Table of Contents
Rhino
Context: Despite a small rise in the global rhinoceros population, poaching remains a serious threat especially in South Africa. Conservationists call for stronger protection and greater community awareness to curb illegal demand for rhino horns and ensure the species’ survival.
About Rhino
- The global rhinoceros population has slightly increased, with white rhinos rising from 15,942 in 2022 to 17,464 in 2023.
- However, poaching remains a major threat, with 586 rhinos killed in Africa in 2023, primarily in South Africa, which has around 16,056 rhinos.
- All five subspecies combined total under 28,000 rhinos, down from 500,000 at the start of the 20th century.
About Greater One-Horned Rhino:
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix – I
- WPA: Schedule – I
- Range: The Indian Rhinoceros (Greater one-horned rhino) can only be found in the Brahmaputra valley,parts of North Bengal and parts of southern Nepal.
- Characteristics:
- It is also known as Indian rhinoceros.
- It is the largest of the three Asian rhinos and, together with African white rhinos it is the largest of all rhino species.
- It has a single black horn that can grow up to 60 cm and a tough, grey brown hide with skin folds, which gives the animal its characteristic look.
- Rhinos in the wild: There are around 3,700 Indian rhinos in the wild today.
- Kaziranga National Park (KNP) of Assam alone has 2,613 animals.
- There are more than 250 other rhinos in the Orang, Pobitora and Manas parks of Assam.
| UPSC PYQ |
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: A |
Robotic Mules
Context: The Indian Army has enhanced its high-altitude capabilities with the induction of 100 robotic mules in forward areas. Logistics drones are also undergoing trials which will significantly streamline support and movement to forward areas, especially in high altitude.
What are Robotic Mules ?

- It is a four-legged, remote-controlled ground robot designed to support military operations in diverse terrains.
- Control: The mule is controlled by a remote control and can be operated using Wi-Fi or Long-Term Evolution (LTE).
- Features:
- It has a payload capacity of 12 kg.
- It can operate in temperatures ranging from -20°C to +45°C, and has a battery life of at least three hours.
- It can climb stairs and steep hills, and navigate snow-clad ground and rugged mountains.
- It also has electro-optics and infrared to help it recognize objects.
- Uses
- The mule can transport small loads to frontline soldiers, and can be used for surveillance in mountainous regions.
- It can also be equipped with small arms to engage enemies.
Scale-Based Regulation (SBR)
Context: According to a RBI Report India’s NBFC sector has shown resilience under the scale-based regulations (SBR) framework with improved asset quality, diversified funding and strong credit growth.
What is SBR for NBFCs (Non Banking Financial Company) ?
It is a revised regulatory framework that aims to align regulations with the changing risk profiles of NBFCs:
- History:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) published the SBR on October 22, 2021, and it became effective on October 1, 2022.
- Purpose:
- The SBR framework aims to align regulations with the changing risk profiles of NBFCs.
- It also aims to reduce risks for the financial sector.
- Classification:
- The SBR classifies NBFCs into four layers based on their size, activity, and perceived riskiness: Base layer, Middle layer, Upper layer, and Top layer.
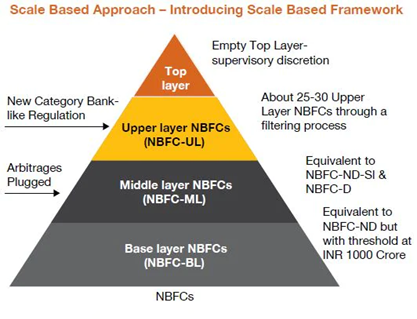
- Consolidation:
- The SBR Master Direction consolidates various regulations for NBFCs into one place, streamlining regulations and ensuring a consistent and transparent framework.
- Board of directors:
- The board of directors of any NBFC must include at least one director with relevant experience in a bank or NBFC
| What are NBFCs ? |
|
Pact for the Future
Context: The United Nations recently adopted an action plan and statement of goals to tackle 21st century challenges called the Pact for the Future.
Key highlights of the Pact
- Sustainable Development and Financing:
- Enhance sustainable development efforts and increase developing nations’ influence in global financial institutions.
- Strengthen the global financial safety net to protect the most vulnerable populations.
- International Peace and Security:
- Renew the commitment to nuclear disarmament with the ultimate goal of eliminating nuclear weapons.
- Prevent the weaponization and misuse of emerging technologies, like autonomous lethal weapons.
- Science, Technology, and Digital Cooperation:
- Promote scientific research conducted responsibly and ethically, with respect for human rights.
- Protect indigenous knowledge, empower women and address gender-based risks from new technologies.
- Transforming Global Governance:
- Strengthen international space governance frameworks and prevent an arms race in outer space.
- Prioritise reforming the United Nations Security Council to improve its representativeness, especially addressing Africa’s underrepresentation.
| Annexures of Pact for the Future |
|
PLFS Data
Context: The National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) has released the Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Annual Report from (July, 2023 – June, 2024).
Key Findings of the Report
- Unemployment Rate (UR)
- It refers to the percentage of persons unemployed among persons in the labour force.
- The unemployment rate for persons aged 15 years and above remained unchanged at 3.2% during the reporting period.
- For males, the unemployment rate slightly declined from 3.3% in the previous year to 3.2%.
- In contrast, the unemployment rate for females increased from 2.9% to 3.2%, marking its first rise in 7 years.
- Labour Force Participation Rate (LFPR)
- It refers to the percentage of persons in the labour force (i.e. working or seeking or available for work) in the population.
- LFPR for individuals aged 15 and above rose to 60.1%, up from 57.9% in the previous year.
- The LFPR for males increased marginally from 78.5% to 78.8%, while for females, it saw a significant rise from 37.0% to 41.7%.
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR)
- WPR indicates the percentage of employed individuals in the population.
- It improved to 58.2%, up from 56.0% in the previous year.
- For males, the WPR was recorded at 76.3%, while for females, it increased from 35.9% to 40.3%.
| Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) |
|


 Micrometeoroids: Tiny Space Particles, M...
Micrometeoroids: Tiny Space Particles, M...
 India Needs a National Insolvency Tribun...
India Needs a National Insolvency Tribun...
 Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...
Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...

























