Table of Contents
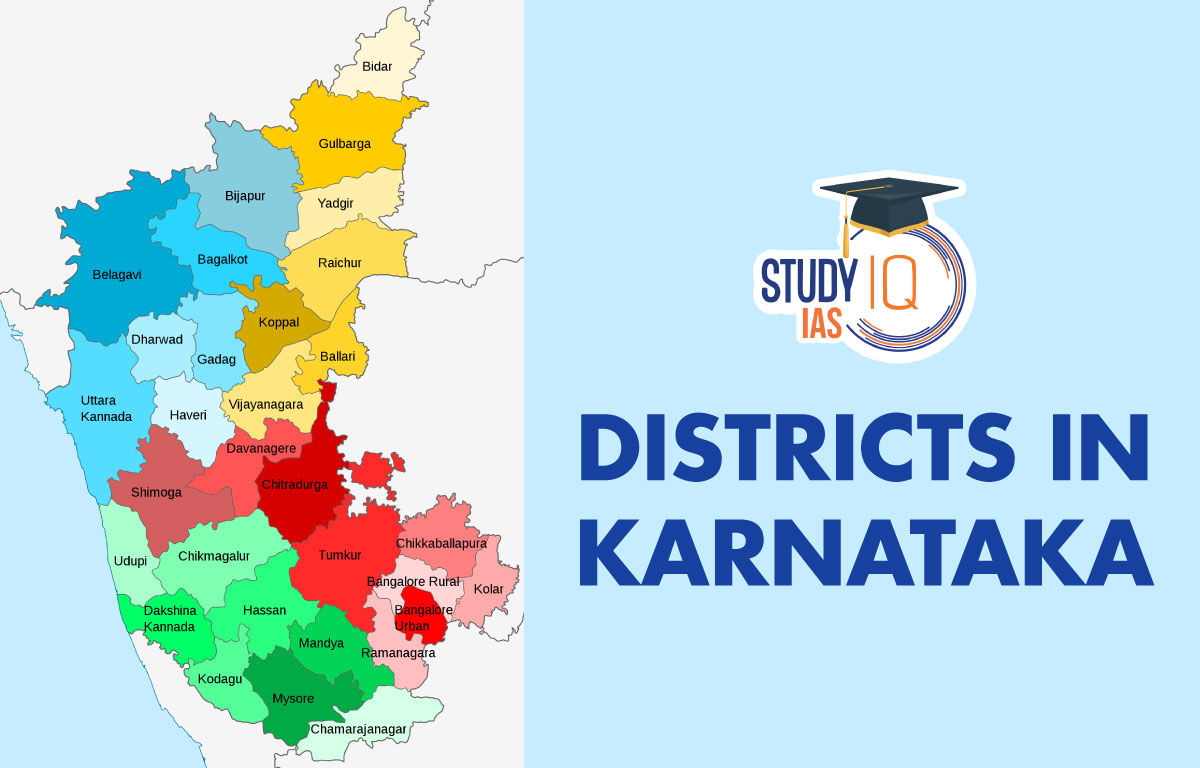
Karnataka is a state in the southern part of India. In total, there are 31 Districts in Karnataka. Each District of Karnataka has its own unique culture, history, and economy. The districts are further divided into smaller administrative units, such as talukas and gram panchayats, and are governed by an elected district council. The Districts of Karnataka vary in size, population, and economic activities, with some being known for their natural beauty, while others are important centres for agriculture, industry, and tourism. Each district has its own story to tell and plays a vital role in shaping the overall growth and development of the state.
Read about: Union Territories
How Many Districts in Karnataka?
The State is divided into 31 districts and about 240 Taluks and 4 Administrative divisions are Bangalore, Belagavi, Mysore and Kalaburagi. However, districts of Karnataka in recent years there have been many changes
- Tipaturu and Madhugiri from Tumakuru district
- Putturu from Dakshina Kannada district
- Jamakhandi from Bagalkote district
- Sedam from Kalaburagi district
- Chikkodi and Gokak from Belagavi district
- Sirsi from Uttara Kannada district
- Hunasuru from Mysuru district
- Indi from Vijayapura district
- Sindhanuru from Raichuru district
List of Districts in Karnataka
There are 31 Districts in State of Karnataka we have discuss about the district and its importance inn below table:-
| S. No | District | Importance |
| 1 | Bagalkot | The district is known for its rich cultural heritage and has several historical monuments and temples, attracting tourists from all over India and abroad. |
| It is also an agricultural hub, with significant production of sugarcane, paddy, and cotton. | ||
| 2 | Ballari (Bellary) | The district is one of the largest producers of iron ore in India and has a significant contribution to the country’s steel industry. |
| It is also home to several ancient temples, historical forts, and monuments, making it a popular tourist destination. | ||
| 3 | Belagavi (Belgaum) | The district is a major producer of horticultural crops, including grapes, pomegranate, and sugarcane. |
| It is also strategically located near the border of Maharashtra and Goa, making it an important centre for trade and commerce. | ||
| 4 | Bengaluru (Bangalore) Rural | The district is known for its beautiful lakes and parks and is often referred to as the “Garden City” of India. |
| It is also a major hub for the IT industry and is home to several multinational corporations, making it a significant contributor to the Indian economy. | ||
| 5 | Bengaluru (Bangalore) Urban | The district is the capital of Karnataka and is one of the fastest-growing cities in India, with a booming IT industry and a thriving startup culture. |
| It is also home to several prestigious educational institutions, making it a hub for higher education and research. | ||
| 6 | Bidar | The district is known for its rich history and has several ancient monuments and forts, making it a popular tourist destination. |
| It is also an important centre for the production of traditional Bidriware handicrafts. | ||
| 7 | Vijayapura (Bijapur) | The district is famous for its architecture, especially the Gol Gumbaz, which is the second-largest dome in the world. |
| It is also an important center for the production of horticultural crops and is known for its sweet and juicy pomegranates. | ||
| 8 | Chamarajanagar | The district is home to several national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, including the Bandipur National Park and the Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Wildlife Sanctuary, making it an important center for ecotourism. |
| It is also a major producer of silk and has several silk industries. | ||
| 9 | Chikkaballapur | The district is known for its production of grapes, and several vineyards in the district offer wine-tasting tours. |
| It is also an important center for the production of silk and handloom weaving. | ||
| 10 | Chikkamagaluru (Chikmagalur) | The district is known for its coffee plantations, and the coffee grown here is highly sought after in the international market. |
| It is also home to several important wildlife sanctuaries, including the Bhadra Wildlife Sanctuary. | ||
| 11 | Chitradurga | The district is home to several ancient forts, including the Chitradurga Fort, and is a popular destination for history enthusiasts. |
| It is also an important center for the production of horticultural crops and has a significant contribution to the economy of Karnataka. | ||
| 12 | Dakshina Kannada | The district is a major producer of cashew nuts and is known for its beautiful beaches and temples, making it a popular tourist destination. |
| It is also a major center for the production of marine products, including fish and prawns. | ||
| 13 | Davangere | The district is an important center for the production of cotton, and several textile industries are located here. |
| It is also known for its high-quality education and is home to several prestigious educational institutions. | ||
| 14 | Dharwad | The district is an important center for the production of agricultural crops, including sugarcane and cotton. |
| It is also an important hub for higher education, with several prestigious institutions located here. | ||
| 15 | Gadag | The district is known for its ancient temples and architecture, including the Trikuteshwara Temple and the Veera Narayana Temple. |
| It is also a major producer of sugarcane and cotton. | ||
| 16 | Kalaburagi (Gulbarga) | The district is known for its rich cultural heritage and is home to several ancient monuments and temples. |
| It is also an important center for the production of agricultural crops, including jowar and pulses. | ||
| 17 | Hassan | The district is known for its natural beauty and has several important tourist destinations, including the Belur and Halebid temples and the Manjarabad Fort. |
| It is also a major center for the production of coffee and has several coffee plantations. | ||
| 18 | Haveri | The district is an important center for the production of horticultural crops, including grapes and pomegranates. |
| It is also known for its unique cultural heritage, with several folk arts and festivals celebrated in the district. | ||
| 19 | Kodagu (Coorg) | The district is known for its beautiful landscape and is often referred to as the “Scotland of India.” |
| It is also an important center for the production of coffee | ||
| 20 | Kolar: | The district is an important center for the production of silk and handloom weaving, with several silk industries located here. |
| It is also known for its rich history and has several ancient temples and monuments, including the Kolaramma Temple and the Someshwara Temple. | ||
| 21 | Koppal: | The district is known for its ancient architecture, including the Mahadeva Temple and the Koppal Fort, and is a popular destination for history enthusiasts. |
| It is also an important center for the production of agricultural crops, including groundnut, sunflower, and jowar. | ||
| 22 | Mandya: | The district is a major producer of sugarcane, with several sugar mills located here. |
| It is also known for its scenic beauty and has several important tourist destinations, including the Shivanasamudra Falls and the KRS Dam. | ||
| 23 | Mysuru (Mysore): | The district is known for its rich cultural heritage and is home to several important tourist destinations, including the Mysore Palace, the Brindavan Gardens, and the Chamundi Hills. |
| It is also an important center for the production of silk and sandalwood, and has several silk industries and sandalwood factories. | ||
| 24 | Raichur: | The district is known for its rich history and has several important monuments and temples, including the Raichur Fort and the Ek Minar ki Masjid. |
| It is also an important center for the production of cotton, and several textile industries are located here. | ||
| 25 | Ramanagara: | The district is a major center for the production of silk and handloom weaving, with several silk industries and handloom units located here. |
| It is also known for its natural beauty and has several important tourist destinations, including the Janapada Loka Folk Arts Museum and the Shivagange Hill. | ||
| 26 | Shivamogga (Shimoga): | The district is known for its beautiful landscape and has several important tourist destinations, including the Jog Falls and the Shivappa Nayaka Palace. |
| It is also an important center for the production of agricultural crops, including paddy, ragi, and areca nut. | ||
| 27 | Tumakuru (Tumkur): | The district is an important center for the production of horticultural crops, including grapes and pomegranates. |
| It is also known for its rich history and has several important monuments and temples, including the Madhugiri Fort and the Sri Siddhaganga Mutt. | ||
| 28 | Udupi: | The district is a major producer of marine products, including fish and prawns, and is known for its beautiful beaches and temples, making it a popular tourist destination. |
| It is also an important center for the production of coconuts and cashew nuts. | ||
| 29 | Uttara Kannada (Karwar): | The district is known for its natural beauty and has several important tourist destinations, including the Jog Falls and the Dandeli Wildlife Sanctuary. |
| It is also an important center for the production of horticultural crops, including mangoes and bananas. | ||
| 30 | Yadgir: | The district is known for its rich cultural heritage and has several important monuments and temples, including the Karez System and the Chandrampalli Fort. |
| It is also an important center for the production of agricultural crops, including jowar, sunflower, and groundnut. | ||
| 31 | Vijayanagara | Carved out of Bellary in 2021. |
| It is known for World Heritage Site of Hampi. |
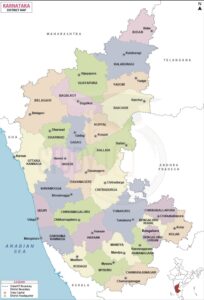
Karnataka District Map
Karnataka’s districts can be seen on the map below, with each district represented by a different colour or symbol. The map can provide an overview of the geographic location of each district, as well as its proximity to neighbouring states and regions. It can also be used to identify important landmarks, tourist destinations, and natural resources within each district.
Divisions of Karnataka
The district administrative divisions are divided into 4 central administrative. Superintendent of Police for looking after the situation of law and order in the administrative division. A District Commissioner heads each of these administrative divisions.
|
Divisions |
Districts |
|---|---|
|
Bengaluru Division |
|
|
Belagavi Division |
|
|
Kalaburagi Division |
|
|
Mysuru Division |
|

 Daily Quiz 19 April 2025
Daily Quiz 19 April 2025
 Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology and its...
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology and its...
 Waqf Act (Amendment) 2025: Key Highlight...
Waqf Act (Amendment) 2025: Key Highlight...





















