Table of Contents
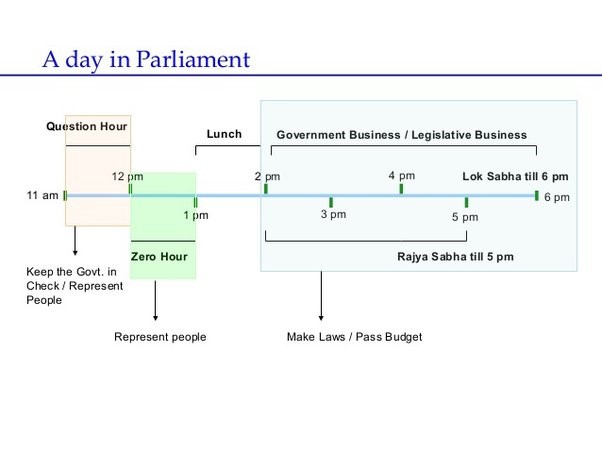
Zero Hour
Context: Some key issues such as Manipur violence, stricter laws against hate speech, etc. were raised during Zero Hour in the Lok Sabha.
About Zero Hour
- It is an Indian innovation in parliamentary proceedings (been used since 1962).
- Not mentioned in rules of procedure of either house of the Parliament
- Commences immediately after question hour and lasts till the day’s agenda (i.e. regular business of the House) is taken.
- Members can raise matters without giving prior notice.
Measures for Parliamentary Oversight
- Question Hour and Zero Hour: It enables Members of Parliament (MPs) to ask questions to ministers regarding government policies, programs, and actions.
- Example: Question hour played an important role in unravelling of Mundhra scam in 1950s
- Parliamentary Committees: They examine the bills, scrutinise government policies and budgets, and make recommendations.
- Example: Public Account Committee examines audit reports of CAG
- Example: Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs) have examined issues like 2G spectrum allocation.
- Debates and Discussions: MPs can raise concerns, express their views, and hold the government accountable through constructive debates.
- Example: Debates on issues like marriage age.
- No confidence motion: If passed results in the collapse of the Government.
- Example: Fall of NDA govt. in 1996.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
| PYQ |
Q. The Parliament of India exercises control over the functions of the Council of Ministers through
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (2017) (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: Option (d) |
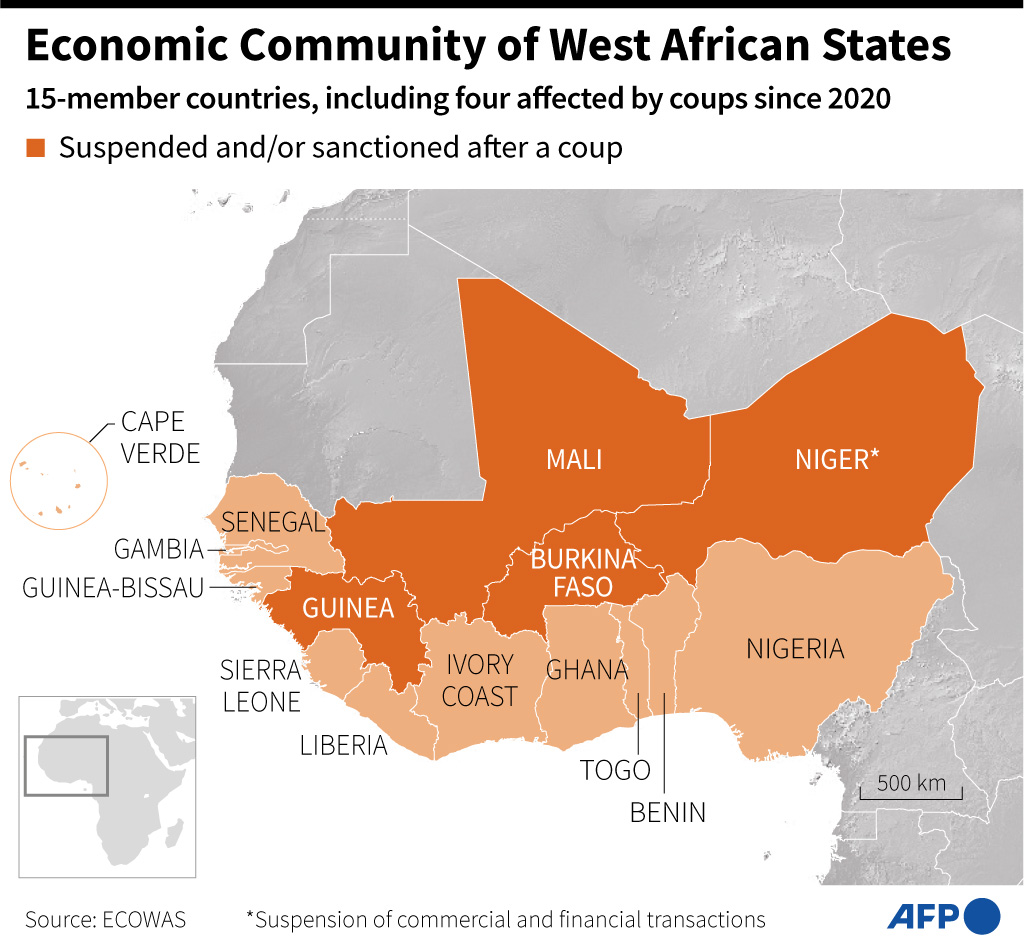
ECOWAS
Context: An extraordinary ECOWAS session was convened following Senegal President Macky Sall’s abrupt election postponement and the exit of Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger from the bloc.
About ECOWAS
- Founded: 1975 (Treaty of Lagos)
- Mission: Foster economic integration among member states
- Vision: Seamless region with democratic governance, rule of law, and effective governance
- Members: Benin, Cape Verde, Côte d’Ivoire, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Togo
- Key Objectives:
- Unified currency
- Single trade zone (in areas: industry, transport, telecommunications, energy, finance, socio-cultural)
- Conflict Resolution: Aims to resolve regional military conflicts
- Managed Economic Community of West African States Monitoring Group(ECOMOG) peacekeeping force (led by Nigeria in 1990s-2000s)
- Headquarters: Abuja, Nigeria


 Grammy Awards 2026: Full Winners List, H...
Grammy Awards 2026: Full Winners List, H...
 World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
World Wetlands Day 2026: Theme, History,...
 Union Budget 2026 Highlights: Key Announ...
Union Budget 2026 Highlights: Key Announ...

























