Table of Contents
Context: Recently, Myanmar was struck by an earthquake of magnitude 7.7, causing significant devastation in the country.
What Caused the Earthquake in Myanmar?
Tectonic Plate Movements
- The Earth’s lithosphere is divided into tectonic plates, which have been moving for billions of years. Their interactions create earthquakes and other geological features.
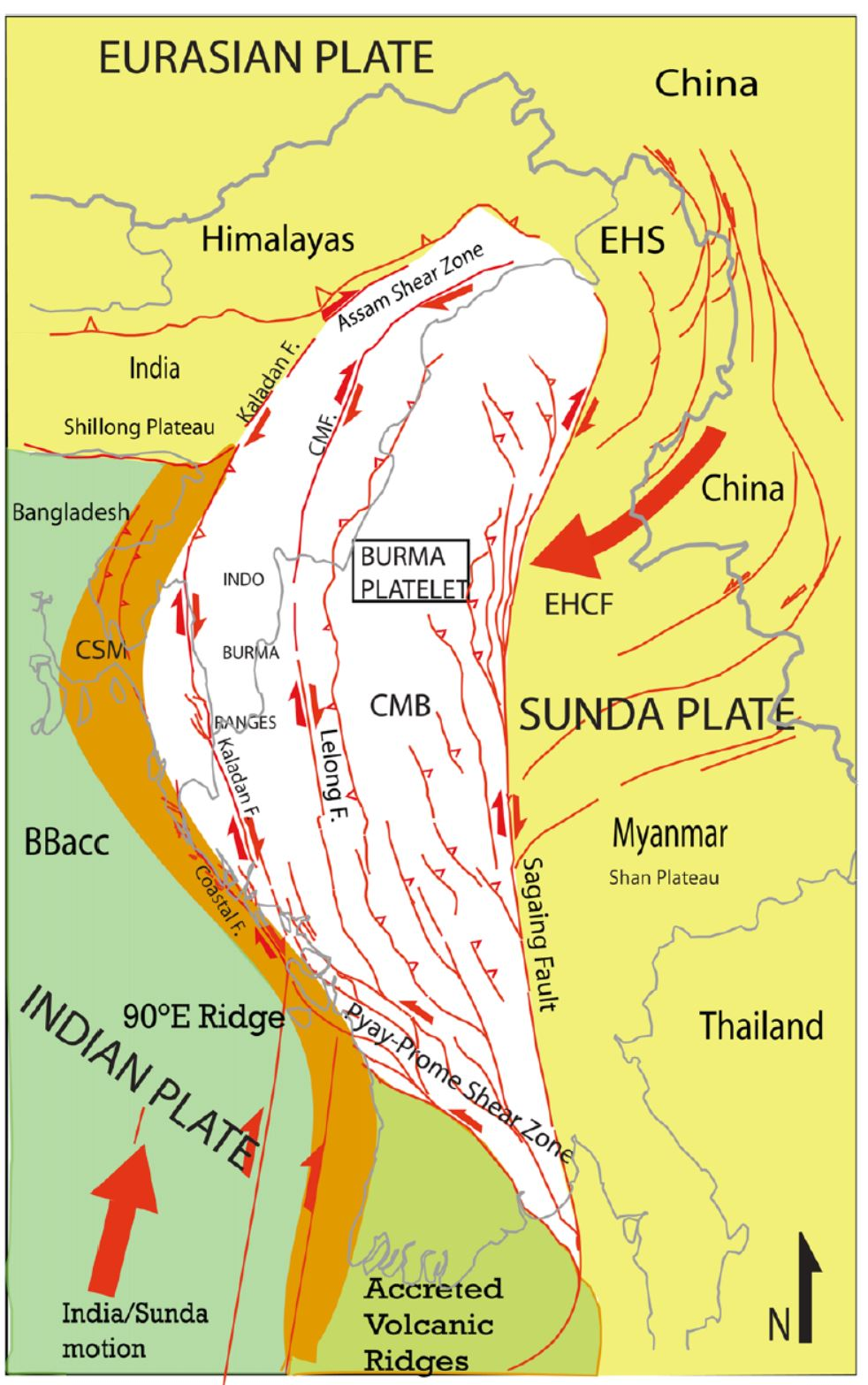
- The earthquake in Myanmar occurred due to “strike-slip faulting“, which happens when two plates rub sideways against each other.
Sagaing Fault
- Sagaing Fault is a 1,200 km long fault line, that runs from north to south through Mandalay and Yangon.
- Areas along this line are one of the country’s most earthquake-prone areas.
Also Read: Operation Brahma
Why Was This Earthquake So Powerful?
- Magnitude: 7, making it one of the strongest quakes worldwide in the last two years.
- Shallow Depth: 10 km, which means seismic energy did not dissipate much before reaching the surface, causing more damage.
- Fault Line: Located on the Sagaing Fault, which is highly active and capable of producing large earthquakes.
Casualties and Damage
- Tragically, more than 1,700 people have died, and many more are still missing.
- Devastating damage, including collapsed buildings and major infrastructure failures, has been incurred in Mandalay and the Sagaing Region.
- The effect was also felt in nearby areas; tremors even reached Bangkok, Thailand, causing fatalities and structural damage.
Rescue and Relief Efforts
- Rescues of Survivors: Teams have been putting in a lot of effort to rescue individuals buried beneath rubble, such as the incredible rescue of a woman in Mandalay who was hauled to safety after 60 hours.
- International Aid: Rescue teams and much-needed medical supplies have been sent in by countries like China and India.
- Challenges: Regrettably, a lack of funding, ongoing civil unrest, and damaged infrastructure are making these efforts extremely difficult.


 Use of AI in Weather Forecasting in Indi...
Use of AI in Weather Forecasting in Indi...
 Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
Cabinet Committee on Security Suspends I...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...





















