Table of Contents
Eco-Sensitive Areas
Context: The Karnataka government has asked the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) to withdraw the sixth draft notification issued by it for declaration of Eco-Sensitive Area (ESAs) of the Western Ghats.
About Eco-Sensitive Areas/Zones (ESZ)
- Definition: Area within 10 km of the boundaries of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
- Areas beyond 10-km range can also be notified as ESZ by the Union government if they hold larger ecological importance.
- Notified by: By MoEFCC under Section 3 of Environment Protection Act (EPA 1986).
- The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 does NOT mention the word “Eco-Sensitive Zones”.
- Purpose of Creating ESZ:
- To Protect environment and avoid its degradation due to anthropogenic activities.
- Create some kind of barrier/shock absorber for the specialised ecosystem (PAs).
- Act as transition zone from areas of higher protection to areas involving lesser protection.
- Activities prohibited in ESZ:
- Commercial mining, stone quarrying and crushing units
- Major hydroelectric project
- Discharge of untreated effluents
- Setting up of polluting industries, which have high potential for environmental damage.
| Did You Know? |
|
Kasturirangan Committee (2013)
- It sought to balance the development and environment protection in contrast to the system proposed by the Gadgil report.
- It distinguished between cultural and natural landscapes in the region.
- It recommended that instead of the total area of Western Ghats, only 37% of the total area should be brought under ESA and a complete ban on mining, quarrying and sand mining be imposed in ESA.
| UPSC PYQ |
Q. With reference to ‘Eco-Sensitive Zones’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: D |
Article-142
Context: While hearing a case of a student whose admission was cancelled due to non-payment of fees, the Supreme Court invoked Article-142 of the Constitution to provide complete justice.
Key Features of Article 142
- Complete Justice: The primary aim of this Article is to ensure that justice is served comprehensively, addressing situations where statutory provisions may fall short.
- Discretionary Nature: The powers under this article are discretionary, meaning the Court can choose when and how to exercise them based on the specifics of each case.
Recent Supreme Court Judgments Involving Article 142
- Shilpa Sailesh v Varun Sreenivasan (2023):
- Context: The Supreme Court ruled that it could directly grant a divorce on the grounds of “irretrievable breakdown of marriage” under Article 142.
- Significance: This judgement allows the Supreme Court to bypass the usual procedural requirements set by the Hindu Marriage Act, which typically involves a cooling-off period for mutual consent divorces.
- Chandigarh Municipal Corporation Elections (2023)
- Context: In this case the Supreme Court overturned election results and ensured electoral democracy was upheld.
- Significance: This case illustrates how Article 142 can be used to rectify procedural irregularities in electoral processes.
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. With reference to the Constitution of India, prohibitions or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following? (2019)
(a) The decisions taken by the. Election Commission of India while discharging its duties cannot be challenged in any court of law. (b) The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by the laws made by Parliament. (c) In the event of a grave financial crisis in the country, the President of India can declare a Financial Emergency without the counsel from the Cabinet. (d) State Legislatures cannot make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of the Union Legislature. Answer: B |
Operation Chakra-III
Context: The Central Bureau of Investigation has arrested 26 accused persons from Pune, Hyderabad and Visakhapatnam, following a crackdown on a major cybercrime network. This action was part of CBI’s ongoing Operation Chakra-III.
What is Operation Chakra-III ?
- It is an ongoing operation of CBI to dismantle cybercrime networks that operate across multiple countries.
- Objectives:
- Combating cybercrime and protecting citizens and global communities.
- Working with international law enforcement agencies like FBI and Interpol to dismantle cybercrime networks.
| Operation Chakra-II |
|
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- Established: In 1963 on the recommendations of Santhanam Committee.
- Legal Status: It is not a statutory body
- It derives its power to investigate from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946. (DSPE Act)
- Works under: CVC (in corruption cases) and DoPT (for all other matters)
- Appointment of CBI Director: Appointed by the Appointment Committee on the recommendation of a Selection Committee, as per the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013
- Selection Committee: PM, LoP, CJI
- Term of CBI Director: 2 years
- After completion of 2 years, he can be given 3 extensions of 1 year each.
- General consent:
- Section 6 of DSPE Act: Requires CBI to obtain consent from the state government to investigate within its jurisdiction unless it’s a union territory or railway area.
- Since 2015, states like Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Kerala, Mizoram, Punjab, Rajasthan, Telangana, Meghalaya, and West Bengal have withdrawn their general consent
- Case where Consent not needed:
- If an investigation is directed by the Supreme Court or High Court.
- For Union Territories.
- Section 6 of DSPE Act: Requires CBI to obtain consent from the state government to investigate within its jurisdiction unless it’s a union territory or railway area.
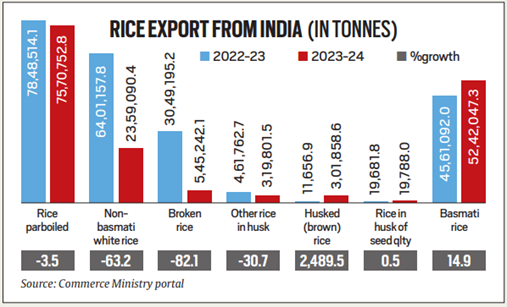
Export ban on Non-Basmati Rice lifted
Context: In a recent decision the Union Government has lifted the ban on export of Non-Basmati White Rice.
Key Decisions and Changes
- Export Ban Lifted: The ban on Non-Basmati White Rice exports was removed, allowing traders to resume exports under new regulations.
- Minimum Export Price (MEP): An MEP of $490 per tonne is fixed for Non-Basmati White Rice exports.
- Reduction in Export Duties:
- Export duty on Non-Basmati rice totally removed. It was 20% earlier.
- The export duty on other rice categories such as brown rice & parboiled rice
was halved from 20% to 10%.
Why was this decision taken ?
- Higher Sowing Rates: As of September 2024, the area under paddy cultivation was reported at 413.50 lakh hectares, a 2.2% increase from last year and a 3% increase from the five-year average.
- Projected Production Increase: India’s total rice production for the 2023-24 season is estimated at 137.82 million tonnes, representing a 1.5% increase from the previous year.
- Declining Wholesale Prices: Wholesale prices for rice dropped to Rs 3,324.99 per quintal, down from Rs 3,597.09 in September 2024.
- Surplus Stocks: The Food Corporation of India reported rice stocks of 323.11 lakh tonnes as of September 1, well above buffer stock norms.
| Facts |
|
VIPER Mission
Context: NASA has cancelled its Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) mission to the moon due to delays and cost overruns.
Key facts about VIPER Mission
- It is NASA’s first mobile robotic mission to the Moon.
- Objective:
- It is designed to map the distribution and concentration of water ice deposits in the permanently shadowed regions (PSRs) of the lunar south pole.
- To collect and analyse samples of the lunar soil and rocks to understand the geology of the south pole region.
- Launch Vehicle: SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
- Relation to Artemis Accord: VIPER was expected to be a crucial component of the US led Artemis Accord.
| Artemis Accords |
|
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. Among the following, which one is the largest exporter of rice in the world in the last five years? (2019)
(a) China (b) India (c) Myanmar (d) Vietnam Answer: B |


 Why India Needs Its Own Economic Model?
Why India Needs Its Own Economic Model?
 Challenges in India’s Airline Sector: ...
Challenges in India’s Airline Sector: ...
 Forest Conservation Act, 1980: Objective...
Forest Conservation Act, 1980: Objective...

























