Table of Contents
What is Ecological Succession?
Ecological Succession is the process where a biological community changes over time. There are two main types:
- Primary Succession happens in lifeless areas, like lava flows or new sand dunes, where soil cannot support life.
- Secondary Succession occurs in areas where an existing community has been disturbed but some life and nutrients remain, like after a fire or flood.
In Secondary Succession, the process starts in places with soil, and it can also happen in abandoned farmland, known as old-field succession. Both types lead to changes in species as the environment evolves. Initially, only a few species can survive, but as new plants grow, they change the habitat, allowing different species to thrive. This pattern continues, with plants and animals influencing each other and the environment as they change over time.
Ecological Succession Definition
It is the process of evolution of a species in a steady and gradual manner in a region over a period of time. It can also be described as the way species move into and take over an empty area in an ecosystem. This process shows how species change and develop over a long time, starting from:
Pioneer Species –> Intermediate Species –> Climax Species
Types of Ecological Succession
There are two main types of Ecological Succession Primary Succession & Secondary Succession:
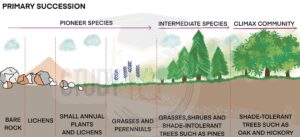
Primary Succession
It thrives in areas with no plants and poor soil, like sand dunes, bare ocean surfaces, new deltas, lava flows, and emerging volcanic islands. The process starts with microorganisms and plants like lichens and mosses. When these pioneers die and decay, they release nutrients into the soil, making the area better for new plants like grasses, shrubs, and sun-loving trees like pines. Over time, this leads to a stable community with shade-tolerant trees like oaks.
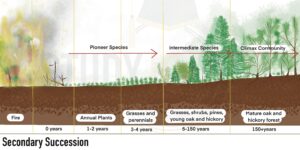
Secondary Succession
It happens when a mature or growing community is damaged or destroyed by natural events like floods, droughts, forest fires, or storms, or by human activities like deforestation, farming, and overgrazing. As some of the sediments from the previous community is already present, the development of the secondary succession is relatively faster than the primary community. And with the passage of time forest community develops.
Stages of Ecological Succession
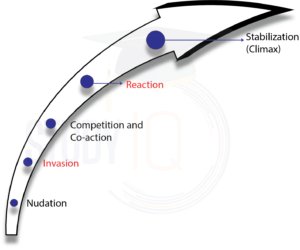
The mixing of species and habitat during the process of ecological succession go through 5 stages:
| Stages | Definition |
| Nudation | It is the formation of the barren area that has formed as a result of – severe floods, volcanic eruptions, landslides, drought, forest fires etc. |
| Invasion | It is the arrival of seeds or other reproductive bodies of different organisms which can help in the spread of habitation in an area. |
| Competition and Co-action | They are the increase in the population of invasive species within a limited span of time. |
| Reaction | The environmental condition gets modified by the action of species that has occupied the region. This triggers the displacement and replacement of one species by another. |
| Stabilization | It is the process or stage that establishes the climax community which is a mature, stable, self-sustaining and final stage of succession. |
Causes of Ecological Succession
Initial Causes: They cause damage to existing habitats. This can happen because of:
- Climatic Factors: Things like wind, fire, erosion, and natural disasters.
- Biotic Factors: This includes competition between living things for survival.
Continuous Causes: It is also known as ecesis. This process involves competition, movement of species, and gathering together. It leads to changes in the soil, such as changes in soil pH, buildup of organic matter, and changes in nutrients.
Ecological Succession in Ecosystem
Ecological succession is essential for the healthy growth and development of the ecosystem as it initiates the colonization and diversification of a new region and the recolonization of a region that has been wiped out due to natural and anthropogenic causes.
Ecological Succession and Stability of Ecosystem: Succession occurs in a series of stages which leads to the establishment of a stable and final community. The final stable community of plants is called the Climax community.
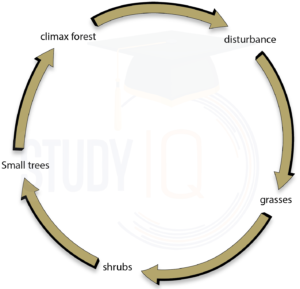
Ecological Succession and Diversity in Ecosystem: Ecological Succession provides diversity as well as depth to a biotic community in an ecosystem. As succession is the gateway of evolution without which life cannot grow or progress.
Ecological Succession Helps Maintaining Equilibrium in Ecosystem: A community goes through stages of ecological succession until it reaches equilibrium. When a community reaches the climax stage of succession the composition of the community becomes stable thus any small changes or disturbances will be counterbalanced by other changes to restore the original stage.


 Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, Map, Climate,...
Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, Map, Climate,...
 Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Impact ...
Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate, Impact ...
 Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCR...
Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCR...





















