Table of Contents
Netherlands – 3rd Largest Export Destination
Context: In FY 2023-24, the Netherlands rose to become India’s third largest destination for exports, following the U.S. and UAE.
More In News
- There was a decline of more than 3% in the country’s merchandise exports.
- The main commodities that saw robust growth in exports to the Netherlands were petroleum products ($14.29 billion), electrical goods, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
- The Netherlands has taken over major destinations such as the K., Hong Kong, Bangladesh and Germany.
Relations Between India and Netherland
- India and the Netherlands established diplomatic ties in 1947.
- In 2023-24, the bilateral trade between the two countries marginally dipped to $27.34 billion as against $27.58 billion in 2022-23.
- India’s trade surplus with the Netherlands has increased to $17.4 billion in the last fiscal from $13 billion in 2022-23.
- India’s exports to the Netherlands rose by about 3.5% to $22.36 billion in 2023-24
- During 2023-24, India received about $5 billion in foreign direct investment from the Netherlands. It was $2.6 billion in 2022-23.
First EV Battery Passport
Context: Volvo Cars is introducing the world’s first Electric Vehicle (EV) battery passport for its new EX90 SUV.
About the EV Battery Passport
- Purpose: The passport includes information about the composition of batteries, origin of materials, carbon footprint, and recycled content.
- Developed: Developed in partnership with UK startup Circulor.
- Circulor’s system tracks battery materials from mining to the finished car and monitors energy sources used in production.
- Technology: The blockchain technology to track supply chain details.
- Battery Health Monitoring: Provides up-to-date information on the battery’s health for 15 years, aiding in assessing used EV values.
- Accessibility: Owners can access a simplified version of the passport via a QR code, while a complete version will be submitted to regulators.
- Regulatory Compliance: Aligns with upcoming EU regulations making battery passports mandatory for all EVs from February 2027.
A Bacteria That Writes New Genes
Context: Recent research suggested that Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria use reverse transcriptase in defence against bacteriophages.
About Reverse Transcriptase (RT)
- Discovery: Discovered in 1970 by Howard Temin and David Baltimore.
- Function: RT catalyses the transcription of RNA into DNA, a process known as reverse transcription.
- This is the opposite of the usual transcription process where DNA serves as a template for RNA.
- Structure: The enzyme typically has two subunits, which include an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity, ribonuclease H (RNase H), and DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity.
- These activities collectively enable RT to convert single-stranded RNA into double-stranded DNA.
- Role in Viruses: Viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B use RT to replicate their genomes.
- After infecting a host cell, the viral RNA is reverse-transcribed into DNA, which can then integrate into the host’s genome and direct the production of new viral particles.
- Applications: RT is used in molecular biology for various applications, including reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which is a technique used to amplify and study specific DNA sequences from an RNA template.
- It’s also used in research for cloning, RNA sequencing, and genome analysis.
| Klebsiella Pneumoniae |
|
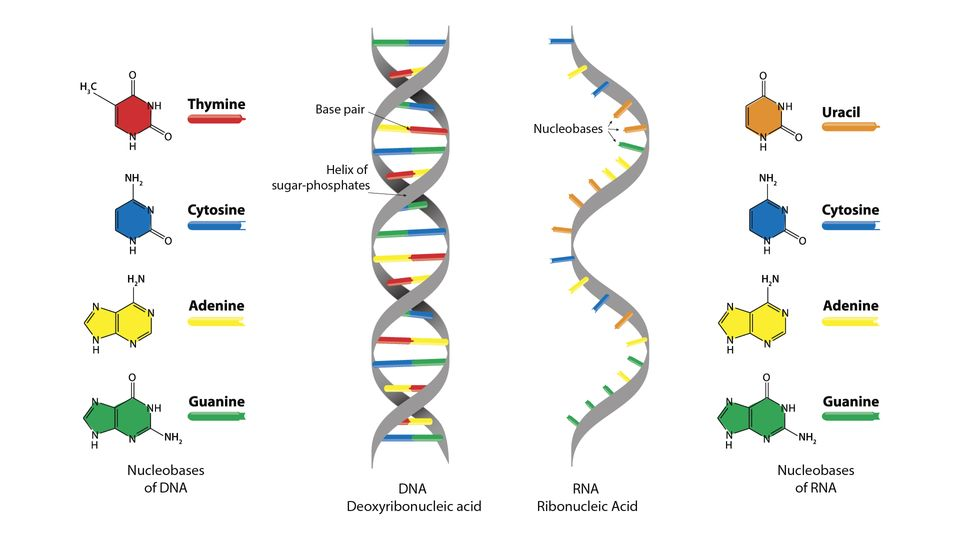
About DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
- Definition and Composition:
- DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a nucleic acid containing the sugar deoxyribose.
- It contains four nitrogenous bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine.
- Structural Features:
- DNA is structured as a double-stranded helix.
- The strands are connected by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases.
- Stability and Replication:
- The DNA backbone is resistant to cleavage.
- It stores biological information which is replicated when the two strands separate during DNA replication.
- Chromosomal Organization:
- Within cells, DNA is organised into chromosomes.
- During cell division, chromosomes are duplicated to ensure each new cell receives a complete set.
- Storage Locations:
- In eukaryotic organisms (like animals, plants, fungi, and protists), DNA is primarily stored in the cell nucleus and partly in organelles such as mitochondria or chloroplasts.
- Prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) store their DNA in the cytoplasm.
- Biological Functions:
- DNA serves as the chemical basis of heredity and is considered the reservoir of genetic information.
- It maintains the identity of different species over millions of years.
- DNA is capable of self-duplication, ensuring identical DNA strands are transferred to daughter cells.
About RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
- Definition and Composition:
- RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a nucleic acid containing the sugar ribose.
- It contains four nitrogenous bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil.
- Structure: RNA molecules are single-stranded.
- Types and Roles:
- There are three main types of RNA: messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
- mRNA carries genetic information that directs the synthesis of specific proteins.
- rRNA and tRNA are involved in the process of protein synthesis based on the information provided by DNA.
- Biological Functions:
- RNA plays diverse roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes.
- It is crucial in the synthesis of proteins within cells.
- Many viruses, such as HIV, use RNA genomes to encode their genetic information and proliferate within host organisms.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Major challenges that ISRO faces in becoming self-sufficient (GS 3):
- Limited Access to Advanced Technologies: ISRO’s growth is hindered by restricted access to cutting-edge aerospace technologies.
- Insufficient Funding for R&D: There is a lack of adequate financial support for research and development within the space organisation.
- Example: India’s space program consumes only about 0.25 percent of the annual national budget, with less than 10 percent of that directed towards scientific missions like the Chandrayaan and Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM).
- Regulatory Hurdles: The agency encounters significant regulatory obstacles that impede its operations and progress.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















