Table of Contents
Spices Board of India
Context: The Spices Board of India is conducting inspections at various MDH and Everest processing plants across the country to ensure that spice exports comply with the standards required by their respective export destinations.
About Spices Board India
- Formation: The Spices Board India is a statutory organisation constituted on 26th February 1987 under the Spices Board Act 1986.
- It was formed through the merger of the erstwhile Cardamom Board and Spices Export Promotion Council.
- Role: The Board serves as an international link between Indian exporters and importers abroad, engaging in activities across all segments of the spices sector.
- Main Functions:
- Cardamom Development: Responsible for the overall development of small and large cardamom, focusing on improving production, productivity, and quality.
- Post-Harvest Improvement: Implement programmes to enhance the quality of 52 scheduled spices for export.
- Export-Oriented Production: Includes various development programmes and post-harvest quality improvement initiatives.
- Organic Production: Promotes organic production, processing, and certification of spices.
- Development in the North East: Focuses on the development of spices in the North Eastern region of India.
- Quality Evaluation: Provides quality evaluation services.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India.
Ghost Gear
- Any fishing equipment lost, discarded, or abandoned in water bodies.
- Primarily consists of gill nets, nylon, and polypropylene ropes.
- Causes for Accumulation:
- Snagging: Gear gets caught on reefs, rocks, and other seafloor obstructions.
- Adverse Weather Conditions: Leading to loss of fishing gear or gear being cut by marine traffic.
- Deep Water Fishing: Gear suffers wear and tear over time.
- Impact on Wildlife: A recent Mongabay India analysis reported 144 animals from 35 species across India trapped in derelict fishing gear.
- Plastic Pollution: India is the second largest contributor to mismanaged plastic in the ocean.
Emblica Chakrabartyi
- It is the 16th New Plant Species from Ernakulam, Kerala
- Taxonomy: Belongs to the gooseberry family (Phyllanthaceae).
- Name: Emblica Chakrabartyi, named after Tapas Chakrabarty, a former scientist at the Botanical Survey of India, in recognition of his contributions to the study of Phyllanthaceae.
- Growing Season: Flowering and fruiting occur from December to June.
- Features:
- Attains a height of approximately 2 meters.
- Leaves:
- Large, shiny, elongated oval shape, up to 13 cm in length.
- Flowers:
- Male flowers: Found in inflorescence.
- Female flowers: Found singly on the leaf axils.
- Each flower has six yellowish-green petals.
- Fruits:
- Brown to black when ripe.
- Seeds are black and about 8-9 mm in diameter.
Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting
Context: India is hosting the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM 46), also known as the Antarctic Parliament in Kochi.
More In News
- Organised by: National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Goa, under the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)
- Participants: 56 member countries of the Antarctic Treaty
The Antarctic Treaty
- Original Signatories: Twelve countries – Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Chile, France, Japan, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, the USSR, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Signing Date: December 1, 1959
- Effective Date: 1961
- Total Members: 56 countries, including India, which joined in 1983.
- Key Features:
- Antarctica was designated for peaceful purposes; no militarization or fortifications were allowed.
- Freedom for scientific investigations, with shared plans and cooperation.
- Prohibition of nuclear testing and disposal of radioactive waste.
India’s Role and Presence in Antarctica
- Consultative Party Status: India has been a consultative party since 1983, participating in key decision-making processes.
- Research Stations:
- Dakshin Gangotri: First research station, established in 1983 in Queen Maud Land, operational till 1990.
- Maitri: Second station, set up in 1989 in the Schirmacher Oasis. Accommodates 65 persons in summer and 25 in winter.
- Bharati: Third station, inaugurated in 2012 on the Prydz Bay coast, supports up to 72 individuals in summer and 47 in winter.
- Future Plans: New station Maitri II, set to begin operations by 2029.
- Legislative Commitment:
- Antarctic Act 2022: Enacted by India to reaffirm its commitment to the Antarctic Treaty.
Agenda and Objectives of ATCM 46
- Global Dialogue: Discussions on law, logistics, governance, science, tourism, and other aspects of Antarctica.
- Peaceful Governance: Promotion of peaceful governance and protection of Antarctica’s resources, ensuring geopolitical tensions do not affect the continent.
- Tourism Regulation:
- Introduction of a new working group to regulate tourism.
- A collaborative effort with the Netherlands, Norway, and other European countries to formulate regulations, track tourist activities and establish guidelines.
- New Construction Plans: Official presentation of India’s plan to construct Maitri II.
- Discussion Topics:
- Sustainable management of Antarctica and its resources.
- Biodiversity prospecting.
- Inspections and information exchange.
- Research collaboration, capacity building, and cooperation.
- Impacts of climate change on Antarctica and beyond.
Peak Power Demand
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Power reported a peak power demand of 233 GW this month.
More In News
- This is a significant increase from 221.42 GW in the previous year.
- This surge is due to the extensive use of cooling appliances like air conditioners and desert coolers during a severe heat wave.
What Is Peak Power Demand?
- Peak demand on an electrical grid refers to the maximum level of electrical power demand observed over a specific period.
- It is typically measured annually, daily, or seasonally and is expressed in units of power.
- Peak demand indicates the highest power requirement reached at a given moment.
- Energy production costs are elevated during peak demand periods due to the reliance on peaking power sources.
Peak Demand Deficit
- An electricity shortage or demand deficit occurs when electricity production and imports do not meet consumption needs.
Electricity Scenario in India
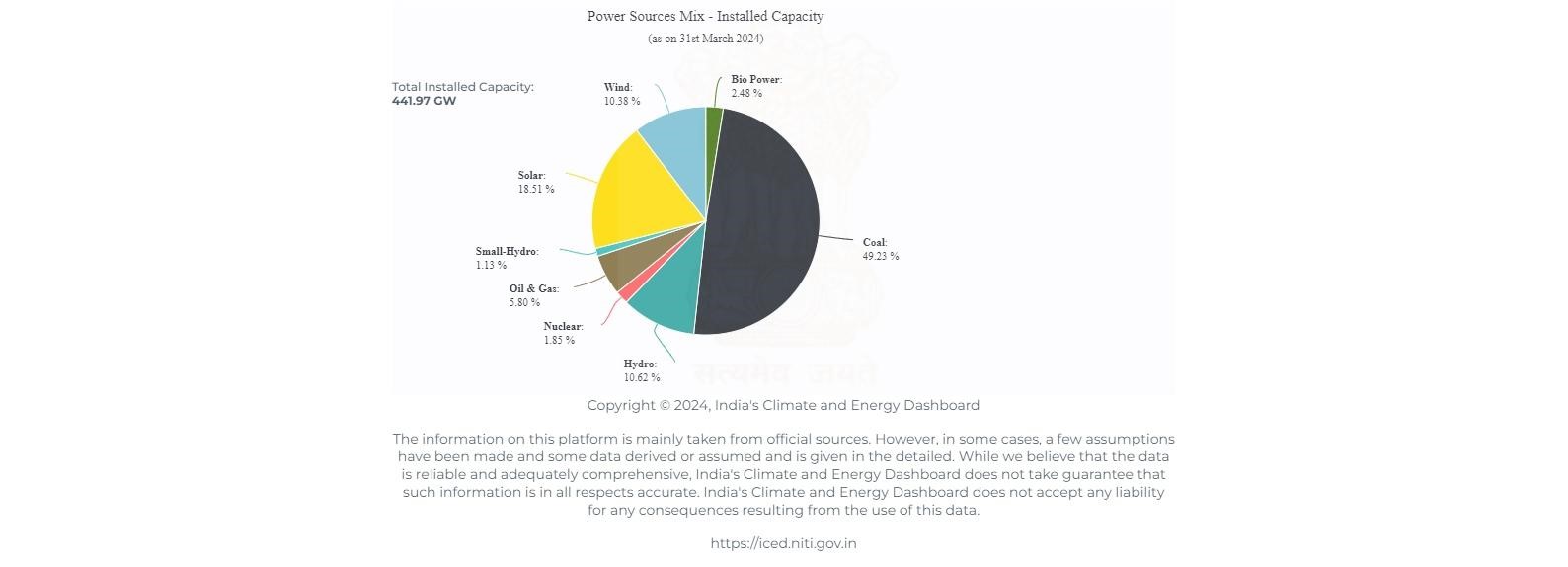
- Installed Capacity as of March 31, 2024:
- Total: 442 gigawatts (GW)
- Renewable energy plants (including large hydroelectric power plants) constitute 43% of the total capacity.
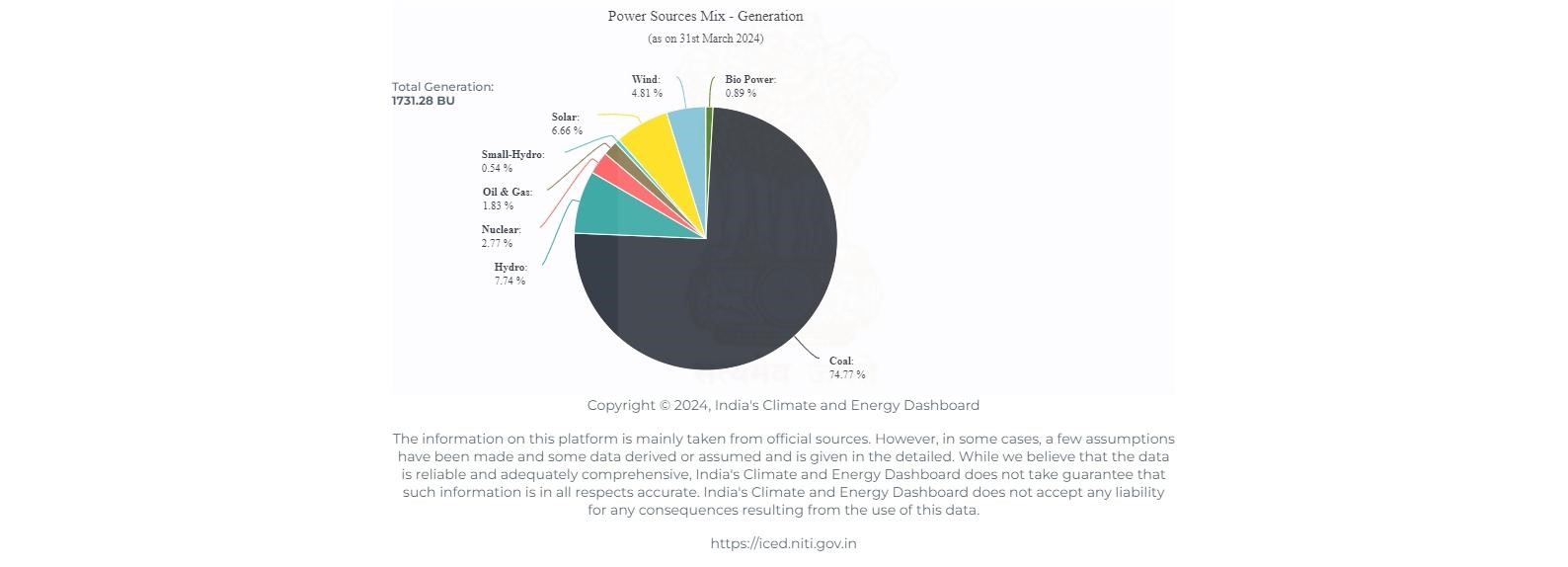
- Sector-wise Breakdown of Installed Capacity:
- Central Sector: 102,274.94 MW
- State Sector: 106,332.93 MW
- Private Sector: 219,691.40 MW
- Electricity Generation for 2023-24:
- Total generation:28 billion units (BU)
- Target set by the Ministry for 2023-24: 1750 BU, including:
- Thermal:110 BU
- Hydro: 700 BU
- Nuclear: 46.190 BU
- Import from Bhutan: 8 BU
Examples Case Studies and Data
Sustainable Development Goals (GS 3): The UN Financing for Sustainable Development Report 2024, released by the United Nations, emphasised the need for increased investment to achieve the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030, which were agreed upon by all UN members in 2015.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















