Table of Contents
Context: Donald Trump was sworn in as the 47th US President in the US.
Key Recent Announcements and Orders by the Trump Administration
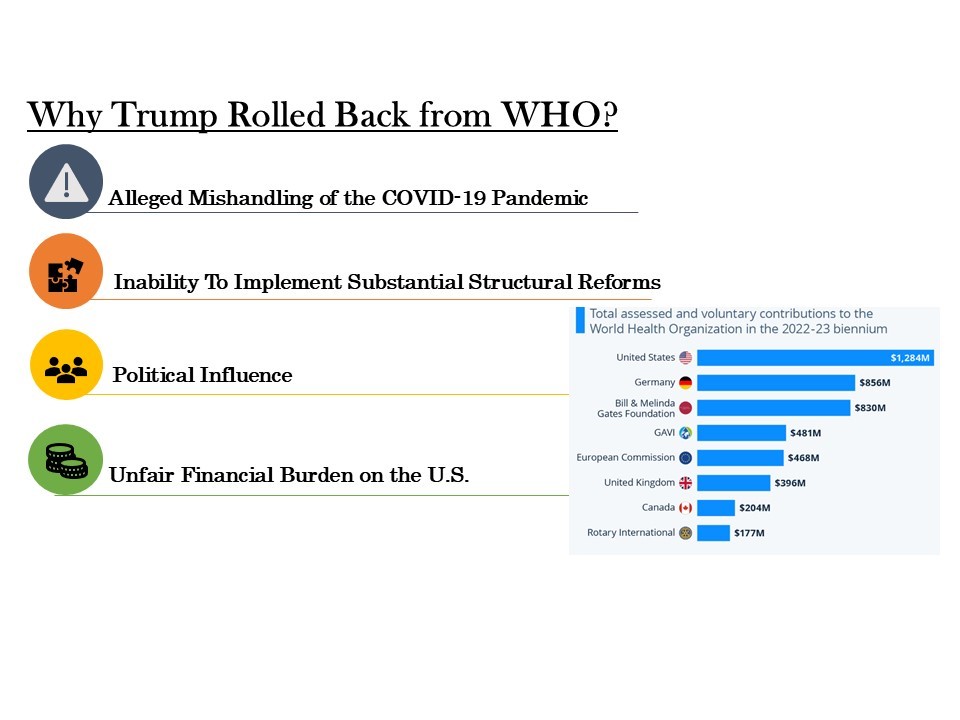
- Withdrawal from International Institutions: Signed executive orders initiating the U.S.’s withdrawal from the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Paris Agreement on Climate Change.
- Protectionist Trade Policies: Proposed a 25% tariff on imports from Mexico and Canada, signaling potential violations of WTO rules.
- Unilateralism in Territorial Ambitions: Expressed ambitions to annex Greenland and the Panama Canal.
- Stated intentions to include Canada as the 51st state of the U.S., invoking practices reminiscent of imperialist-era conquests.
- End Birthright Citizenship: An executive order was signed aiming to end birthright citizenship for children of undocumented immigrants.
- Onslaught on Multilateral Institutions: Continued blockage of WTO Appellate Body reforms, further impairing the global trade dispute mechanism.
- Plans to bypass multilateral treaties and prioritize bilateral negotiations, reflecting a sovereigntist approach.
- Alarming Statements on Force: Statements violating norms of non-intervention under the UN Charter, such as coercive territorial ambitions, risk undermining the rule-based international order.
What are Implications of a Renewed Unilateralist Agenda on the International Order?
- Erosion of Multilateralism: A potential exit from key institutions like the WHO and WTO would weaken their authority and legitimacy.
- Violations of UN Charter principles, particularly non-intervention and the prohibition of the use of force, risk eroding the legitimacy of international law.
| Global Implication OF US’s WHO Withdrawal |
|
- Global Trade Instability: The weakening of the WTO Appellate Body hampers dispute resolution, increasing uncertainty for international trade.
- Additionally, this will limit the ability of developing nations (particularly the global south) to push for equitable global trade policies.
- Revival of Power Politics: Territorial ambitions signal a regression to 19th-century-style conquest diplomacy, which could embolden other revisionist powers like China and Russia to challenge global norms.
- Empowering Domestic Policy Influence: A strengthened majority in Congress may enable smoother implementation of Trump’s policies, reducing internal checks on his sovereigntist approach.
- Global Climate Action Setback: The U.S., being the second-largest greenhouse gas emitter, is crucial for achieving global emission reduction targets. Its exit weakens the collective effort to combat climate change.
- Additionally, it will impact the International Climate Finance Plan and diminish contributions to global climate funds.
- Also, it will create a gap in global climate leadership.
What are the Impacts of Recent Orders and Announcements for India
- Termination of Birthright Citizenship: President Trump’s executive order ending birthright citizenship could affect Indian families with U.S.-born children, potentially altering their legal status and future opportunities.
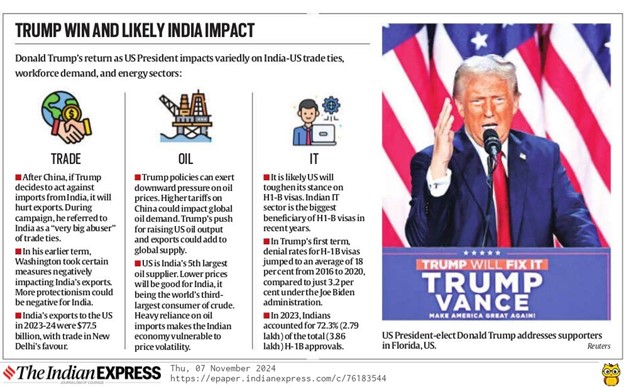
- Trade and Economic Relations: The ‘America First’ policy may lead to increased tariffs on Indian goods, impacting India’s export economy and trade balance
- India is expected to boost purchases of U.S. oil and gas following President Trump’s initiative to maximize American energy production, affecting India’s energy sourcing and trade dynamics.
- H-1B Visa Reforms: Potential reforms to the H-1B visa program could impact Indian IT professionals, affecting the technology sector and bilateral workforce exchange.
- Healthcare: US withdrawal from WHO disrupts India’s health programs like immunization, increases financial strain, and affects global health guidelines, but offers India an opportunity to lead global health initiatives and strengthen south-south cooperation.
What are the Different Implications of the Trump Presidency?
Historical Context of U.S. Foreign Policy in West Asia
Biden Administration’s Approach
- Under President Joe Biden, the U.S. sought to build on the Abraham Accords initiated by Trump, which aimed at normalising relations between Israel and several Arab states.
- However, Biden’s tenure has been marred by the resurgence of violence in Gaza following the Hamas attacks on October 7, 2023.
- The Biden administration’s dual approach involved supporting Israel’s military actions while attempting to mitigate the conflict’s escalation into a larger regional war.
- This strategy has been criticised for failing to achieve stability, with over 43,000 Palestinians reportedly killed and increasing tensions with Iran and Hezbollah.
Trump’s Previous Policies
- During his first term, Trump adopted a robustly pro-Israel stance:
- He moved the U.S. embassy to Jerusalem.
- He recognized Israel’s annexation of the Golan Heights.
- He withdrew from the Iran nuclear deal, which had been a cornerstone of U.S. diplomacy in the region.
- His administration facilitated the Abraham Accords, promoting normalisation between Israel and several Arab nations.
- Trump’s policies were largely aimed at countering Iran, perceived as a common adversary for both Israel and the Gulf Arab states.
Implications of Trump’s Second Term
- Continuation of Pro-Israel Policies: Trump is unlikely to take a strong moral stance against Israel’s actions in Gaza or elsewhere.
- His previous record suggests he would support Israeli military operations while avoiding deeper U.S. military entanglement in regional conflicts.
- This could lead to:
- Increased Military Support
- Limited Pressure for Ceasefires
- Avoiding Regional Wars: Despite his pro-Israel stance, Trump is aware of his base’s opposition to prolonged military engagements in West Asia:
- Focus on domestic issues such as rising inflation and economic concerns
- Avoid direct military confrontation with Iran or other regional actors unless provoked and focus on countering China’s influence globally.
- Challenges with Arab Allies: The ongoing violence and humanitarian crisis in Gaza could complicate Trump’s relationships with Arab nations (normalisation agreements with Arab nations) may face setbacks.
- Countries like Saudi Arabia may hesitate to fully embrace normalisation without significant concessions from Israel regarding Palestinian rights.
- Potential for Increased Tensions: If Trump continues aggressive policies against Iran or supports Israeli operations against Hezbollah, it could lead to broader regional conflicts.
- The already strained relations could worsen, particularly if Trump attempts to reassert pressure on Iran through sanctions or military posturing.
Implication For India
Positive Implications for India
- Strengthening Bilateral Ties: Trump has expressed interest in resuming negotiations for a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) with India, which had stalled during Biden’s administration.
- This could enhance market access for Indian goods and services in the U.S. and vice versa,
- This will potentially boost bilateral trade, which was valued at approximately $128.78 billion in 2023.
- Defence Cooperation: Trump is likely to continue facilitating military hardware sales to India.
- This aligns with India’s strategic interests amid rising regional tensions, particularly concerning China and Pakistan.
- Limited Pressure on Domestic Issues: Unlike the Biden administration, which raised concerns over democratic norms and human rights in India, Trump’s administration is expected to adopt a more lenient stance on these issues.
- This could relieve India from facing public scrutiny regarding its internal policies, such as those affecting minority rights and press freedoms.
- Energy Partnerships: Trump may encourage India to invest in U.S. energy resources, particularly oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG), rather than pressuring India on carbon emission cuts.
- This aligns with previous agreements like the Driftwood LNG project.
- Focus on Countering China: Trump’s administration is likely to maintain a hard line against China, which could further solidify the U.S.-India partnership as both nations seek to counter Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The revival of the Quad alliance (involving India, the U.S., Japan, and Australia) is expected to continue under Trump.
Challenges Ahead
- Trade Tariffs and Protectionism: Trump’s emphasis on reducing trade deficits and cutting tariffs could renew friction. His administration might push India on issues like tariffs, as seen with previous disputes over GSP (Generalised System of Preferences) and counter-tariffs on U.S. imports.
- Impact on Professionals: Likely visa (H1B and L1 visas) and trade restrictions will likely affect IT services and pharmaceuticals.
- Unpredictability and Diplomatic Disclosures: Trump’s tendency to disclose or embellish private conversations with leaders can lead to diplomatic missteps.
- India may face unwanted complications, especially if Trump offers to mediate sensitive issues like Kashmir or makes public comments about India’s stance on China or other regional matters.
- Pressure on Iran Policy: Although Trump might be less concerned with India’s ties with Russia, he could resume pressure to cut oil imports from countries like Iran.
- This could impact India’s energy security, as seen when Trump previously pressured India to stop importing Iranian oil.
- Regional Instability Concerns: India’s neighbours might face challenges under Trump’s presidency, with reduced U.S. aid and potential neglect of diplomatic engagements in South Asia.
- Countries like Pakistan and Bangladesh could see decreased U.S. support, which may impact regional stability and potentially create security and economic spillover effects for India.
- Limited Influence on Middle Eastern Peace: Although Trump might not be heavily involved in the Israel-Palestine issue, India may still hope for his intervention to help stabilise the Middle East, which impacts India’s plans for initiatives like the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
Impact on Global Economy
- Escalating Trade Wars: Trump’s “America First” policy is likely to reignite trade tensions not only with China but also with other countries, including India.
- His previous administration imposed tariffs on various imports, and he has indicated a willingness to do so again. This could lead to:
- Higher Tariffs: Trump has suggested a blanket 10% tariff on all imports and up to 60% on Chinese goods, which may extend to Indian products as well.
- Trade Deficits: The focus on reducing trade deficits could lead to aggressive negotiations that might disadvantage countries with trade surpluses with the U.S., including India.
- His previous administration imposed tariffs on various imports, and he has indicated a willingness to do so again. This could lead to:
- Withdrawal from Multilateral Agreements: Trump’s preference for bilateral trade deals over multilateral frameworks like the World Trade Organization (WTO) could lead to increased instability in global trade norms, making it more challenging for countries to resolve trade disputes.
- Global Supply Chain Disruptions: As the U.S. commands a significant share of global exports in technology and agricultural products, inflationary pressures in the U.S. could ripple through global markets, affecting prices elsewhere.
- Impact on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): While Trump’s policies may attract some investment back to the U.S., they could deter foreign investment in other regions:
- Companies may reconsider their global supply chains and investment strategies in response to increased tariffs and trade uncertainties.
- Emerging markets like India may face capital outflows as investors seek higher returns in a potentially more favourable U.S. economic environment.
Impact of the Trump Administration on Environmental Pledges
- Withdrawal from the Paris Agreement: President Trump pulled the United States out of the Paris Climate Agreement, a global accord aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This withdrawal signalled a reduction in U.S. commitment to collective global climate goals.
- Defunding of the World Health Organization (WHO): Under Trump, the U.S. stopped funding the WHO, which affected global efforts on health and environmental fronts, as WHO plays a role in addressing the health impacts of climate change.
- Censorship and Promotion of Anti-Scientific Policies: The administration censored scientific research findings and promoted pseudoscience.
- This included supporting carbon-intensive industries and restricting scientific collaborations that focused on climate research.
- Environmental Deregulation through Judicial Changes: Appointees by Trump to the Supreme Court overturned the Chevron Doctrine, which limits federal agencies’ ability to interpret regulatory statutes. This decision weakened federal agencies’ capacity to regulate industries, especially in emerging environmental and technological fields.
- Transnational and Domestic Policy Shifts: The administration’s shift towards transactionalism over international cooperation could impede the implementation of climate agreements, making it challenging to secure sustained global climate commitments.
- Funding Reduction for Biodiversity and Adaptation Initiatives: The Trump administration’s hesitation in financing climate adaptation and biodiversity management created gaps in global environmental funding, which other countries or organisations had to fill.


 International Laws on Immigrants Right t...
International Laws on Immigrants Right t...
 SQUAD Grouping of USA, Key Members and I...
SQUAD Grouping of USA, Key Members and I...
 India and New Zealand Relation, Areas of...
India and New Zealand Relation, Areas of...





















