Table of Contents
World’s First Rocket with Fully 3D Printed Engine
Context:
- Agnikul Cosmos, an Indian space startup, successfully conducted a sub-orbital test launch using their vehicle Agnibaan SOrTeD.
- This vehicle was powered by the world’s first single-piece 3D-printed semi-cryogenic rocket engine.
About Agnilet
- Agnilet is the world’s first fully 3D-printed single-piece rocket engine.
- Characteristics: The Agnilet engine is a semi-cryogenic engine printed out of Inconel-718, a nickel super-alloy valued for its high temperature resistance and dimensional stability.
- It uses a semi-cryogenic setup, fueled by liquid oxygen (LOX) and Aviation Turbine Fuel (ATF) and is capable of pumping out 3kN of thrust at sea level.
| Semi-cryogenic engines use a fuel or oxidizer that is cryogenically stored but not as cold as those used in fully cryogenic engines, like liquid hydrogen or helium. |
- Collaboration: The development of Agnilet involved collaboration with academic institutions like IIT Madras, specifically the National Centre for Combustion Research and Development.
- Innovation: By utilising 3D printing technology, Agnikul aims to streamline the manufacturing process, reducing the number of components typically required for rocket engines, which can lead to reduced costs and faster production times.
About Vehicle
- Objective: The primary goal of this test launch was to assess the performance of the world’s first single-piece 3D-printed semi-cryogenic engine, known as Agnilet, in a controlled flight environment.
- Launch: The launch occurred from a private launchpad at Sriharikota, marking it as the first use of a private launchpad and the second launch by a private Indian space startup.
- Height: The mission was designed to reach a height of approximately 8 kilometres before returning to Earth, specifically splashing into the sea.
Future Prospects
- Capability: While this was a suborbital test, Agnibaan SOrTeD and future vehicles based on this technology are intended to cater to the small satellite launch market, with capabilities of carrying payloads ranging from 30 kg to 300 kg.
- Plans: Agnikul Cosmos plans to perform its first orbital launch by the end of the financial year, aiming to establish regular commercial services in the following year.
RBI’s Income Rise
Context: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) reported a significant increase in income, rising 17% to ₹2,75,572.32 crore in FY24.
Financial Performance
- Expenditure: There was a dramatic decrease in expenditure, which shrunk by 56.3% to ₹64,694.33 crore, down from ₹1,48,037.04 crore in FY23.
- Surplus: The reduction in expenditure resulted in a substantial increase in the RBI’s transferable surplus, which was ₹2,10,873.99 crore compared to ₹87,416.22 crore in the previous year.
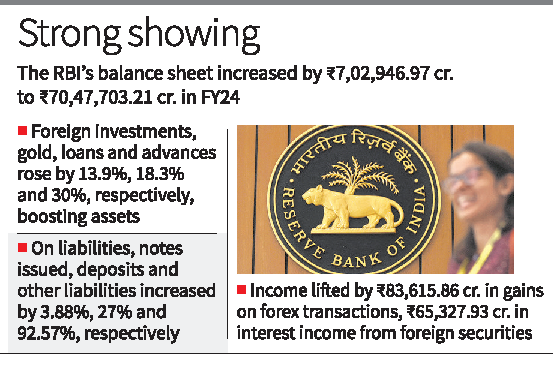
- Revenue Sources:
- Foreign Exchange Transactions: Gains from these transactions amounted to ₹83,615.86 crore.
- Interest Income: Income from foreign securities increased to ₹65,327.93 crore.
Balance Sheet Growth
- Total Size: The RBI’s balance sheet grew by 11%, reaching ₹70,47,703.21 crore from ₹63,44,756.24 crore in FY23.
- Asset Increase: Assets rose due to a 9% increase in foreign investments, an 18.26% increase in gold, and a 30.05% increase in loans and advances.
- Liability Expansion: Liabilities expanded due to a 3.88% increase in notes issued, 27% increase in deposits, and a 92.57% increase in other liabilities.
- Asset Composition: Domestic assets constituted 23.31% of total assets, while foreign currency assets, gold, and loans to financial institutions outside India made up 76.69%.
Provisions and Economic Outlook for 2024-25
- Contingency Fund: A provision of ₹42,819.91 crore was transferred to this fund for future contingencies.
- Growth Forecast: The RBI projected a real GDP growth of 7% for 2024-25, noting that risks to this outlook are evenly balanced.
- Positive Outlook: The RBI highlighted the strengthening of macroeconomic fundamentals, robust financial and corporate sectors, and a resilient external sector as positive indicators.
- Government Spendings: Continued focus on capital expenditure and fiscal consolidation, coupled with optimism in consumer and business sectors, are expected to support investment and consumption demand.
- Headline Inflation: As headline inflation moves toward the target, there is an expectation of reviving consumption demand, particularly in rural areas.
- External Factors: Strong foreign exchange reserves are seen as a buffer to protect domestic economic activities from global disruptions.
- Risks: The RBI pointed out several risks, including geopolitical tensions, economic fragmentation, financial market volatility, commodity price fluctuations, and unpredictable weather patterns, which could impact growth negatively and push inflation upwards.
Turbulence
Context:
- Recently, a flight from London to Singapore experienced severe turbulence over Myanmar, resulting in one fatality and injuries to over 70 passengers and crew.
- Additionally a flight from Doha to Dublin encountered severe turbulence over Turkey, injuring twelve passengers and crew, described by the airline as minor injuries.
About Turbulence
- Turbulence is an irregular motion of the aircraft caused by eddies and vertical currents of air and can occur close to the ground or at high altitudes. It is most common on the edges of jet streams.
- Although rare, turbulence can cause serious injuries and, in exceptional cases, fatalities.
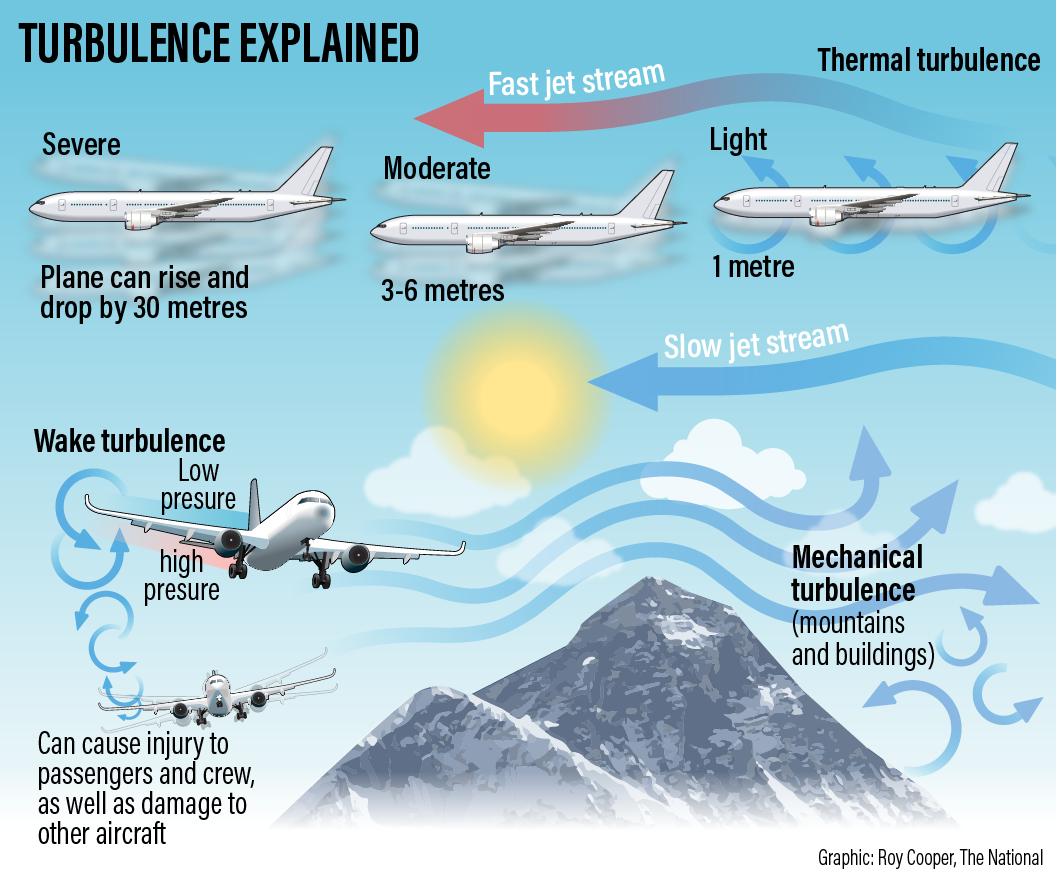
Types and Causes of Turbulence:
- Mechanical Turbulence: Caused by air friction due to irregular terrain or obstacles, commonly found at lower altitudes or over mountain ranges.
- Convective or Thermal Turbulence: Arises from rapid rising of hot air and descending cool air, affecting the aircraft during descent.
- Frontal Turbulence: Occurs due to the interaction of warm and cold air masses, common near thunderstorms.
- Wind Shear: Involves changes in wind direction and/or speed over certain distances and can lead to clear air turbulence (CAT).
- Clear Air Turbulence (CAT): Occurs at altitudes above 15,000 feet, generally outside of cloud cover, making it difficult to predict and virtually invisible, posing sudden and severe risks to flights.
Impact of Climate Change
- Studies indicate an increase in CAT occurrences due to climate change, which strengthens jet streams, leading to more frequent and severe turbulence.
- Research from the University of Reading and the UK Meteorological Office shows a 55% increase in severe CAT over the North Atlantic between 1979 and 2020.
Safety Recommendations and Measures
- The US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) recommends improved communication, weather briefings, real-time information sharing, and enhanced training to avoid turbulence-related injuries.
- Post the May 21 incident, Singapore Airlines has revised cabin crew procedures to suspend meal services and ensure all are seated with belts fastened during turbulence.
- Preventive Measures for Passengers: Passengers are advised to keep their seat belts fastened at all times when seated, even if the seat belt sign is off, to prevent injuries caused by sudden turbulence.


 Bihar BPSC 70th Mains Result 2025 Out: C...
Bihar BPSC 70th Mains Result 2025 Out: C...
 Pax Silica Initiative: Meaning, Objectiv...
Pax Silica Initiative: Meaning, Objectiv...
 Tapanuli Orangutan: Habitat, Characteris...
Tapanuli Orangutan: Habitat, Characteris...

























