Table of Contents
Digital Payments Intelligence Platform
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to establish a Digital Payments Intelligence Platform.
About the Initiative
- Aim: Enhancing security across the digital payments ecosystem by enabling network-level data sharing and intelligence.
- Formation of a Review Committee: A committee chaired by A.P. Hot has been formed by the RBI to investigate the various aspects of creating this digital public infrastructure.
- The committee is expected to provide its recommendations within two months.
- Scope: This new initiative will involve a detailed examination of the potential features and impacts of implementing such a platform within the existing payments infrastructure.
- Recurring payments: Fastags, NCMC, UPI Lite
- The RBI has announced the inclusion of auto replenishment facility for Fastag, National Common Mobility Card (NCMC), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) Lite wallets, under the e-mandate framework.
- This will be activated when balances in Fastag or NCMC drop below a customer-set threshold.
- The RBI plans to remove the requirement for a pre-debit notification 24 hours before an actual debit for automatic replenishments.
- UPI Lite will be included in the e-mandate framework, allowing automatic wallet reloads when the balance falls below a set threshold. This is aimed at facilitating smaller transactions without additional authentication.
- Bulk Deposits Limit Adjustment: The RBI proposes to redefine bulk deposits as single rupee term deposits of Rs 3 crore and above, up from Rs 2 crore, for commercial banks and small finance banks.
- The definition for local area banks will be aligned with that for regional rural banks (RRBs) at Rs 1 crore and above.
- Interest Rate Flexibility on Bulk Deposits: Banks are given the discretion to offer different interest rates on bulk deposits based on their Asset-Liability Management (ALM) needs.
- Revising Export and Import Guidelines: The RBI intends to update and simplify the guidelines governing the export and import of goods and services to better align with the evolving global trade dynamics and enhance ease of business operations.
- The RBI has announced the inclusion of auto replenishment facility for Fastag, National Common Mobility Card (NCMC), and Unified Payments Interface (UPI) Lite wallets, under the e-mandate framework.
| Facts |
|
Senkaku Island
Context: Japan lodged a protest against Beijing after four armed Chinese coast guard vessels entered waters that Tokyo considers its territory.
About Senkaku Island
- Location: The islands are located in the East China Sea, northeast of Taiwan, consisting of eight uninhabited islands covering a total area of about 7 sq km.
- Strategic Importance: The islands are situated near crucial shipping lanes, provide rich fishing grounds, and are believed to contain oil deposits.
- About The Dispute: The dispute involves a group of uninhabited islands known by different names: Senkaku Islands in Japan, Diaoyu Islands in China, and Tiaoyutai Islands in Taiwan.
- Both Japan and China, along with Taiwan, claim ownership of these islands.
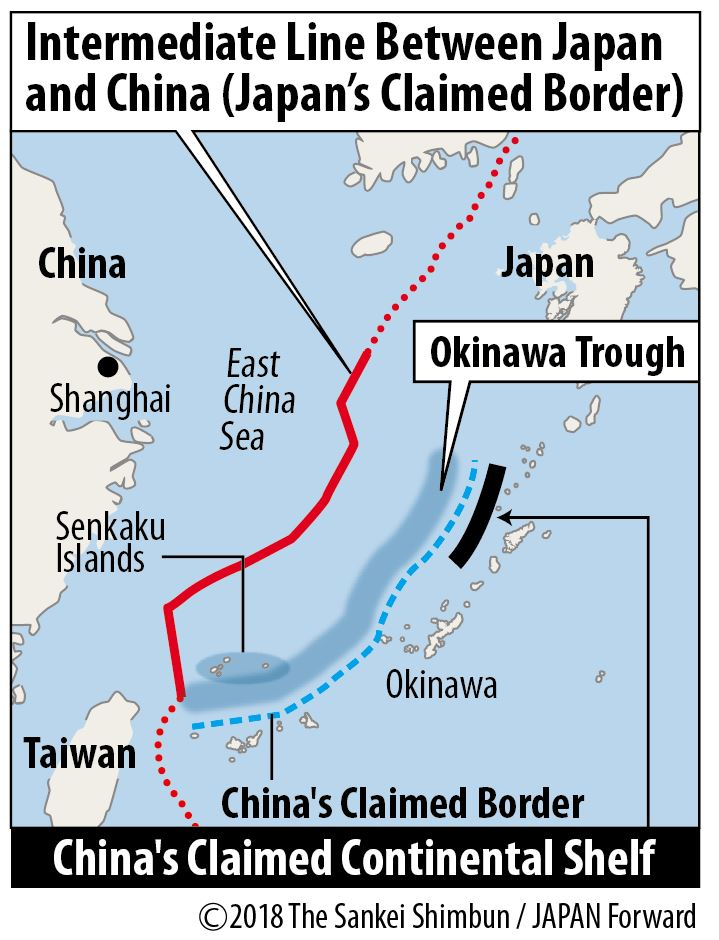
- Japan’s Claim:
- Post World War II, Japan relinquished claims to several territories including Taiwan as per the 1951 Treaty of San Francisco.
- Under this treaty, the Nansei Shoto islands, which Japan claims include the Senkaku Islands, were placed under U.S. trusteeship and later returned to Japan in 1971.
- Recently, a local council in southern Japan passed a bill to rename an area including the Senkaku Islands from Tonoshiro to Tonoshiro Senkaku.
- China did not initially object to the islands’ status under the San Francisco Treaty but began to assert claims in the 1970s following the discovery of potential oil resources.
- China’s Claim:
- China contends that the islands have been part of its territory since ancient times, primarily used as important fishing areas, and were administratively part of Taiwan province.
- China argues that when Taiwan was returned in the Treaty of San Francisco, the islands, as a part of Taiwan, should also have been returned to Chinese control.
Russia’s Growing Footprints in Africa
Context: Russia is increasing its presence in Africa’s sub-Saharan region, particularly the Sahel, through military assistance and political support.
Russia’s Growing Influence In Africa
Strategic Security Partnership:
- Russia is becoming the preferred security partner over traditional Western allies like France and the U.S.
- It utilises private security companies like Wagner and its successor, Africa Corps, to establish a military presence.
Objectives and Strategies
- Political and Economic Motives: Russia aims to secure political support or neutrality from African countries concerning its actions in Ukraine.
- Africa’s 54 countries form the largest voting bloc at the United Nations, where opinions on Russia’s actions in Ukraine have been divided.
- Disinformation Campaigns: Russia-linked entities have conducted disinformation campaigns to weaken ties between African states and Western countries, targeting over 22 countries with 80 documented campaigns.
Why African Nations Are Turning to Russia
- Appeal of Russian Partnership: Russia offers security assistance without political interference, appealing to countries like Mali, Niger, and Burkina Faso— all governed by military juntas.
- African nations are discontent with former colonial powers and perceive Western demands on democracy and human rights as hypocritical.
- Resource Access: Russia seeks access to Africa’s rich mineral resources, such as cobalt and lithium, vital for electronics and batteries.
- It has signed mining deals in several countries, including the Central African Republic (gold and diamonds), Congo (cobalt), and Sudan (gold and oil).
Russian Mercenary Activities
- Wagner Group Operations: Wagner mercenaries first appeared in Sudan in 2017 to support then-President Omar al-Bashir in exchange for gold mining rights.
- Their presence has expanded to Libya, where they supported Khalifa Hifter, and the Central African Republic, gaining access to gold and diamond mines.
| The Wagner Group is a private military company (PMC) known for its operations in conflict zones around the world, particularly in regions where Russia seeks to extend its influence but maintain plausible deniability about its involvement. |
- Impact of Coups: Military coups in Mali (2020 and 2021), Burkina Faso (2022), and Niger (2023) have led to the ousting of French and other Western forces, with these countries turning to Russia for military support.
Economic and Trade Relations
- Trade and Economic Impact: Despite Russia’s increasing role in the military and mining sectors, it remains a minor overall trading partner with Africa, accounting for less than 1% of Africa’s exports.
- The European Union, by contrast, accounts for 33% of Africa’s exports.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
Ethical Leadership and Environmental Stewardship in Public Administration (GS 4):
- Anshul Gupta, an IAS officer, spearheaded the restoration of the Yam Talaiya pond in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh.
- He took on the task of restoring the dilapidated Yam Talaiya pond, which is connected to the primary Vishnu Sagar Talab and receives flow from nearby farm fields.
- Significance: This pond holds cultural significance as it is near the Chitragupta Mandir, associated with Lord Chitragupta. Historically, it was essential for local farmers and had rich biodiversity.
- Challenges: Over the years, the pond suffered from neglect, excessive silt deposition, invasive weeds, and encroachments, diminishing its water-holding capacity and ecological health.
- Restoration Efforts:
- Planning: In partnership with the Environmentalist Foundation of India (EFI), a scientific and environment-friendly restoration plan was developed.
- Execution: The project involved de-weeding, garbage removal, desilting, and construction of new embankments and sedimentary wells. Approximately 125 volunteers participated, and the project was funded through CSR and private donations without government funds.
- Outcome: The restoration enhanced the pond’s capacity by a third, improved groundwater levels, and revitalised local flora and fauna. It now serves as a model for other conservation efforts under India’s Mission Amrit Sarovar, aimed at rejuvenating water bodies across the country.
- Impact: The restored pond has not only supported local biodiversity but also boosted tourism and local pilgrimage, significantly benefiting the community and environment.


 National Red List Assessment (NRLA): Ind...
National Red List Assessment (NRLA): Ind...
 India–Australia Defence Agreement 2025...
India–Australia Defence Agreement 2025...
 Embryos from Human Skin DNA: A Groundbre...
Embryos from Human Skin DNA: A Groundbre...




















