnerable to extreme heat events, leading to disruptions in services.
- Investment in climate-resilient infrastructure and heat mitigation strategies essential to enhance resilience.
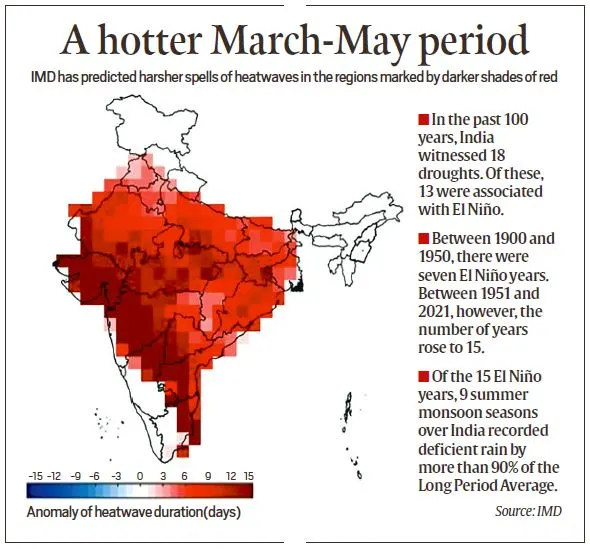
Predicted Heat Conditions for India in 2024
Summer Heat Forecast: The IMD predicts above-normal temperatures across India for March-May 2024.
Regions Affected
- Areas like Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, and several others will experience higher maximum temperatures.
- Nights will be warmer across most of the country, except in some regions of Eastern India.
Heatwave Predictions:
- Central and Northern Peninsular India may face longer and harsher heatwaves, possibly extending to 12-15 days in places like Maharashtra, Telangana, and North Karnataka.
- States like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and several others are expected to experience heatwaves in the coming months.
El Nino’s Impact on Indian Monsoon
- El Niño Phenomenon: El Nino, characterized by the warming of the equatorial Pacific, affects global weather patterns and can lead to temperature increases and droughts.
- Influence on Southwest Monsoon: Although there’s no direct correlation, El Nino Phenomenon often coincides with weaker monsoons in India, leading to below-average rainfall.
- Current Status of El Nino: The 2023-24 El Nino has peaked and is weakening, impacting global climate, with sea surface temperatures recently reaching 2°C above normal.
- ENSO Neutral Conditions: Global climate models indicate a shift to ENSO neutral conditions by April-June, potentially aligning favourably with the onset of India’s southwest monsoon.
Southwest Monsoon Outlook for 2024
- Monsoon’s Economic Importance: The southwest monsoon is vital for India, delivering 70% of annual rainfall and sustaining agriculture and water reservoirs.
- Forecast Development: MMCFS model forecasts ENSO neutral conditions by May, which may favour the timely onset of the monsoon.
- Monsoon Progression: Expected to reach the Andaman and Nicobar Islands by mid-May and mainland India around June 1, the monsoon covers the country by mid-July.
- Upcoming Long Range Forecast: The LRF by the IMD, expected in mid-April, will provide more insights, and current predictions suggest the monsoon may not be heavily impacted by El Niño.
- Normal Rainfall Potential: If other climatic factors like wind patterns and low-pressure systems are favourable, India could see normal monsoon rainfall this year.
Super El Nino in 2024
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predicts a 75%-80% chance of a strong El Niño event in the Northern Hemisphere from March to May 2024, with a 1 in 3 chance of it being a “super El Niño.”
A super El Niño happens when sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean are at least 2.5 degrees Celsius above average. These events can significantly impact global weather patterns, including:
- Warmer and drier conditions in the southwestern United States and southern California.
- Increased rainfall and flooding in the western United States, Alaska, and Hawaii.
- Drier conditions in Australia, Indonesia, and Southeast Asia.
- Increased rainfall and flooding in South America.
- Drier conditions in Africa and India.
Super El Nino Implications For Indian Monsoon
In India, a strong El Nino is associated with reduced rainfall during the monsoon season. This could lead to drought conditions in some parts of the country, and could also impact agricultural production. Here are some of the implications of a super El Nino in 2024 for the Indian monsoon:
- Reduced rainfall: A super El Nino is typically associated with reduced rainfall during the monsoon season in India. This could lead to drought conditions in some parts of the country, particularly in the north and east.
- Impact on agriculture: Reduced rainfall could have a significant impact on agricultural production, leading to higher food prices and food insecurity.
- Water shortages: Reduced rainfall could also lead to water shortages, particularly in areas that rely on monsoon rains for irrigation.
- Increased risk of heatwaves: Super El Niños can also lead to increased risk of heatwaves in India. Heatwaves can be dangerous for human health, and can also impact crop yields.
- Impact on human health: Heatwaves and drought conditions can have a significant impact on human health, leading to increased cases of heat-related illnesses, malnutrition, and waterborne diseases.
You can check below the complete Phenomenon of El Nino and La Nina in detail.
El Nino and La Nina
El Nino and La Nina are two opposite climate events that affect the global economy, ecosystems, and weather. These events usually occur every two to seven years, though not consistently. El Nino happens more frequent than La Nina. Both are caused by changes in water temperature in the eastern central equatorial Pacific.
El Nino and La Nina Meaning
El Nino
El Nino refers to sporadic climate changes and the warming of ocean surface waters along the coasts of Peru and Ecuador, first noticed by South American fishermen in the 17th century.
During El Nino, the trade winds that usually blow from east to west along the Equator weaken. This causes high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific, pushing warm surface water towards the northern South American coast. This warming lasts about six months and reduces the usual upwelling of cold, nutrient-rich water in the central and eastern Pacific.
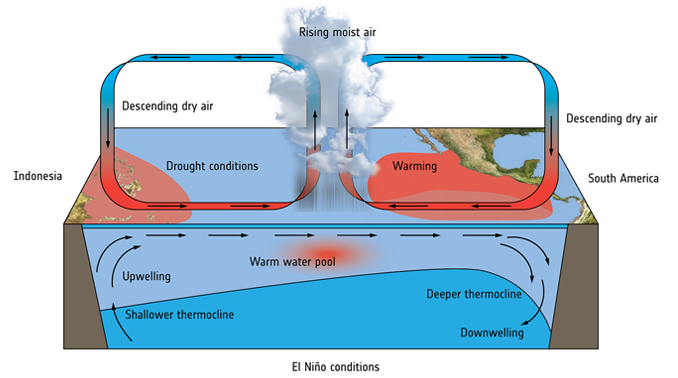
The East Pacific Ocean’s warmer waters cause the winds in some areas to change direction.
- Usually lasting a few weeks to a few months, the El Nino impact happens around Christmas. Depending on how warm the water is at the moment, it could occasionally last for significantly longer lengths of time.
- When a climate like this warms for seven to nine months, it is referred to as El Nino “conditions,” and when it lasts longer, it is referred to as an El Nino “episode.”
- The El Nino effect typically happens more often than the La Nina effect. The relationship between the ocean-atmosphere climate interaction and the rise in sea surface temperature in the Central and East-Central Equatorial Pacific can be inferred from fluctuations in ocean temperature.
- These complex meteorological conditions develop in the Equatorial Pacific Ocean. El Nino happens regularly, but the “cold phase” of ENSO is infrequent. The Indian monsoon has had a disastrous effect on the nation’s agricultural activity as a result of the El Nino influence.
- The El Nino effect is unpredictable; it never follows a set rhythm. El Nino occurs erratically every 2–7 years as well. El Nino is sometimes thought of just a coastal surface water warning, but it is also known to cause significant climate change.
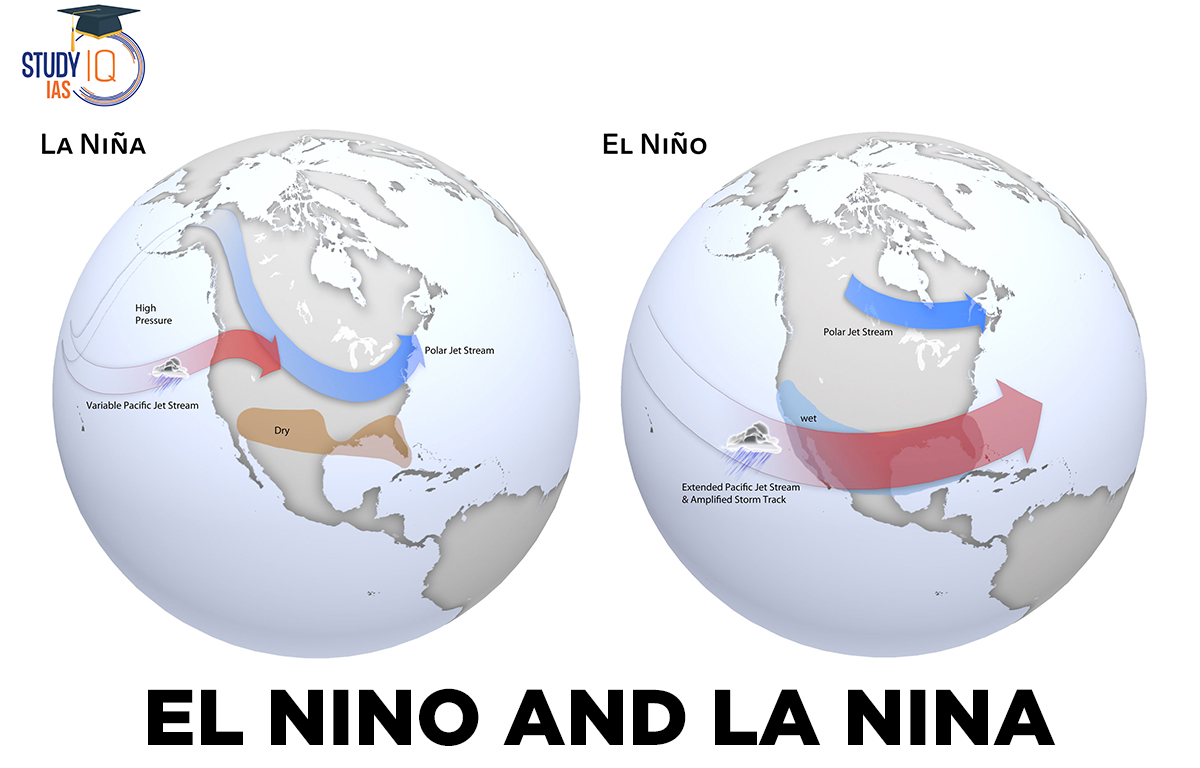
La Nina
La Nina, also known as El Viejo, Anti El Nino, or a “cold occurrence,” means “little girl” in Spanish. It is the opposite of El Nino. During La Nina, stronger trade winds push warmer water towards Asia. This causes cold, nutrient-rich water to rise off the west coast of the United States, leading to more marine life.
The cold Pacific waters push the jet stream north, causing droughts in the southern United States and heavy rain and flooding in the Pacific Northwest and Canada. The South experiences warmer winters, while the North gets colder ones. La Nina can also lead to more hurricanes. The colder waters support more marine life, attracting coldwater animals like squid and salmon to areas like the California coast.
El Nino and La Nina Effect
Since 1950, ten out of India’s thirteen droughts have happened during El Nino years, and one during a La Nina year. This is because El Nino usually brings less rain to India. Indian agriculture relies heavily on monsoon rains, so when there is less rain, crop production often falls below average.
Effect of El Nino
- Warmer surface water increases the chance of rain.
- In South America, more rainfall has led to erosion and coastal flooding.
- Areas hit by natural disasters like floods and droughts are more prone to disease outbreaks.
- Many regions believe El Nino flooding has increased the spread of diseases like cholera, dengue fever, and malaria, causing respiratory issues.
- El Nino causes dryness in Australia and Indonesia, leading to water shortages as reservoirs dry up and rivers carry less water, threatening agriculture.
- El Nino has reduced the number of hurricanes in the Atlantic.
Effect of La Nina
- It causes heavy monsoons in Southeast Asia and India.
- It creates drought-like conditions in Peru and Ecuador.
- It brings cold, wet winters to Southeast Africa and rainy weather to Eastern Australia.
- It causes dry winters in the Southern United States.
- It makes winters in the northwest United States and western Canada very cold.
- It leads to major flooding in Australia.
- It raises temperatures in the Western Pacific, the Indian Ocean, and off the coast of Somalia.
- It results in intense monsoon rains in India.
El Nino Vs La Nina
| Basis of comparison | El Niño | La Niña |
| Meaning | El Niño means Little Boy, or Christ Child in Spanish. | La Niña means Little Girl in Spanish. |
| Sea surface temperature | It represents the above-average sea-surface temperatures that periodically develop across the east-central equatorial Pacific. | It represents the periodic cooling of sea-surface temperatures across the east-central equatorial Pacific. |
| Pressure | It is laden with high air surface pressure in the western Pacific. | It contain low air surface pressure in the eastern Pacific |
| Mechanism | During El Niño, trade winds weaken. Warm water is pushed back east, toward the west coast of the Americas, resulting in a weaker Walker cell. Cold Peruvian (Humboldt) current gets replaced by warm Elnino (Cromwell) current. | During La Niña events, trade winds are even stronger than usual, pushing more warm water toward Asia, resulting in a stronger Walker cell. |
| Period of occurrence | Typically occurs every 3-5 years and lasts 9-12 months. | Typically occur every 3-5 years and lasts 1-3 years. |
| Impacts |
|
|
| Impact on Indian Monsoon | The monsoon is affected so heavily that 70% reduction of the rainfall is expected. The winds don’t carry the moisture towards the Indian landmass during El Nino causing deficiency in rainfall. | La Nina causes high temperatures over the Indian Ocean, off the Somalian coast, and a comparatively better monsoon rains in India. |
El Nino and La Nina Facts for UPSC
- The trade winds that blow from east to west intensify during La Nina.
- The 1997–98 El Nino was the first to be systematically tracked from beginning to end.
- The 1997–1998 events had an impact on many areas; Peru and California had significant rain and flooding, whereas the Philippines, Malaysia, and Indonesia experienced drought conditions.
- La Nina is primarily brought on by an increase in easterly trade winds.
- The El Nino – Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle has two opposing phases, El Nino and La Nina.

 Indus River System, Tributaries, and Sin...
Indus River System, Tributaries, and Sin...
 Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...






















