Table of Contents
Context: The Union Home Minister Amit Shah led a committee convened to review disaster mitigation projects.
More in News
- The committee sanctioned several projects aimed at mitigating and preventing natural disasters including urban flooding and glacial lake outbursts.
- Funding Approval: A total of nine proposals were sanctioned, drawing funds from both the National Disaster Mitigation Fund (NDMF) and the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF).
- During the current financial year, ₹6348 crore was released to 14 states under the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF).
- Additionally, ₹672 crore was released to six states under the State Disaster Mitigation Fund (SDMF), and ₹4265 crore to 10 states under NDRF.
- Urban Flood Management: Projects approved for urban flood management in six cities (Mumbai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, and Pune) across Telangana, Gujarat, Karnataka, West Bengal, and Maharashtra.
- The total allocation for these projects is ₹2514.36 crore.
- Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services: Three project proposals were sanctioned for Assam, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- The total budget for these initiatives is ₹810.64 crore.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) Mitigation: A project aimed at mitigating GLOF risks in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh was approved with a budget of ₹150 crore.
- Yuva Aapda Mitra Scheme (YAMS):
- The scheme received approval for a budget of ₹470.50 crore from NDRF.
- It aims to train 1300 Aapda Mitra Volunteers as Master Trainers and 2.37 lakh volunteers in 315 disaster-prone districts. These volunteers are from organisations like NCC, NSS, NYKS, and BS&G.
- Previous Approvals and Allocations:
- In November 2023, an integrated solution for flood management in Chennai was approved at ₹561.29 crore.
- Overall, ₹5000 crore has been allocated under NDRF, with ₹1691.43 crore already approved for 11 states.
What is Disaster Management?
- Disaster management refers to the systematic approach of planning, organising, coordinating, and implementing measures to prevent, prepare for, respond to, and recover from disasters.
- It involves a range of activities and strategies aimed at reducing the impact of disasters on human lives, infrastructure, and the environment.
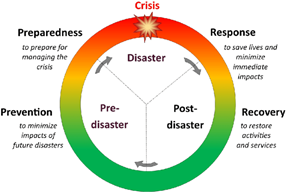
- It includes the sum total of all activities, and measures which can be taken up before, during and after a disaster. A typical disaster management continuum consists of:
- A pre-disaster Risk Management Phase: This includes prevention, mitigation and preparedness.
- Post-disaster Crisis Management Phase: This includes relief, response, rehabilitation, reconstruction and recovery.
Disaster Management in India
The Government of India enacted the Disaster Management (DM) Act, of 2005, which envisaged the creation of a three-tier structure comprising the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) and District Disaster Management Authorities (DDMAs).
| Level | Details |
| Institutional framework at the National Level |
|
| Institutional Framework at State Level |
|
| Institutional Framework at the District Level |
|
| Local Authorities |
|


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















