Table of Contents
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF)
Context: India signed key agreements under the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s recent visit to the USA. These agreements focused on clean and fair economies, aim to foster economic cooperation, promote clean energy, and enhance transparency among the member nations.
About IPEF
- It is an economic initiative launched by the United States and other partner countries of the Indo-Pacific region at Tokyo in May 2022.
- Aim: Enhancing economic cooperation and integration in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Members: IPEF has 14 member states which includes
- QUAD nations (India, USA, Japan and Australia),
- 7 of the 10 ASEAN nations except Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar
- South Korea, Newzeland and Fiji.
- Size: The 14 IPEF partners represent 40% of global GDP and 28% of global goods and services trade.
Pillars of IPEF
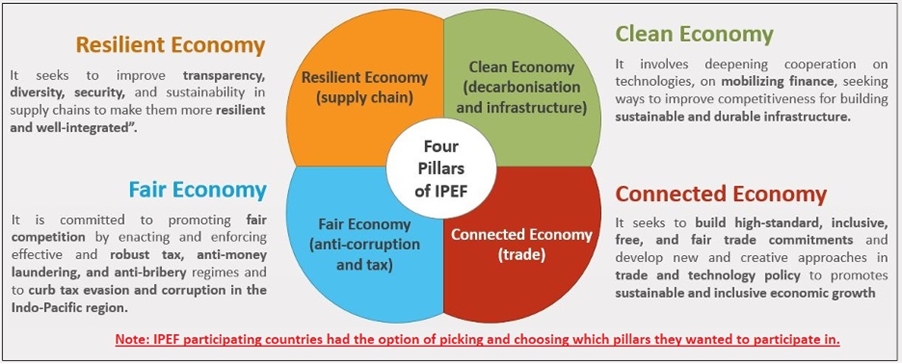
India and IPEF
India joined 3 of the 4 pillars (II, III & IV)of the Indo-Pacific Framework (IPEF) at the framework’s first in-person ministerial summit in Los Angeles in 2022.
New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG)
Context: Azerbaijan is hosting the 29th UN Climate Change Conference (COP29) in November 2024, in Baku. A major focus of this conference is the negotiation of a climate finance agreement, particularly the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG)
About NCQG
- Aim: To establish a new financial target to support developing countries in combating climate change.
|
Fact |
| Developed countries are currently obligated to mobilise at least $100 billion annually, but this amount is set to increase after 2025, as mandated by the Paris Agreement. |
Key Elements of the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG)
- Ambitious Financial Target:
- The NCQG is intended to replace the existing $100 billion goal with a more substantial and needs-based target.
- Estimates suggest that developing countries require between $1 trillion and $1.5 trillion annually to effectively address climate change, with some reports indicating total needs could reach $5.8-$13.6 trillion by 2030.
- Broadening the Donor Base: There is a push to include emerging economies like China and South Korea in financing obligations, as many countries that were once classified as developing have now become significant economies.
- Adaptation vs. Mitigation: Developing nations have expressed concerns over the disproportionate focus on mitigation projects, which receive most climate finance, while adaptation efforts—vital for local resilience—have been severely underfunded (less than 20% of total climate finance).
- Quality of Finance: The NCQG discussions emphasise not just the quantity but also the quality of climate finance, ensuring that funds are effectively utilised for sustainable projects.
MRSA Infection
Context: In 2019, MRSA caused over 100,000 deaths, although vancomycin has been the main treatment for 40 years, a new study shows it may not stay effective for long.
About MRSA Infection
- MRSA stands for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria that’s resistant to many antibiotics.
- How it spreads: Through skin-to-skin contact or by touching contaminated objects.
- Types of MRSA:
- Healthcare-associated (HA-MRSA): It is associated with invasive procedures or devices, such as surgeries, intravenous tubing or artificial joints.
- Community-associated (CA-MRSA): This type of MRSA often begins as a painful skin boil and is usually spread by skin-to-skin contact.
| About Staphylococcus Aureus (S. aureus) |
|
| Indian Government Initiatives to tackle AMR (Antimicrobial Resistance) |
|
GDP Estimation
Context: The current GDP series with the base year of 2011-12, is due for revision, with 2020-21 proposed as the new base year.
Proposed Changes in GDP Estimation
- The National Statistical Office (NSO) is considering using Goods and Services Tax (GST) data to estimate value addition for the next GDP revision.
- Base year for current GDP series is 2011-12, It is due for revision, proposing 2020-21 as the new base year.
- Major datasets for this revision are mostly available, except for Census data
- This data is proposed to replace the Ministry of Corporate Affairs’ MCA-21 database, which is currently used for estimating the Private Corporate Sector (PCS), accounting for about 38% of GDP.
- This shift is intended to enhance the accuracy of GDP estimates.
| What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)? |
|


 Bihar Assembly Election 2025 Dates, Poli...
Bihar Assembly Election 2025 Dates, Poli...
 Bharat Bandh 9 July 2025: Over 25 Crore ...
Bharat Bandh 9 July 2025: Over 25 Crore ...
 Sukhoi Su-57: Will India Choose Russia�...
Sukhoi Su-57: Will India Choose Russia�...





















