Table of Contents
World Association of Zoo & Aquariums (WAZA)
Context: The World Association of Zoo and Aquarium suspended the membership of Delhi’s National Zoological Park for six months, over concerns related to the welfare of an African elephant, Shankar, who has been kept chained in his enclosure.
About WAZA
- It is a global organisation that represents zoos, aquariums, and other organisations that care for animals and their habitats.
- WAZA is the only organisation representing zoos and aquariums at the global level.
- History: It was established in 1935 and has been an international NGO since
- It is based in Barcelona (Spain).
- Mission: To promote the care and conservation of animals and their habitats.
- Activities:
- Promoting cooperation between zoos and aquariums
- Encouraging high standards of animal welfare
- Promoting wildlife conservation
- Promoting environmental education
- Membership: WAZA’s membership includes leading zoos and aquariums, regional and national associations, and affiliate organisations.
- A zoo being suspended means it cannot attend conferences or activities organised by WAZA.
Central Zoo Authority (CZA)
- It is an autonomous body that oversees the management and development of zoos in India.
- Formation: In 1992 under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. (Statutory Body)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
- The CZA’s functions include:
- Evaluating zoos to ensure they adhere to relevant legislation
- Granting recognition to zoos that meet the CZA’s standards
- Regulating the exchange of animals between zoos
- Approving the exchange of animals between Indian and foreign zoos
- Coordinating capacity building programs for zoo personnel
- Implementing conservation breeding programs
- Conducting ex-situ research
- CZA is a companion member of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA).
Mineral Reserves
Nations with mineral reserves needed for energy transition
| Mineral | Uses | Reserves (Top 3) |
| Bauxite | ● Primary source of Aluminium.
● Essential for wind turbines, solar panels, batteries, electrolyzers and transmission cables. |
● Guinea
● Vietnam ● Australia ● India (8th) |
| Chromium | ● Used in wind turbines and for radiation shielding in nuclear power plants. | ● Kazakhstan
● South Africa ● India |
| Cobalt | ● Used in consumer electronics, catalysts for the oil industry, resistant metal alloys,
● critical components in many lithium-ion battery technologies. |
● Congo
● Australia ● Indonesia |
| Copper | ● Critical elements in solar photovoltaics, wind power, battery storage and electricity grids. | ● Chile
● Peru ● Australia |
| Graphite | ● Key component of battery anodes and therefore important for the transition to electric vehicles, and stationary batteries for balancing electricity grids. | ● Chian
● Brazil ● Mozambique ● India (7th) |
| Lithium | ● Core component of lithium-ion batteries. | ● Chile
● Australia ● Argentina |
| Manganese | ● Widely used in solar and wind power and in lithium-ion batteries for electric cars. | ● South Africa
● Australia ● China ● India (7th) |
| Molybdenum | ● Used as a catalyst in the petroleum industry also used in semiconductor base plates | ● China
● USA ● Peru |
| Nickel | ● Key component in the cathodes of lithium-ion batteries in electric cars. | ● Indonesia
● Australia ● Brazil |
| Rare Earths | ● Used in wind power for permanent magnets. | ● China
● Indonesia ● Brazil ● India (5th) |
| Silver | ● key component in the energy transition, with uses in solar panels, electric vehicles, and carbon capture and storage | ● Peru
● Australia ● Russia ● India (10th) |
| Uranium | ● Primary fuel for nuclear energy production | ● Kazakhstan
● Namibia ● Canada ● India (9th) |
Indian Wild Ass
Context: According to the latest population estimate, the number of Wild Ass has seen a significant increase in Gujarat.
About Indian wild Ass

- It is a subspecies of Asian Wild Ass (locally called KHUR)
- Characteristics:
- It is usually sand-coloured but can also appear in bluish-grey or pale chestnut shades.
- Male wild asses are significantly larger in size and strength than female wild asses
- It is one of the fastest land animals in India, it can run at speeds of 70 to 80 km/h.
- They are significantly larger than donkeys.
- Distribution:
- World’s last population of Indian WildAss is restricted to Rann of Kachchh, Gujarat.
- Historically, wild asses were found in North-West India, Pakistan and Central Asia, but presently they are limited only to the Little Rann of Kutch and Great Rann of Kutch.
- Habitat: Hot & Arid environment, Saline Deserts & arid Grasslands.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN: Near threatened.
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife Protection Act (1972): Schedule- I
Current Population Estimates
- The population of wild asses in Gujarat has been estimated at 7,672 as per the 10th Wild Ass Population Estimation (WAPE) conducted by the Gujarat government.
- This represents a 26.14% increase from the previous estimation in 2020, which recorded a population of 6,082.
| Wild Ass Sanctuary |
|
Marburg Virus
Context: Rwanda is facing its first outbreak of the Marburg virus, a highly lethal pathogen, with at least 46 confirmed cases and 12 fatalities reported so far.
About Marburg Virus
- It is a zoonotic RNA virus that causes Marburg virus disease (MVD),
- First Outbreak: Occurred in 1967 in Marburg, Germany, associated with laboratory exposure to African green monkeys.
- Family: Belongs to the Filoviridae family, similar to the Ebola virus.
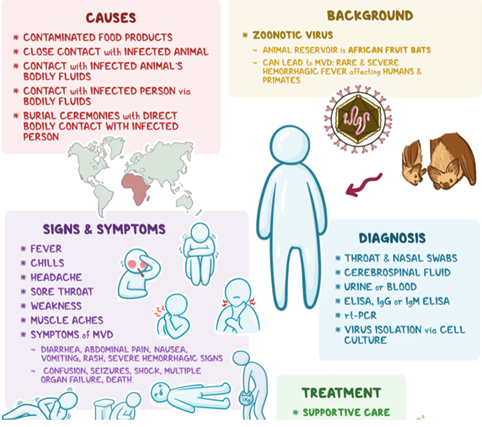
Prevention and Treatment
- No Approved Treatments or Vaccines: Currently, there are no specific antiviral drugs or vaccines for MVD. Supportive care is critical for improving survival rates.
- Supportive Care Measures: Includes rehydration (oral or intravenous fluids) and treatment of specific symptoms.
- Experimental Vaccines and Treatments: Rwanda is seeking candidate vaccines and treatments; the Sabin Vaccine Institute has provided 700 doses of an experimental vaccine for healthcare professionals.


 Bihar Assembly Election 2025 Dates, Poli...
Bihar Assembly Election 2025 Dates, Poli...
 Bharat Bandh 9 July 2025: Over 25 Crore ...
Bharat Bandh 9 July 2025: Over 25 Crore ...
 Sukhoi Su-57: Will India Choose Russia�...
Sukhoi Su-57: Will India Choose Russia�...





















