Table of Contents
New Treatment regimen for MultiDrug-Resistant TB
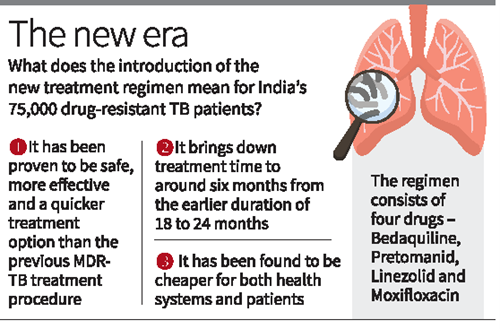
Context: The Union Health Ministry has approved the introduction of a new treatment regimen for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in India.
About Tuberculosis (TB)
- It is a bacterial infection spread through inhaling tiny droplets from the coughs or sneezes of an infected person.
- TB is caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis, belonging to the Mycobacteriaceae family.
- Transmission: TB spreads from person to person through the air.
- Tests: Truenat MTB Test, CBNAAT Test etc.
- Types:
- Pulmonary TB: Affects the lungs
- Extra-Pulmonary TB: Affects other organs.
- TB is a treatable and curable disease.
- Treatment:
- Vaccine: Currently, Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is the only licensed vaccine available for the prevention of TB.
- Major drugs (4): Isoniazid (INH), Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide & Ethambutol.
| Types of Drug-Resistant TB |
|
| Facts |
TB Elimination Targets:
|
NPS Vatsalya Scheme
Context: The Union Government has announced the launch of the NPS Vatsalya Scheme. The government and the Pension Fund Regulatory & Development Authority (PFRDA) are finalising the details of the scheme.
About National Pension System (NPS) Vatsalya
- It is a modified version of the National Pension System (NPS), designed specifically for minors.
- Implementing Agency: PFRDA
- Aim: To enhance financial literacy by introducing minors to disciplined savings and investments.
- Features:
- Under this scheme, parents or guardians will be able to open an NPS account for their children.
- The funds will accumulate until the child turns 18.
- Once the child reaches adulthood, the account will convert seamlessly into a regular NPS account.
- When the minor turns 18, they will have the option to exit the scheme.
- 80% of the total accumulated corpus is required to be invested in an annuity plan.
- Remaining 20% can be withdrawn as a lump sum.
| About PFRDA |
|
NTCA letter on Relocation from Tiger Zones
Context: Recently the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has issued letters to 19 States asking them to prioritise the removal of villagers who are residents in the core tiger zones. Several organisations and activists have criticised this move of NTCA.
About NTCA
- Established: In 2005 (Under Wildlife Protection Act (1972)
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC)
- Composition:
- Chairperson: The Minister in charge of the MoEFCC
- Vice-Chairperson: The Minister of State in the MoEFCC
- 3 members of Parliament: Two elected by the Lok Sabha and one by the Council of States
- Eight experts or professionals: With experience and qualifications in wildlife conservation
- Inspector-General of Forests: In charge of Project Tiger, who serves as the ex-officio Member Secretary
- Tiger Census: NTCA Conducts Tiger Census every 4 Years.
- Functions:
- Monitors tiger populations and works to prevent poaching, hunting, and other threats.
- Approves state governments’ tiger conservation strategies.
- Sets standards for tourism in tiger reserves.
- Addresses conflicts between humans and wildlife and promotes coexistence.
- Evaluates the ecological sustainability of tiger reserves and prevents harmful activities near them.
| Project Tiger |
|
VisioNxt
Context: The union Minister of Textiles recently launched the ‘VisioNxt Fashion Forecasting Initiative’ of National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT).
What is VisioNxt ?
- It is a bilingual web portal to support weavers, manufacturers, domestic businesses, homegrown designers etc.
- Aim:
- Foster healthy global competition
- Elevate Indian culture and design on the global stage
- Establish India as a leader in the global fashion sector
- Technology Used: AI model ‘Deep Vision’
- It is designed to decode patterns and interpret fashion trends in India.
- Features:
- It will offer trend-related consultancy services, academic courses, and workshops
- It is India’s first initiative to integrate Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Emotional Intelligence (EI) to forecast fashion trends.
- It will empower Indian fashion professionals with India-specific data and will reduce their reliance on international forecasting systems.
La-Nina
Context: La Nina forecasts from leading international agencies were significantly off-target this year. It’s crucial to assess both the potential impact of the delayed La Nina onset and the reasons behind the inaccurate global weather model predictions.
About La-Nina
- La Nina refers to the periodic cooling of ocean surface temperatures in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific.
- Occurrence: It occurs every 3 to 5 years, but on occasion can occur over successive years.
- La Nina represents the cool phase of the El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- During a La Nina event, the changes in Pacific Ocean temperatures affect the patterns of tropical rainfall from Indonesia to the west coast of South America
- In the ‘La Nina year’, rainfall associated with the summer monsoon in Southeast Asia tends to be greater than normal, especially in northwest India and Bangladesh.
| El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) |
|
| Impact of La-Nina on India’s Weather |
|


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















