Table of Contents
Fragile Five
Context: India’s remarkable rise from “Fragile Five” status to the world’s fifth-largest economy inspires global optimism and positions it as a key player in driving future prosperity.
About Fragile Five
- Term and Origin:
- Coined in 2013 by a Morgan Stanley analyst.
- Describes emerging market economies with risky foreign investment dependence.
- Original Members:
- India
- Brazil
- Turkey
- South Africa
- Indonesia
- Vulnerability Factors:
- Heavily impacted by the 2008 global financial crisis.
- Sudden capital outflows caused financing difficulties.
- Challenges in managing current account deficits and foreign debt.
- Economic vulnerabilities and growth slowdown as consequences.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Namdapha flying squirrel
Context: The Namdapha flying squirrel has been rediscovered in Arunachal Pradesh.
About Namdapha Squirrel
- Status: Classified as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List,
- Habitat: Found only in Namdapha National Park, a protected area in the Eastern Himalayan biodiversity hotspot (Arunachal Pradesh, India).
- Park Established: Namdapha National Park was established in 1983, covering nearly 2000 square kilometres.
- Species Rarity: The Namdapha flying squirrel is known for its rarity, with only a single confirmed specimen collected in 1981.
- Specialised Habitat: Requires specific conditions within the park’s ecosystem, including tall Mesua ferrea jungles and possibly specific valleys.
- Conservation Concern: The rarity, specialised habitat, and potential threats like habitat loss and poaching highlight the need for conservation efforts to protect this unique species.
International Year of Camelids
Context: The United Nations has declared 2024 as the International Year of Camelids to emphasise the significant importance of camelids.
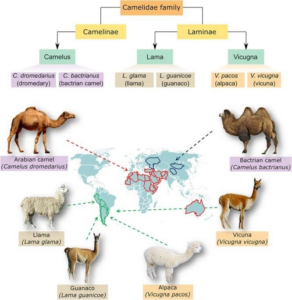
About Camelids
- Diverse Group:
- Includes Bactrian camels, dromedaries, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos.
- Tall, long-necked, thin-legged animals, some with humps.
- Unique Traits:
- Strict herbivores.
- Tripartite stomachs for efficient plant digestion.
- Split upper lips for precise grazing.
- Oval-shaped red blood cells for improved blood flow in dehydration.
- Primarily social creatures.
- Global Significance:
- Crucial for food security, nutrition, and economic development in over 90 countries.
- Particularly beneficial for indigenous and local communities.
- Contributions to Sustainability:
- Provide milk and meat (combating hunger) for Sustainable Development Goals.
- Offer fibre for textiles and shelter.
- Utilised for transportation.
- Waste acts as natural fertilizer, boosting agricultural productivity.
- Essential in Harsh Environments:
- Vital to livelihoods in Andean mountains, African and Asian arid/semi-arid zones.
- Thrive in extremes, showcasing resilience and adaptability.
- Climate Change Symbol:
- Camelid endurance exemplifies adaptation to challenging conditions.
- Can serve as an emblem for climate change awareness.
Himalayan phenomenon
Context: A new study in Nature Geoscience reveals a surprising phenomenon in the Himalayas that may offer a way to mitigate the effects of climate change.
About the Phenomenon
- Cold Air Winds in the Himalayas:
- When high temperatures hit Himalayan ice, it triggers “katabatic winds” that rush cold air down slopes.
- These winds are like rivers of cold air flowing from high peaks to lower valleys.
- Temperature Gap Triggers the Flow: Warm mountain air and cool ice air create a temperature difference, causing turbulent heat exchange.
- Downhill Rush of Dense Air: The cooled, heavy air sinks down the slopes, creating katabatic winds.
- A Possible Ally against Climate Change: These cold winds might help counteract global warming in some areas.
| Katabatic Winds Explained |
|
New EU Pact on migration and asylum
Context: The European Union and Member states have reached an agreement to reform the bloc’s migration policy through ‘New Pact on Migration and Asylum’.
About New Pact on Migration and Asylum
- Faster Processing: This aims to speed up asylum claims through a pre-entry screening process that gathers basic information like nationality, age, fingerprints, and facial images.
- Centralised Database: Creates a large-scale database to store biometric data collected during screening, facilitating identification and tracking.
- Two-Track System: Introduces two pathways for migrants:
- Traditional asylum procedure for thorough case evaluation (several months).
- Fast-tracked border procedure for quicker decisions (max. 12 weeks).
- Mandatory Solidarity: Ensures EU member states share responsibility through “mandatory solidarity.” Countries have three options:
- Relocate a set number of asylum seekers.
- Pay a financial contribution for each refused relocation.
- Provide operational support for migration management.
- Emergency Measures: Allows for stricter measures in extraordinary situations involving sudden mass arrivals, like during the COVID-19 pandemic. These may include longer detention periods.
| Note |
| The pact still needs to be formally approved by the European Council, representing the 27 member nations, and the European Parliament, before it enters the bloc’s law books, likely in 2024. |
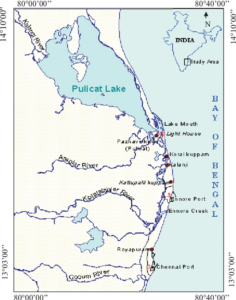
Ennore Creek
Context: Recently, massive oil spillage occurred due to flood water from cyclone Michaung from the state-run Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited’s (CPCL) refinery in Chennai.
About Ennore Creek
- Located on the Coromandel Coast, Ennore Creek acts as a vital buffer between the sea and the aquifers of the Araniyar-Kosasthalaiyar Basin.
- The creek is situated in the floodplains of three rivers.
- With Chennai’s location on a coastline vulnerable to disasters, Ennore Creek’s wetlands serve as natural safeguards.
- These wetlands absorb the impact of natural disasters, helping to mitigate their effects on the city.


 SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
 BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
 150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...
150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...





















