Table of Contents
Forum for India–Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC)
Context
- The Government of India has allocated $1 million as immediate assistance to Papua New Guinea, which has experienced a devastating flood and landslide killing 2,000 people, to support relief, rehabilitation, and reconstruction efforts.
- This was an effort to reinforce their partnership under the Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC).
About Forum for India-Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC)
- Established: 2014
- Purpose: To enhance cooperation between India and 14 Pacific Island nations.
- Member Countries: Cook Islands, Fiji, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Nauru, Niue, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu.
- Focus Areas:
- Development assistance: Capacity building (training, scholarships, grant-in-aid) and community development projects.
- Trade and Investment: FIPIC Trade Office at FICCI promotes economic opportunities.
- Annual Summit: Initiated in Suva, Fiji in November 2014 which provided a platform for dialogue and collaboration.
Pravaah Portal
Context: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced three significant initiatives.
About RBI’s New Initiatives
Mobile App for Retail Investors
- Purpose: To enable retail investors to participate in the government securities (G-Secs) market.
- Functionality: Retail investors can transact in G-Secs using this app.
- Accessibility: The app is available for download from the Play Store for Android users and the App Store for iOS users.
- Related Platform: The app complements the existing retail direct portal launched in November 2021, which allows retail investors to buy and sell G-Secs both in primary auctions and the secondary market.
PRAVAAH Portal
- Full Name: Platform for Regulatory Application, Validation, and Authorisation.
- Purpose: Provides a centralised web-based portal for individuals or entities to apply online for various regulatory approvals.
- Features:
- Offers 60 application forms from different regulatory and supervisory departments of RBI.
- Users can track and monitor the status of their applications.
- RBI can issue decisions on applications in a time-bound manner.
- Future expansions are planned to include more application forms as required.
- Benefits: Enhances the efficiency of the processes related to granting regulatory approvals and clearances by the RBI.
Fintech Repository
- Purpose: To serve as a data storehouse for Indian FinTech firms, improving the understanding of the sector from a regulatory perspective and aiding in policy formulation.
- Participation: Open to both regulated and unregulated FinTech firms.
- Management: Both repositories are managed by the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH), a wholly owned subsidiary of the RBI.
- Benefits:
- Captures essential information about FinTech entities, their activities, technology usage, etc.
- Provides aggregate sectoral level data, trends, analytics, etc., useful for policymakers and industry participants.
- Related Initiative: EmTech Repository, specifically for RBI regulated entities like banks and NBFCs, focusing on their adoption of emerging technologies such as AI, ML, Cloud Computing, DLT, Quantum, etc.
La Nina
Context: Recently the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) said that the ocean temperatures along the central and equatorial Pacific Ocean were cooling off and neutral El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions are set to emerge anytime soon.
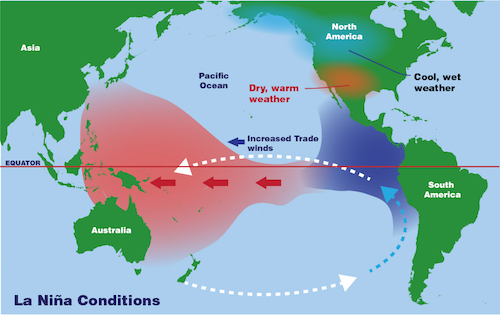
About La Nina
| Aspect | La Niña |
| Meaning | La Nina, meaning “little girl” in Spanish, is part of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. |
| Sea surface temperature | It represents the periodic cooling of sea-surface temperatures across the east-central equatorial Pacific. |
| Pressure | It contain low air surface pressure in the eastern Pacific |
| Mechanism | During La Niña events, trade winds are even stronger than usual, pushing more warm water toward Asia, resulting in a stronger Walker cell. |
| Period of occurrence | Typically occurs every 3-5 years and lasts 1-3 years. |
| Impacts |
|
| Occurrence | Typically occurs every 3-5 years and lasts 1-3 years. |
| Impact on Indian Monsoon | La Nina causes high temperatures over the Indian Ocean, off the Somalian coast and a comparatively better monsoon rains in India. |
| Short Introduction |
|
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Role of Urbanisation in Global Warming (GS 1): Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology-Bhubaneswar determined that urbanisation is accountable for 60 percent of the rising temperatures in Indian cities, with tier-2 cities in eastern India experiencing the most severe effects.
- It highlights that urban centres are particularly susceptible to the combined impacts of climate change and swift urban development.
- Challenge in Transitioning to Renewable Energy (GS 3): India is seeing a growing market for clean energy assets, with increasing investments in renewable energy projects exceeding annual targets necessary to meet its 2030 renewable energy goals.
- However, the market dynamics are challenged by lower-than-desired valuations and a lack of secondary demand for these assets.
- Despite progress in renewable energy capacity, India still heavily relies on coal due to challenges like grid integration, cost-effective storage solutions for renewable energy, and economic factors favouring fossil fuels.
- Effective reforms, increased subsidies, direct investments, and the potential implementation of a carbon market are necessary to support India’s transition to a cleaner energy future and meet its climate goals.


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















