Table of Contents
Public Accounts Committee (PAC)
Context: The Public Accounts Committee will hold a performance review of regulatory bodies established by Act of Parliament.
About PAC
- Origin:
- IIt was established in 1921 on the basis of the Government of India Act, 1919. (Montague-Chelmsford Reforms).
- It is one of the oldest Parliamentary Committees in India.
- Composition: 22 members (15 from Lok Sabha + 7 from Rajya Sabha).
- Election method: Members of the committee are elected through a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
- Chairman: Appointed by the Speaker from amongst members of the committee.
- Since 1967, it has been a Parliamentary tradition to appoint the Chairman from the Opposition party.
- Tenure: 1 Year (Chairman & Members)
- Functions:
- It is responsible for scrutinising the audit reports of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG).
- It holds the government accountable for its financial decisions and actions.
- It examines the accounts of state corporations and accounts of autonomous
- and semi-autonomous bodies audited by CAG.
- PAC does not examine reports of those public undertakings which are allotted to the Committee on Public Undertakings.
| Did You Know ? |
| Financial Control by Parliament with the help of committee system originated in England in the sixteenth century and thereafter in the USA. |
Loss and damage Fund
Context: Recently Kerala’s Wayanad District was hit by devastating landslides. A key discussion has emerged on whether subnational entities can seek compensation from the UNFCCC’s Loss and Damage Fund (LDF).
About Loss & Damage Fund
- It is a financial mechanism that helps developing countries to deal with the economic and non-economic loss and damage caused by climate change.
- Established: In COP-27 (Conference of Parties) of UNFCCC at Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt
- Managed by: World Bank (Interim trustee for 4 Years)
- Objectives:
- Supporting vulnerable nations
- Addressing and compensating for losses and damages incurred due to climate change
- Financing humanitarian assistance in the immediate aftermath of a disaster
- Addressing medium– and long-term impacts of Climate Change
| UNFCCC |
|
Critical Minerals Mission
Context: Recently Ministry of Mines organised a seminar to discuss objectives of Critical Minerals Mission
About Critical Minerals Mission
- It is a strategic initiative announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 to help India become self-reliant in critical minerals.
- The government has waived customs duty on 25 critical minerals and blister copper.
- Objectives of the Mission:
- Streamline the supply chain of critical minerals by boosting domestic output and recycling of critical minerals like copper and lithium.
- Reduce India’s import dependency on critical minerals, which is currently 100% for some elements
- Identify critical minerals and plan for their acquisition and preservation.
- Increase India’s capacity for refining and processing critical minerals and find substitutes for critical minerals through R&D.
| What are Critical Minerals? |
|
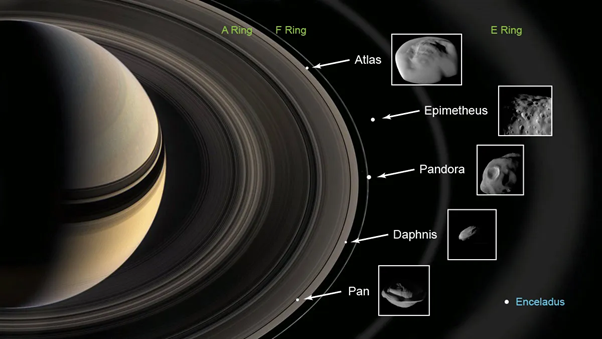
Saturn & Its Rings
Context: Saturn’s rings will briefly disappear from Earth’s view in March 2025 due to an optical illusion.
Reason behind Disappearance
- This phenomenon occurs due to Saturn’s axis tilt (26.73 degrees).
- This occurs when Saturn’s rings align edge-on with Earth, making them appear invisible due to their thinness (tens of metres thick), reflecting minimal light.
- Every 13 to 15 years, the edge of Saturn’s rings aligns directly with Earth. It last occurred in 2009.
- Saturn takes 29.4-years orbit around the Sun.
Rings of Saturn
- Composition: The rings are made up of water ice, dust and other materials.
- Size: The pieces range in size from smaller than a grain of sand to the size of a mountain.
- Origin: The pieces are thought to be from comets, asteroids, or moons that were broken apart by Saturn’s gravity before reaching the planet.
- Thickness: The rings are generally about 30 feet (10 metres) thick.
- Rings: The main rings are A, B, and C, and the D ring is very faint and closest to Saturn.
| Facts about Saturn |
|
Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI)
Context: Many States have raised the demand that the share of tax devolution from the net proceeds must be fixed at 50% by the 16th Finance Commission.
What is VFI ?
- When different levels of government, like the central and state governments, don’t have a fair balance between the money they can raise and the responsibilities they need to pay for.
- This means one level might have more financial duties but less ability to generate revenue, creating an uneven situation.
Role of Finance Commision
- The 15th Finance Commission highlighted that States in India face a significant Vertical Fiscal Imbalance (VFI).
- States incur 61% of the revenue expenditure but collect only 38% of the revenue receipts.
- This imbalance makes states rely heavily on the centre.
- The 14th and 15th FC recommended devolving 42% and 41% of net proceeds to states.
- However, estimates suggest that an average share of 48.94% was necessary between 2015-2023 to eliminate the VFI.
| 16th Finance Commission |
|


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















