Table of Contents
Delhi is located in Seismic Zone IV, which is classified as a “High Damage Risk Zone“. It has the potential to experience moderate to strong earthquakes due to its proximity to active fault lines and the seismically active Himalayan belt. It is the second major quake in Delhi-NCR in the past five months, with a 4.0 magnitude earthquake reported on February 17, 2025. In this article, we will delve into the causes of the earthquake in Delhi, why it felt stronger than expected, the history of seismic activity in Delhi, and essential earthquake preparedness tips for residents.
Earthquake in Delhi Today
An earthquake jolted Delhi-NCR on Thursday, July 10, 2025, in the morning. Severe jolts were experienced throughout Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR), including Noida, Ghaziabad, Gurugram, and Faridabad. Tremors were even experienced as far as Meerut and Shamli in western Uttar Pradesh. The tremors made buildings oscillate, and many people panicked and ran out of their offices and homes. Luckily, no immediate damage to property or injury has been reported
Key Earthquake Details
-
Magnitude: 4.4 (shallow quake)
-
Occurred at: 9:04 AM on July 10, 2025
-
Epicentre: Jhajjar district, Haryana, approximately 60 km from Delhi
-
Depth: ~10 km below the surface
Areas Affected
Tremors were widely felt across:
-
Delhi
-
Noida
-
Ghaziabad
-
Gurugram
-
Faridabad
-
Also felt as far away as Meerut, Shamli, Rohtak, and Hisar
Delhi Earthquake of February 17, 2025
At 5:36 AM IST, a 4.0 magnitude earthquake struck Delhi with its epicenter located in Dhaula Kuan, a residential area in the south of the city. According to the National Centre for Seismology (NCS), the quake occurred at a shallow depth of just 5 kilometers, which explains the intensity of the tremors.
Although a 4.0-magnitude earthquake is generally considered to be of moderate strength, the proximity to the epicenter and the shallow depth led to stronger vibrations felt across Delhi-NCR. This is because seismic waves from shallow earthquakes travel less distance before reaching the surface, making them more amplified when they strike buildings and structures.
Why Did the Earthquake Feel So Strong?
Several factors contributed to the stronger-than-expected tremors:
- Shallow Depth: Earthquakes that occur at a shallow depth typically result in stronger shaking compared to those occurring at greater depths. The shallow 5 km depth of the February 17 earthquake meant that seismic waves reached the surface quickly, amplifying their impact.
- Proximity to the Epicenter: Since the earthquake’s epicenter was within Delhi, the seismic waves had less distance to travel, resulting in stronger shaking and a more intense experience for residents.
- Urban Infrastructure: Delhi’s high-rise buildings, which are designed to sway to some extent during seismic activity, could have further amplified the perceived intensity of the tremors. These buildings are more sensitive to vertical shaking, making them feel much more intense.
- Soil Composition: The soft alluvial soil in some parts of Delhi also plays a role in amplifying seismic waves. Soft soil can amplify ground shaking, resulting in stronger tremors in certain areas compared to others.
- Booming Sounds: Many residents reported hearing loud, rumbling noises during the tremors. These sounds are often associated with shallow earthquakes, as the seismic waves generate high-frequency vibrations that transform into sound waves upon reaching the air.
Why Delhi is Earthquake-Prone
Seismic Zone Classification
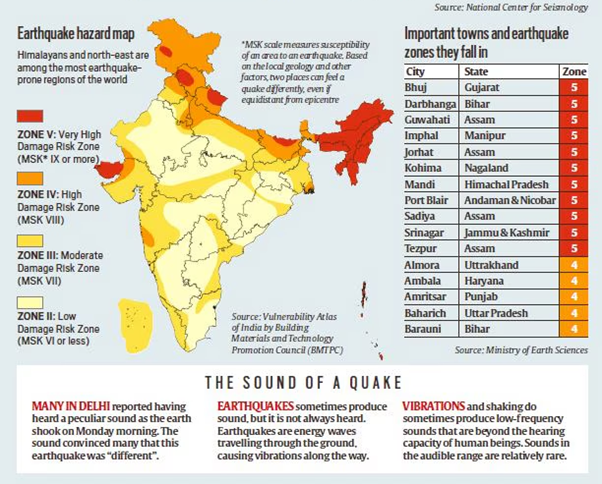
- Delhi falls under Zone 4 of India’s earthquake hazard map.
- This zone is classified as having a high to moderate earthquake risk, making the region more vulnerable to strong seismic activity compared to other areas in the country.
Aravalli-Delhi Fold Belt
- Delhi is situated in the Aravalli-Delhi Fold Belt, a seismically active geological zone that stretches from Rajasthan to Haryana and Delhi.
- This region is characterised by deformed layers of rock, which were created due to tectonic processes that occurred hundreds of millions of years ago.
Local Stress Pockets
- These rock deformations have created local stress pockets. Over time, this stress can be released in the form of earthquakes, though not as frequently or intensely as in the Himalayan region.
Proximity to the Himalayan Fault
- Although Delhi is not as close to the active fault lines of the Himalayan region, it is still connected to a broader tectonic system.
- Earthquakes originating in the Himalayan region can affect Delhi, though it is more likely to experience smaller or moderate quakes.
|
Shallow Earthquakes |
|
Historical Earthquakes in Delhi
Delhi has experienced several significant earthquakes in its history. Notable incidents include:
- The 2001 earthquake (5.4 magnitude), which struck Delhi, caused significant damage and sparked fears of further seismic activity.
- The 2007 earthquake (4.6 magnitude) in Dhaula Kuan was another reminder of the region’s seismic vulnerability.
- The 2015 earthquake (3.3 magnitude), was less severe but still significant in terms of its psychological impact on residents.
The region has witnessed 420 shallow earthquakes over the years, making it clear that seismic activity is not uncommon. While many of these events have been of low magnitude, the 4.0 magnitude tremor of February 2025 highlights the need for continued vigilance.
Causes of Earthquakes in Delhi
Delhi is located near active tectonic fault lines, such as the Delhi-Hardwar Ridge and the Mahendragarh-Dehradun Fault. These fault lines are the result of the collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, which has been ongoing for millions of years. As these plates move and collide, stress builds up over time, eventually being released as an earthquake.
The Himalayan region and northern India, in general, experience significant seismic activity due to this tectonic collision. Earthquakes in this region are often caused by tectonic movements along fault lines, with energy being released in the form of seismic waves.
Earthquake Preparedness: How to Stay Safe in Delhi
While the risk of earthquakes in Delhi cannot be eliminated, there are several measures that residents can take to ensure their safety during such events:
-
Know Your Risk: As Delhi is in Seismic Zone IV, residents need to understand the risk of earthquakes in their area and prepare accordingly.
-
Secure Heavy Furniture: Ensure that heavy furniture and objects are anchored to the walls to prevent them from toppling during an earthquake.
-
Create an Emergency Kit: Keep an emergency kit with essentials such as water, food, a flashlight, a first aid kit, and important documents. This will ensure you are prepared in case of an emergency.
-
Know Safe Places in Your Home: Identify safe spots in your home, such as under sturdy furniture or in doorways, where you can take cover during a quake. Avoid standing near windows, glass doors, or heavy objects.
-
Practice “Drop, Cover, and Hold On”: This is the recommended action during an earthquake. Drop to the ground, take cover under a table or sturdy piece of furniture, and hold on until the shaking stops.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with information from seismologists and authorities regarding earthquake preparedness, aftershocks, and other safety measures.
-
Stay Calm: During a tremor, it is important to remain calm. Panic can lead to accidents and injuries. Follow the safety procedures and wait for the shaking to stop.


 Denotified Tribes and 2027 Census: Deman...
Denotified Tribes and 2027 Census: Deman...
 Mummified Cheetahs Found in Saudi Arabia...
Mummified Cheetahs Found in Saudi Arabia...
 NDMA Disaster Victim Identification Guid...
NDMA Disaster Victim Identification Guid...

























