Table of Contents
Early Warning & Control Aircraft
Context: The Indian Air Force (IAF) is planning to procure 12 early warning aircraft.
What are Early Warning Aircraft?
- They are special military planes that have powerful radars and sensors which help them detect and track other aircraft, ships or vehicles from very far away.
- They act like flying radar stations, giving military forces a clear view of the battle area and improving awareness during operations.
- They are often referred to as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System).
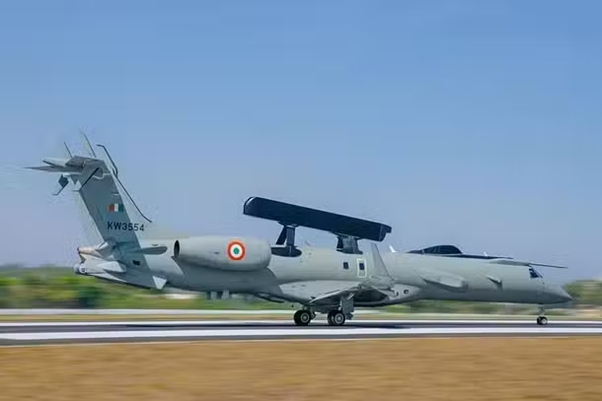

Current AWACS Fleet of Indian Air Force (IAF)
- 5 operational (3 Phalcon + 2 Netra Mk-1)
- Phalcon:
- Procured from
- Mounted on Russian IL-76 transport aircraft.
- It has 360-degree radar coverage and a range of 400 km.
- Netra Mk-1:
- Indigenously developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Centre for Airborne Systems (CABS).
- Mounted on Brazilian Embraer ERJ-145 jets.
- It provides 240-degree coverage and a range of 500 km.
| Defense Research and development Organisation (DRDO) |
|
Civil War in Sudan
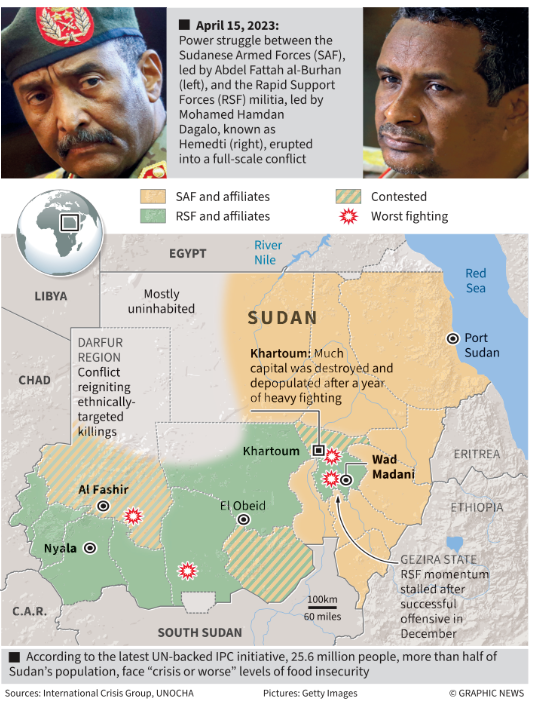
Context: Sudan has been undergoing a civil war between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) for the past 18 months. Recently, a major offensive was launched by the Sudanese Armed Forces against the RSF in Khartoum and Bahri. The war has led to the death of about 20,000 people and the International Organisation for Migration (IOM) has estimated that more than 10 million people have been displaced.
Key Actors in the Civil War
Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF)
- Leadership: Led by General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan.
- Claims: The SAF positions itself as the legitimate government of Sudan, despite coming to power via a coup in 2021.
- Military Strategy: The SAF has recently intensified airstrikes and captured regions around
Rapid Support Forces (RSF)
- Leadership: Commanded by General Hamdan Dagalo, also known as Hemedti.
- Background: Originally formed from the Janjaweed militia, the RSF has gained control over significant territories, particularly around the capital.
- International Relations: The RSF seeks alliances with various Arab nations to bolster its legitimacy.
About Sudan
- Location: Northeastern Africa. (Capital- Khartoum)
- Bordering Countries: North by Egypt, on the east by the Red Sea, Eritrea, and Ethiopia, on the south by South Sudan, on the west by the Central African Republic and Chad and on the northwest by Libya.
- Geography:
- It is mainly composed of vast plains and plateaus that are drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
- Sudan is Africa’s 3 largest country by area.
- Major rivers: Blue Nile, White Nile & Arbata.
- Nubian Desert: Rocky, arid desert in northeastern Sudan.
- Important Mountains: Murrah (Highest Peak -Deriba Caldera), Nuba
- National Parks: Dinder NP and Radom NP (Both designated as UNESCO biosphere reserves)
- Major Ports: Port Sudan, Osaief Port and Suakin Port.
- Important Regions:
- Darfur Region: Located in western Sudan. There has been an ongoing civil war between the Arab and African communities. This has led to widespread violence and human rights abuses.
- Abyei Region: It is a border town that is disputed between South Sudan and Sudan. It is an Oil rich region.
| Facts |
|
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. In recent years Chad, Guines, Mali and Sudan caught the international attention for which one of the following reasons is common to all of them? (2023)
(a) Discovery of rich deposits of rare earth elements (b) Establishment of Chinese military bases (c) Southward expansion of Sahara Desert (d) Successful coups
Answer: D |
Chaukhamba-III massif
Context: Two women trekkers who went missing during a trek to the Chaukhamba-III massif in Chamoli were located by a group of French mountaineers and later airlifted by IAF helicopters.
About Chaukhamba Massif
- Chaukhamba massif, a group of 4 mountains (Chaukhamba I, II, III & IV) in the Garhwal Himalayas of Uttarakhand.
- It is a popular destination for trekking and peak climbing.
- Gangotri glacier originates from the Chaukhamba Massif.
- Highest Peak of the group: Chaukhamba I (7,138 metres)
- Location: Between the Gangotri, Bhagirathi and Satopanth glaciers. (Garhwal Himalayas)
- Other Important Mountain Peaks of Uttarakhand:
- Nanda Devi, Mount Kamet, Trisul, kedarnath, Gaumukh
| What is a Mountain Massif? |
| It refers to a group of mountains that are part of a mountain range, or a compact portion of a mountain range that contains one or more summits. |
Cabinet approves India’s joining of Energy Efficiency Hub
Context: The Union Cabinet has approved for India to join the ‘Energy Efficiency Hub’.
About Energy Efficiency Hub
- Energy Efficiency Hub or ‘the Hub’ is a government-to-government platform for global collaboration on energy efficiency.
- The Hub is a voluntary collaboration of governments seeking to strengthen their effectiveness in deploying energy efficiency.
- History: At the G20 Leaders’ Summit in Hamburg in 2017, Germany as the president of G20 proposed to establish the Energy Efficiency Hub. The Hub was established in 2019, and the secretariat started operations in 2021.
- Task Groups: It pursues solutions through thematic Task Groups focused on topics of common interest to Hub Members. These task groups inform policy making, communicate international best practices and share information between countries, international organisations and private sector.
- Currently, five task groups are operational under the Energy Efficiency Hub:
- Digitalisation Working Group (DWG): Advances digitalisation of energy-efficiency technologies.
- Super-efficient Equipment & Appliances Deployment (SEAD): Promotes manufacture, purchase and use of efficient appliances, lighting and equipment worldwide.
- TOP TENS: Prepares list of best energy efficient technologies and best practices in key energy-consuming sectors the governments can promote.
- Energy Management Action Network (EMAK): Facilitates public-private exchanges on systems for raising energy efficiency in industry and buildings.
- Energy Efficiency in Buildings (EEB): Serves as a platform to exchange policy information about improving energy efficiency in buildings.
- Secretariat:
- Hosted by the International Energy Agency (IEA).
- Secretariat seeks to foster coordination
- Membership:
- As of July 2024), 16 countries are members of the Energy Efficiency Hub. They are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Denmark, European Commission, France, Germany, Japan, Korea, Luxembourg, Russia, Saudi Arabia, USA and UK.
- Member governments get to learn international best practices on how to design and implement energy efficiency policies.
- IEA Members, IEA Association Countries and Clean Energy Ministerial Members are eligible to join the Hub.
- Governance of Energy Efficiency Hub: Members oversee and direct the functioning of the Hub through a Steering Committee, composed of one representative from each member.
India and Energy Efficiency Hub
- Currently, India is an Association country of International Energy Agency (IEA), which makes India eligible to join the Energy Efficiency Hub as a member country.
- Energy Efficiency Hub is a successor of International Partnership for Energy Efficiency Cooperation (IPEEC). India was a member of IPEEC.
- India’s nodal agency for Energy Efficiency Hub: Bureau of Energy Efficiency, a statutory body, have been designated as the implementing agency on behalf of India.
- Benefits for India by Joining the Energy Efficiency Hub:
- Promoting energy efficiency technologies and processes.
- Solidifies India’s commitments towards sustainable development.
- Aligns with India’s goal of transition to net zero and low carbon economy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Helps improve India’s energy security.
- Opportunities for India to collaborate with other member countries, sharing India’s expertise and learning international best practices on energy efficiency.


 Industrial Parks in India: Driving Manuf...
Industrial Parks in India: Driving Manuf...
 National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC...
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC...
 Reforming Fertiliser Subsidy in India: N...
Reforming Fertiliser Subsidy in India: N...

























