Table of Contents
India’s First Underwater Metro
Context: PM Narendra Modi inaugurated India’s first underwater metro in Kolkata.
More In News
- The newly opened stretch is the Esplanade-Howrah Maidan section of the Kolkata Metro.
- The underwater journey is part of the country’s first underwater transportation tunnel.
- The Esplanade-Howrah Maidan stretch, measuring 4.8 kilometres, is part of the East-West Corridor.
- Additionally, Kavi Subhash-Hemanta Mukhopadhyay section, connecting the New Garia-Airport line, was also inaugurated.
- This new stretch, extending 5.4 kilometres, aims to connect southeastern parts of Kolkata with the Metro network.
INS Jatayu, MH -60R Helicopters
- The Indian Navy commissioned INS Jatayu at Minicoy island, its second base in Lakshadweep after INS Dweeprakshak in Kavaratti.
- Additionally, the Navy commissioned its first MH-60R multi-role helicopter squadron INAS 334 ‘Seahawks’ at Kochi, a major capability boost for its rotary fleet and its anti-submarine warfare capabilities.
INS Jatayu Significance
- Strategic Enhancement: Launch of INS Jatayu as part of India’s initiative to strengthen surveillance near the Nine Degree channel.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Plans for infrastructure improvement on Minicoy Island, including jetty enhancements for larger vessel accommodation.
- Naval Capabilities Boost: INS Jatayu expected to extend the Indian Navy’s operational reach and contribute to the Lakshadweep islands’ development.
- Security and Anti-Piracy Operations: The Indian Navy’s proactive stance on threats in the Arabian Sea, focusing on anti-drone and anti-piracy measures.
Nine Degree Channel
- Geographical Position: The Nine Degree Channel divides Minicoy Island from the primary Lakshadweep group, including Kalpeni, Suheli Par, Maliku Atoll, and the Amindivi Subgroup, which constitute the Union Territory of Lakshadweep.
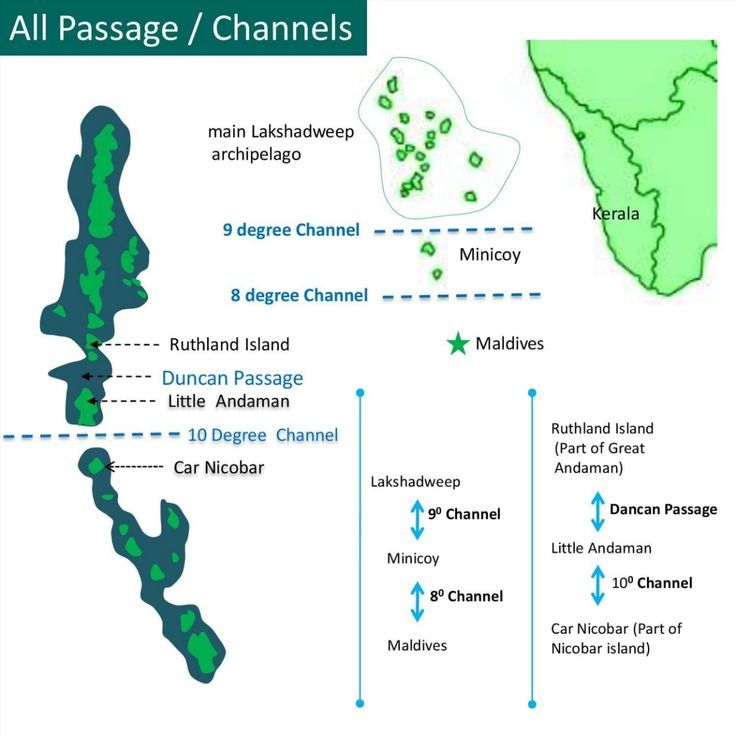
- Dimensions and Depth: Spanning 200 kilometres in width, the channel has a depth reaching 2,597 metres.
- Investigator Bank: This submerged feature lies in the southern part of the channel.
- Commercial Significance: The channel is a crucial maritime route for trade vessels travelling between Europe, the Middle-East, Western Asia, and regions of South-East Asia as well as the Far-East.
- Naming Origin: Its nomenclature comes from its location along the latitude of 9 degrees north of the equator.
| MH-60R Helicopter |
| Role and Functions: The MH-60R Seahawk is a versatile helicopter designed for multiple missions including anti-submarine warfare, anti-surface warfare, search and rescue operations, medical evacuation, and vertical replenishment. |
2023 – Deadliest year in Decade for Migrants
Context: As per the UN’s International Organization for Migration at least 8,565 people died on migration routes worldwide in 2023.
More in News
- This death toll marks a 20% increase from 2022, signalling an urgent call to action to save lives, according to the IOM.
- The previous record was in 2016 with 8,084 deaths.
- The IOM cites the lack of safe, regular migration pathways as a reason many resort to dangerous, irregular routes.
- The Mediterranean was the most lethal migration route in 2023, with over 3,129 reported deaths and disappearances.
- Drownings accounted for over half of all migrant deaths in 2023, followed by 9% from vehicle accidents and 7% from violence.
- The IOM’s Missing Migrants Project, an open-access database on migrant deaths, was initiated in 2014.
- Over 63,000 cases have been recorded by the database, with actual numbers presumed higher due to data collection difficulties.
| International Organization for Migration |
|
Forgotten Women of Science in India
Context: Despite initiatives to promote women in science, India faces a persistent challenge in supporting their scientific careers.
| Facts |
|
Women in Science: Breaking Barriers and Achieving Milestones
Pioneers and Their Struggles
- Rosalind Franklin: Contributed to discovering the DNA structure in 1951, went unrecognised during her career.
- Jocelyn Bell: Discovered the first radio pulsars in 1967, faced similar lack of recognition.
- Rajinder Jeet Hans-Gill: Dressed as a boy in the 1950s to study mathematics in Punjab.
- Kamala Sohonie: Conducted a satyagraha for IISc Bangalore to admit women.
Notable Indian Women Scientists
- Gagandeep Kang: Renowned for her work in virology.
- Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw: Pioneered in biotechnology and founder of Biocon.
- Rohini Godbole: Acclaimed for her contributions to particle physics.
- Prajval Shastri Majumdar: Known for her work in astrophysics.
Recognition and Celebrations
- ISRO’s ‘Rocket Women’- Ritu Karidhal: Played a crucial role in Chandrayaan-II and III Moon missions.
- K. Janaki Ammal: The first Indian woman to receive a PhD in botanical science in 1931, notable for her work with sugarcane and hybrids.
- Archana Sharma: Cytogeneticist who made significant contributions to her field.
- Raman Parimala: Mathematician celebrated for her work in algebra.
- Bibha Chowdhuri: Physicist who made her mark in physics.
- Asima Chatterjee: Chemist known for her contributions to organic chemistry.
Publications Highlighting Women’s Contributions in Science
- Lab Hopping- Women Scientists in India by Aashima Dogra and Nandita Jayaraj: Explores gender inequality in Indian science.
- Vigyan Prasar’s Resource Book: Profiles Indian women scientists across history.
- Lilavati’s Daughters- The Women Scientists of India edited by Ram Ramaswamy and Rohini Godbole: An anthology of women scientists in India.
- Women Scientists in India- Lives, Struggles, and Achievements by Anjana Chattopadhyay: Details the neglect and challenges faced by women in science.
- Gutsy Girls of Science by Ilina Singh: Celebrates the lives of women who overcame obstacles to achieve in STEM.
- Janaki Ammal: Life and Scientific Contributions by Nirmala James: Insights into the life of Janaki Ammal, a pioneer in botany.
- Chromosome Woman, Nomad Scientist, a Life – 1897 to 1984 by Savithri Preetha Nair: A biography of E.K. Janaki Ammal, detailing her journey and challenges.
- A Braided River- The Universe of Indian Women in Science by Christopher Coley, Christie Gressel, and Abhijit Dhillon: Discusses the impact of the gender gap in science.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Law Commission recommends new law to protect trade secrets
Context: The 22nd Law Commission, led by Justice Ritu Raj Awasthi, advocated for new laws to safeguard trade secrets, including provisions for whistleblower protection, compulsory licensing, government use, and the public interest.
About Trade Secrets
- Trade secrets, as a form of intellectual property, relate to confidential information that holds value due to its secrecy, offering the potential for sale or licensing and capable of indefinite protection, unlike other intellectual property types.
- Current Legal Framework in India: In the absence of specific legislation for trade secret protection, India relies on general contract laws, criminal law, and principles related to breach of confidence and equity.
Need For New Law
- The report highlights that trade secrets, including those held by the Government of India, are targets of economic espionage by foreign entities, emphasising the need for comprehensive legislation to address trade secret breaches and espionage activities.
- The 289th Law Commission Report on ‘Trade Secrets and Economic Espionage’ was prompted by governmental discussions recognizing the need for specific legislation on this matter.
- The Department of Legal Affairs and Legislative Department contemplated the enactment of the Economic Espionage Act and Trade Secrets Protection Act, producing a concept paper, draft cabinet note, and draft bill.
Efforts By Law Commission
- Due to the complexity of trade secrets, the Law Commission was tasked in October 2017 to explore the feasibility of enacting specific laws after receiving a request via a letter.
- The Law Commission engaged in detailed consultations with experts across judiciary, academia, government, and industry sectors to thoroughly investigate trade secrets and economic espionage law.
- The Commission considered the TRIPS Agreement, India’s international obligations, and how trade secrets are handled in jurisdictions like the UK, USA, EU, and Germany, proposing a draft Protection of Trade Secrets Bill, 2024.
Historical Context
- The importance of trade secrets emerged in 1977 following the Coca-Cola formula incident, leading to the company’s withdrawal and later re-entry into India.
- The National Intellectual Property Rights Policy of 2016 and a Parliamentary Standing Committee Report underscored the importance of legislating trade secret protection.
| About Law Commission |
Nature and Formation: The Law Commission of India is neither a constitutional body nor a statutory body, it is an executive body.
History of Establishment:
Functions:
|
| Article 39A |
The state must:
|
Examples, Case Studies and Data Points For Value Edition
- Agriculture related Government Schemes (GS 3): Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution has recently launched ‘e-Kisan Upaj Nidhi’– a digital gateway of Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA).
- Poverty (GS 1): Latest data of the World Poverty Clock showed India has managed to bring down ‘extreme poverty’ below 3% of its population.
- Sustainable Development (GS 3): In the Tian-Shan mountains of Kyrgyzstan, villagers have made an artificial glacier to provide water for their drought-hit farms.
- Women Empowerment (GS 1): New Delhi has no pending cases of sexual harassment at workplace, as the sole designated court (The Industrial Tribunal) to deal with these at the district level has brought the pendency down to zero.


 Pariksha pe Charcha 2025, Overview, Even...
Pariksha pe Charcha 2025, Overview, Even...
 National Policy on Framework on Agricult...
National Policy on Framework on Agricult...
 How Scientists used Scotch tape to Creat...
How Scientists used Scotch tape to Creat...




















