Table of Contents
First hi-res landslide risk map for India
Context: Following intense monsoon rains causing floods and landslides, a team from IIT Delhi has created the nation’s first high-resolution landslide susceptibility map.
Features Of National Landslide Susceptibility Map
- Landslide Event Data: Incorporates data from around 150,000 recorded landslide events from the Geological Survey of India (GSI) and includes 16 factors influencing landslides.
- Machine Learning Analysis: Utilises ensemble machine learning techniques to balance the impact across multiple models.
- Factors Used: They collected information on factors like soil cover, number of trees covering the area, distance from roads or mountains, etc.
- They used GeoSadak, an online system with data on the national road network in India, displaying data on roads located outside cities
- High-Resolution Overview: Provides a high-definition (100 square metre resolution) perspective of landslide-prone zones throughout India.
- Identification of Risk Zones: Highlights known risk areas like the Himalayan region and uncovers new high-risk zones in parts of the Eastern Ghats.
- Online Accessibility: The map is publicly available online for interactive use by anyone without the need for specialised knowledge.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
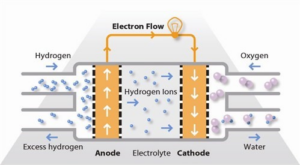
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully tested a 100-watt Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Power System (FCPS) on its orbital platform POEM3.
What Is Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell?
- Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, operate using a polymer-based proton-conducting membrane as their electrolyte, with hydrogen typically serving as the fuel source.
- It is an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- They function within lower temperature and pressure ranges, typically between 50 to 100 degrees Celsius.
- They are being developed for transportation, stationary, and portable applications.
Agriculture And Commodity Summit 2024
Context: The Chairman of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices gave a clarion call to increase private investments in the agriculture sector five times by 2030 while urging farmers to look at opportunities beyond food.
About Agriculture And Commodity Summit 2024
- Held at: New Delhi
- Increase in Private Investment: Experts emphasised the need to boost private sector investment in agriculture from 2% to 5-10% by 2030 and urged farmers to explore beyond food production, like producing crops for industrial needs such as ethanol.
- Integrated Farming Model by SBI: An “integrated farming model” to help diversify farmers’ incomes, promoting the concept of producers becoming processors.
- Credit and Insurance Democratisation: Highlighted the importance of increasing formal credit in agriculture, suggesting that a 10% rise in formal credit could result in a 1% increase in agriculture’s GDP contribution.
- Productivity Enhancement: NABARD stressed investing in productivity-enhancing agricultural practices that are sustainable and resource-efficient.
- Sugar Sector’s Leadership in Smart Agriculture: The potential for the sugar sector to lead in smart agriculture practices was discussed, along with the growing importance of maize as a water-efficient crop for ethanol production and climate change mitigation.
- Resilient Supply Chains: Experts called for promoting technologies and infrastructure that provide farmers with price visibility and better market access.
- Role of Women in Agriculture: The panel emphasised the centrality of women in agricultural policy design, advocating for greater access to technology and recognition of women as entrepreneurs.
- Financial Technology in Agriculture: The fintech agri ecosystem could significantly boost India’s GDP, with an estimated addition of $100 billion in the next five years due to increased agricultural investment.
- Food Security and Sovereign Agreements: There was a call for realistic policies in distributing free food grains and consideration of destination production on foreign soil under sovereign agreements to mitigate risks.
- Livestock Sector Potential: Industry experts discussed the role of dairy, poultry, and fisheries in providing affordable nutritional security.
Sloth Bear
Context: A 36-year-old male sloth bear died due to multi-organ failure at a zoo-cum-animal rescue centre in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
About Sloth Bear
- One of the eight bear species found across the world.
- Scientific Name: Melursus ursinus
- Distribution:
- Their range includes India, Sri Lanka and southern Nepal.
- 90% of the global Sloth Bear population is found in India.
- Habitat: They live in a variety of dry and moist forests and in some tall grasslands, where boulders, scattered shrubs and trees provide shelter.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Schedule I.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES): Appendix I.
- World Sloth Bear Day: First observed on 12th October 2022.
Rise in child marriages in West Bengal
Context: A recent study on child marriage in India published in the Lancet noted the overall decrease in child marriage across the country but pointed out that four States, mainly Bihar (16.7%), West Bengal (15.2%), Uttar Pradesh (12.5%), and Maharashtra (8.2%) accounted for more than half of the total headcount burden of child marriages in girls.
Current Status Of Child Marriage In India
Lancet Report
- Child marriage in India is decreasing but still prevalent, particularly in Bihar (16.7%), West Bengal (15.2%), Uttar Pradesh (12.5%), and Maharashtra (8.2%).
- West Bengal saw an alarming increase of over 500,000 child marriages, a 32.3% rise in headcount.
NFHS-5 Report
- West Bengal’s child marriage rate remains high at 41.6% for women aged 20-24.
- Murshidabad, an economically challenged district, shows a rise in child marriage rates from 53.5% to 55.4%.
Impact of Child Marriage
- Increased Infant Mortality: Child marriage is associated with higher rates of infant mortality, as highlighted by the instance of 10 infant deaths in a single day at Murshidabad Medical College.
- Low Birth Weight Issue: The incident also revealed a prevalence of extremely low birth weight among infants, often linked to child marriage.
- Health Risks to Young Mothers: Child marriage escalates risks during pregnancy and childbirth for young mothers, adversely impacting both their health and that of their infants.
- Generational Health Impact: High rates of child marriage, like the 41.6% in West Bengal, suggest a significant, ongoing health challenge for multiple generations.
- Educational Setback: Early marriage typically disrupts a girl’s education, curtailing her potential for future opportunities and financial independence.
Initiatives to overcome the issues of child marriage in India
- Kanyashree Prakalpa: A West Bengal initiative providing cash transfers to promote girls’ education and deter child marriage, benefiting about 81 lakh girls.
- Rupashree Prakalpa: This scheme offers financial incentives for the marriages of girls, with the goal of postponing their marriage age.
- Legal Age Revision: The Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2021, proposed to increase the legal marriage age for women to 21.
- Focused District Strategies: In 2022, West Bengal initiated district-level action plans targeting child marriage, emphasizing tailored local solutions.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















