Table of Contents
Catatumbo Lightning
- A natural phenomenon involving near-constant lightning strikes over Venezuela’s Catatumbo River.
- Location: Primarily occurs where Catatumbo River flows into Lake Maracaibo.

How Catatumbo Lightning Forms
- Warm Air from the Caribbean: Warm, humid air from the Caribbean Sea moves towards the Andes mountains.
- Collision with Cool Air: This warm air meets cooler air from the mountain peaks, creating an unstable mixture.
- Rapid Uplift and Clouds: The terrain forces the warm air to rise quickly, cooling and forming massive storm clouds (cumulonimbus).
- Electrical Charge Buildup: Winds and temperature differences within the clouds generate powerful electrical charges.
- Lightning Discharge: When the electrical buildup gets too strong, it’s released as intense lightning.
Why is Catatumbo Unique?
- Frequency: Strikes happen up to 160 nights per year.
- Intensity: Averages 28 lightning strikes per minute during its peak.
- This consistent electrical activity makes the area the “lightning capital of the world.“
FSSAI increases pesticide Limit in Spices
Context: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) approved a tenfold increase in the default Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) for pesticide residue in spices and herbs.
More in News
- The new MRL is set at 0.1 mg/kg compared to the previous limit of 0.01 mg/kg, applicable where specific limits are not defined in Indian or international regulations.
- For other food products, the default MRL remains unchanged at 0.01 mg/kg.
|
Maximum Residue Limit (MRL) |
| MRLs are determined dynamically based on field trial data submitted to the Central Insecticides Board and Registration Committee (CIB&RC). |
About Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI)
- Establishment: FSSAI is an autonomous statutory body created under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- The Act consolidates previous food-related laws like the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act, 1954, the Fruit Products Order, 1955, the Meat Food Products Order, 1973, and others, which were overseen by various ministries and departments.
- Goal: To provide a unified reference point for all food safety and standards matters by streamlining control under a single line of command.
- Mandate: FSSAI operates under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, tasked with regulating and supervising food safety and quality to protect public health.
- Headquarter: New Delhi,
- It has regional offices in eight zones
- Structure: The Chairperson and Chief Executive Officer, appointed by the central government, have ranks equivalent to a Secretary in the Government of India.
- Functions and Powers:
- Regulations and Standards: Establishes regulations and standards for food products and additives.
- Licensing and Registration: Issues licences and registration for food businesses.
- Enforcement: Enforces food safety laws and regulations.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Monitors and ensures food safety and quality through surveillance.
- Risk Assessment and Research: Conducts risk assessments and scientific research on food safety issues.
- Training and Awareness: Offers training and raises awareness about food safety and hygiene.
- Promotion: Promotes food fortification and organic food.
- Coordination: Coordinates with other agencies and stakeholders on food safety issues.
Maharashtra Tiger Translocation
Context
- The Maharashtra forest department is preparing to relocate several tigers from the Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR) in Chandrapur to Sahyadri, the state’s only tiger reserve in the western region.
- The goal is to revive the absent tiger population in the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR), located in Maharashtra’s Western Ghats region.
About Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR)
- Location: Spans parts of Kolhapur, Satara, Sangli, and Ratnagiri districts.
- Size: 1,165 sq km
- Created: In 2010 by combining the Chandoli National Park and Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary.
- STR is one of the few tiger reserves in India with no current tiger population.
Project Overview
- Aim: The project aims to strengthen the crucial tiger corridor between Maharashtra and Karnataka, facilitating natural movement and population growth.
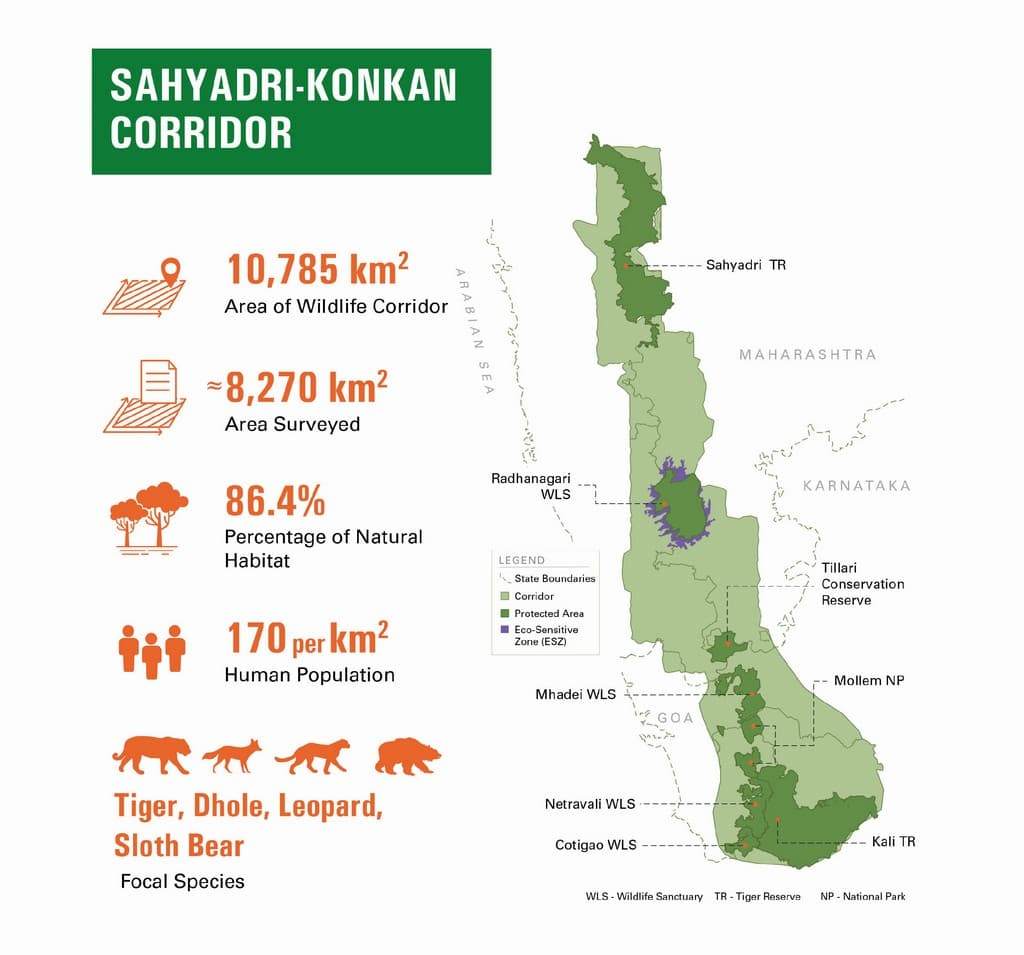
- Threats to Corridor: The 2023 tiger estimation report highlights risks to this corridor from mining, road projects, and human settlements.
- Habitat and Prey Preparation
- Preparation of STR for tigers began in December 2021.
- Introduction of Chital and Sambar deer to bolster the reserve’s prey base.
- STR is estimated to be able to support a population of 10-12 tigers.
- Long-Term Focus
- Tigers will initially be kept in an enclosure for observation before full release.
- Experts emphasise the need for ongoing landscape conservation efforts to ensure the tigers’ long-term survival and success in the region.
Goldene
Context: Goldene, a freestanding gold sheet only one atom thick, was developed by scientists at Sweden’s Linköping University.
About Goldene
- Goldene is a single-atom layer of gold.
- It is the first freestanding 2D metal, overcoming challenges associated with metals clustering into nanoparticles rather than forming 2D sheets.
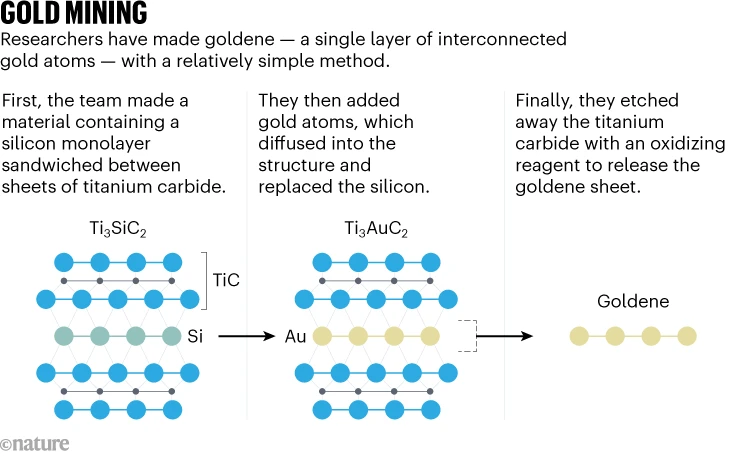
How Goldene is Created?
- Researchers first sandwiched a silicon atomic monolayer between layers of titanium carbide. Gold was then deposited on this structure, and the gold atoms replaced the silicon, forming a trapped monolayer of gold atoms.
- By etching away the titanium carbide layers using Murakami’s reagent (a chemical used in traditional Japanese katana forging), the team was able to create a free-standing, single-atom-thick gold sheet.
Characteristics:
- The goldene sheets are approximately 100 nanometres thick, which is about 400 times thinner than commercially available gold leaf.
- Each gold atom in goldene is surrounded by only six neighbouring atoms compared to 12 in 3D crystal structures, giving it unique properties.
Applications and Future Potential:
- Catalysis and Electronics: Goldene could revolutionise the electronics industry due to its efficient electrical conductivity and economic viability, as fewer atoms are required compared to 3D gold.
- Broader Metal Applications: The technique used to create goldene could be applicable to other metals. Researchers are working on 2D sheets of iridium and platinum.
- Special Properties: The unique atomic arrangement of goldene could provide it with special properties beneficial for carbon dioxide conversion, selective chemical production, hydrogen production, catalysis, and water purification.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Urea Consumption (GS 3): India’s urea consumption in 2024 is 16.9% higher than the urea consumption in 2013-14.
- Species in News (Prelims): A Golden- Backed frog with a mushroom growth from its skin was found in foothills of the Kudremukh Ranges in the Western Ghats, Karkala taluk of Karnataka.


 Waqf Act (Amendment) 2025: Key Highlight...
Waqf Act (Amendment) 2025: Key Highlight...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...





















