Table of Contents
Tuvalu Struggles Amid Rising Sea Levels
Context: Tuvalu is pushing for international recognition of its maritime boundaries and statehood even if it is submerged by rising seas. Tuvalu wants to amend the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea to recognize its maritime borders as permanent.
About Tuvalu
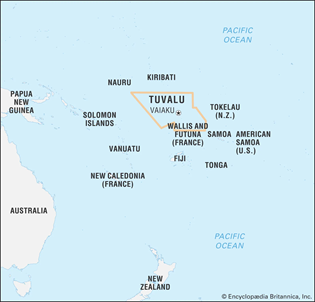
- Location: West-central Pacific Ocean. It is composed of nine small coral islands.
- Capital: Funafuti
- History: It was formerly Known as Ellice Islands. It got independence from the United Kingdom in
- Neighbouring Countries: Kiribati – North and Fiji – South.
- Population: Around 11,000, it is one of the world’s least populous countries.
- The economy relies on fishing, agriculture, and remittances, while its culture is deeply rooted in Polynesian traditions.
| Migration and Climate Treaty with Australia |
| Tuvalu has signed a climate and security treaty with Australia in 2023, offering a migration pathway for 280 Tuvaluans per year starting in 2024. |
| About United Nations’ International Law Commission (ILC) |
|
Body Roundness Index (BRI)
Context: The discussion surrounding the effectiveness of Body Mass Index (BMI) as a health metric has led to the emergence of the Body Roundness Index (BRI), which aims to provide a more accurate assessment of health risks associated with body composition.
About Body Roundness Index (BRI)
- Definition:
- It measures body roundness based on waist circumference and height.
- It was developed by mathematician Diana Thomas in 2013.
- BRI is designed to better reflect body shape and fat distribution, addressing the limitations of BMI.
- Scoring: BRI scores range from 1 to 15, with scores above 6.9 or below 3.41 indicating higher health risks.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Definition: BMI is calculated by dividing a person’s weight in kilograms by their height in metres squared.
- Classification:
- Normal weight: 18 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 and above
- Limitations:
- Does not differentiate between fat, muscle, and water weight.
- Fails to account for fat distribution in the body, which can lead to misleading assessments of health.
- It was created using data primarily from 19th-century Europeans, making it less applicable to diverse ethnic groups.
Key Differences Between BRI and BMI
- Measurement Focus:
- BMI: Weight relative to height; assumes bodies are cylindrical.
- BRI: Considers waist circumference; reflects how “round” a person is.
- Health Risk Assessment:
- BRI provides a more nuanced view of health risks associated with body fat distribution, particularly visceral fat around internal organs.
Plan for Reliability Improvement and Maintenance Effectiveness (PRIME)
Context: The Indian Railways has initiated a plan to replace ageing signalling systems that have exceeded their operational lifespan, addressing safety concerns following recent train accidents.
About PRIME
- It is an initiative by Indian Railways aimed at enhancing the reliability and maintainability of its signalling systems.
- This initiative comes in response to several major train accidents over the past two years, highlighting the urgent need for improved signalling systems
Key Objectives of PRIME:
- Replacement of Outdated Signal Assets: The plan prioritises replacing signal assets that have exceeded their operational lifespan to prevent failures and enhance safety1.
- Staff Training: Regular training and counselling for staff on safety and maintenance protocols are emphasised to maintain high standards of work quality1.
- Addressing Signal Failures: The plan targets stations with the highest number of signal failures for immediate maintenance and rectification.
- Innovative Solutions: Successful innovations in enhancing reliability will be expanded to other zones.


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















