Table of Contents
Rudra M Missile
Context: The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) announced a successful trial of the RudraM-II launched from a Su-30 MKI jet off the coast of Odisha.
About RudraM-II
- Type: An indigenously developed air-to-surface anti-radiation missile (AMR).
- Developer: Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- Name Meaning: “Rudram” means “remover of sorrows.”
- Performance: Validated through extensive flight data captured by various tracking instruments.
- Launch Capability: Can be launched from various altitudes.
- Target Detection: Picks up enemy radio frequencies and radar signals from over 100 kilometres.
- Guidance System: Features internal guidance for self-navigation after launch.
- Range: 300 kilometres.
- Speed: Reaches Mach 5.5 (hypersonic).
- Payload: Can carry a 200-kilogram warhead.
- Technology: Incorporates various state-of-the-art indigenous technologies.
- Replacement: Will replace Russia’s Kh-31 missiles currently used in Indian Sukhoi fighter jets.
| RudraM- I |
|
Trade Disruptions and Rising Temperatures
Context: Global trade disruptions, particularly in the Red Sea, are forcing ships to take longer routes, leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions.
More In News
- Red Sea Crisis: Attacks by Yemen’s Houthi rebels on ships in the Suez Canal have caused rerouting of hundreds of vessels around the Cape of Good Hope, adding 10-15 days to voyages and increasing emissions.
- Suez Canal Traffic Decline: Transits through the Suez Canal have decreased by 42% compared to its peak due to the ongoing crisis.
- Environmental Impact: A container ship travelling from China to Germany emits 38% more carbon dioxide (4.32 million kilograms) when rerouted around Africa instead of using the Suez Canal.
- Multiple Disruptions: The world faces simultaneous disruptions in the Red Sea, Black Sea (due to the war in Ukraine), and Panama Canal (due to droughts), with serious implications for inflation and food/energy security.
- UNCTAD’s Call for Action: UNCTAD Secretary-General Rebeca Grynspan highlights the urgent need for more inclusive, sustainable, and resilient global production and distribution networks.
Data and Statistics:
- Over 600 vessels have been rerouted since Houthi attacks began in October.
- By February 2024, 586 container vessels had been rerouted, and container tonnage crossing the Suez Canal fell by 82%.
- The global maritime trade faces simultaneous disruptions in two major waterways for the first time.
| About UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development) | |
|
Rising Global Temperature
Context: Recent years have seen record-breaking temperatures worldwide.
Rising Temperatures Globally
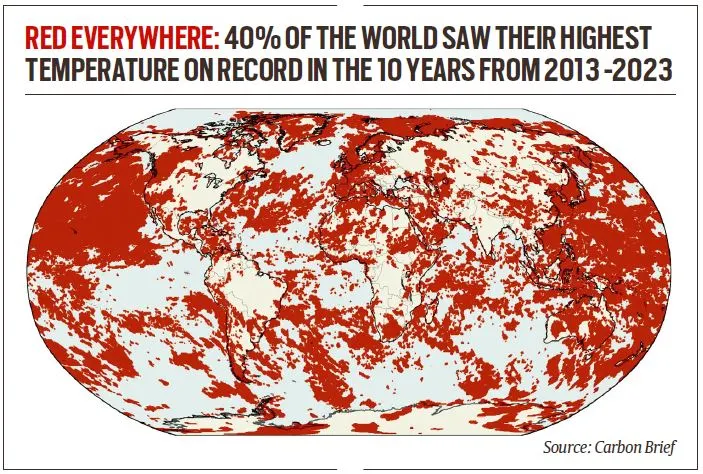
- UK (40°C in 2022), China (52°C in 2023), Sicily (48.8°C in 2021).
- Carbon Brief analysis: 40% of the Earth experienced its highest-ever daily temperature between 2013-2023.
- Highest ever recorded temperature: 56.7°C in Death Valley, California, in 1913.
Delhi’s Anomaly
- A reading of 52.9°C was recorded at one station in Delhi on May 15, 2024, potentially an all-time high for India.
- The reading is under scrutiny due to no other stations recording similar temperatures.
- Najafgarh station recorded the highest at 49.1°C, while Safdarjung (representative of Delhi) recorded 46.8°C, an 80-year high.
- Verification of extreme weather events is crucial and takes time, as seen in the UK and Sicily.
Severity of Heatwaves in India
- While not record-breaking, the current heatwave in Delhi and North India is severe.
- Temperatures are 5-10°C above normal in most places.
- Safdarjung station has recorded temperatures above 45°C for four consecutive days.
- Heatwaves are the biggest threat to India’s well-being, with annual trends showing 5-9°C temperature departures from normal.
Global Warming and India
- 2024 was predicted to be very warm following the warmest year on record in 2023.
- April 2024 was the 11th consecutive month with record-breaking global average temperature.
- The period from May 2023 to April 2024 was 1.61°C warmer than the pre-industrial average.
- India’s annual mean temperature has risen by 0.7°C compared to 1900, lower than the global land average of 1.59°C.
- However, Indian heatwaves are more severe, with heatwave conditions occurring even in February 2023.
Future Outlook
- Temperatures above 45°C may become the new normal in Delhi and North India.
- A 50°C reading will likely not be as unusual in the future.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Increase in Demand of Natural Gas (GS 3): India’s natural gas demand is projected to rise by 7% in 2024, primarily due to increased consumption in the industrial and fertilizer sectors.
- Additionally, the ongoing heatwaves are expected to boost demand from the power sector.
- This growth, however, is slightly lower than the 10% increase seen in 2023.
- Case Study: Transformation of Sundarbans Through Ecotourism
- Background:
- The Sundarbans, a large delta region in West Bengal formed by the confluence of the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, is known for its rich biodiversity and tiger population.
- Transition to Ecotourism:
- Over the past decade, tigers in the Sundarbans have shifted from being viewed as threats to becoming central to the region’s ecotourism.
- This shift has provided alternative livelihoods to hundreds of locals who previously relied on traditional and often illegal means like fishing or logging, which were risky due to tiger attacks.
- Economic Impact:
- Ecotourism has become a lucrative industry in the area, significantly impacting the local economy.
- Residents, who once ventured into the forest for crabs or fishing, now engage in tourism-related activities.
- For example, boat operators and local guides now earn substantial incomes, with operators able to make a profit of at least 15%-20%, and up to 25% if they run additional services like homestays.
- Cultural Shifts:
- The introduction of ecotourism has reduced the dependency of locals on the forest for livelihood, decreasing illegal entries and enhancing tiger conservation efforts.
- The visibility of tiger cubs and increased tiger sightings are taken as indicators of a growing tiger population and successful conservation practices.
- Government and Political Engagement:
- Local and national governments advocate for expanding ecotourism.
- Proposals include opening new routes, creating more entry points to the reserve, and diversifying tourism activities to include bird watching and other nature experiences.
- Challenges and Management:
- The region faces challenges such as human-animal conflicts and the need for sustainable management practices to ensure the safety of both wildlife and people. Efforts are underway to improve infrastructure and manage tourist inflow more effectively.
- Future Outlook:
- The focus is on strengthening ecotourism as a sustainable development tool that benefits both the conservation of the Sundarbans and the economic welfare of its inhabitants. The strategy includes enhancing tourist experiences while maintaining ecological integrity.
- Background:


 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
 Amrit Gyaan Kosh Portal: A Comprehensive...
Amrit Gyaan Kosh Portal: A Comprehensive...
 UpLink Initiative: Launched by World Eco...
UpLink Initiative: Launched by World Eco...





















