Table of Contents
China – Nuclear Warhead
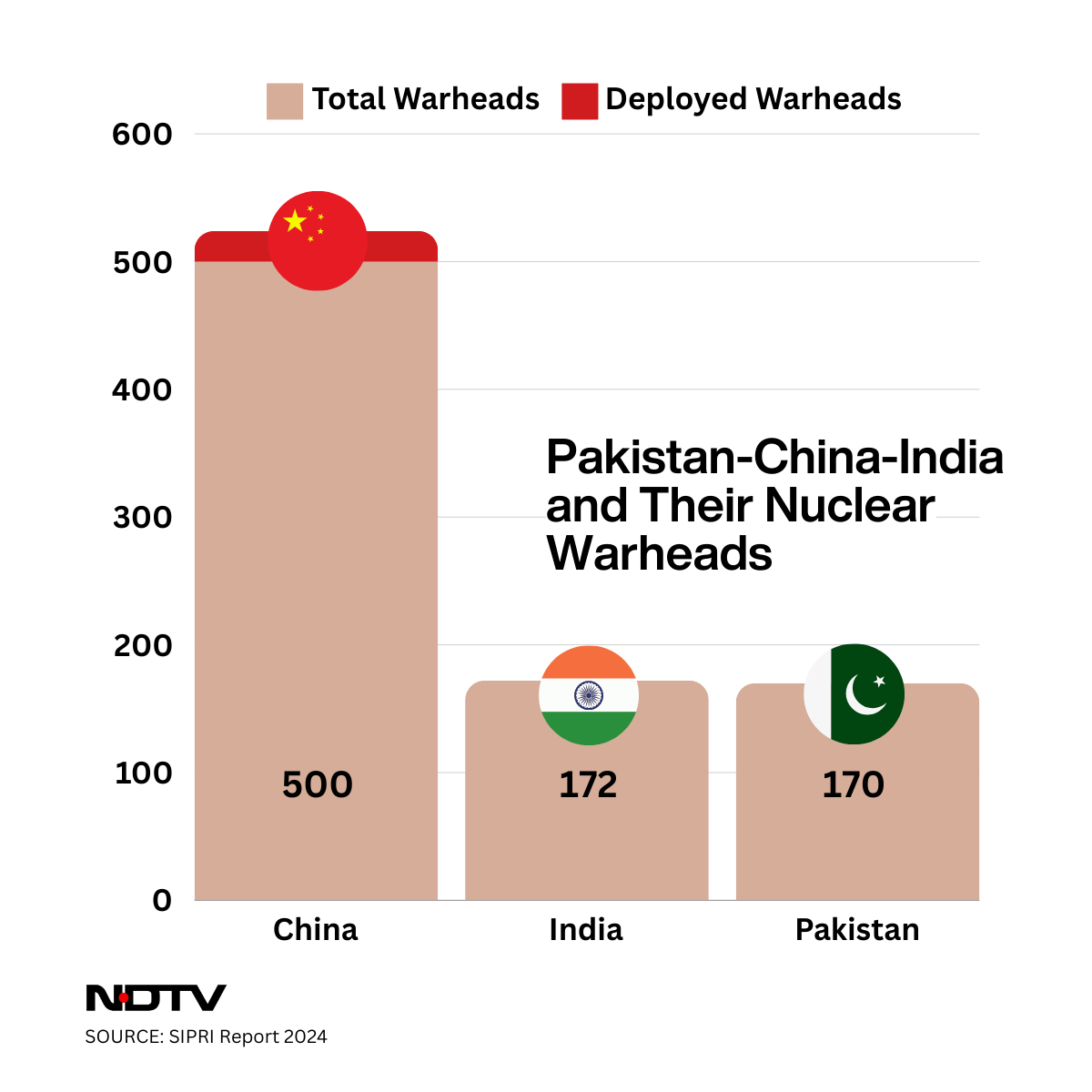
Context: According to a report by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), India’s nuclear arsenal increased to 172 warheads, slightly surpassing Pakistan’s count of 170 in 2023.
More In News
- China’s Nuclear Capabilities: China possesses approximately 500 warheads, which is three times the number India and Pakistan have. Some of these warheads are on high operational alert for the first time, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
- Strengthening Undersea Capabilities: India is bolstering the undersea leg of its nuclear triad and is also focusing on developing long-range missiles.
- Submarine Developments: India launched its third SSBN (nuclear-powered submarine carrying ballistic missiles) in November 2021.
- A fourth SSBN is currently under construction and is expected to be launched in 2024. These newer submarines are significantly larger, approximately 20 metres longer than the first two, as indicated by satellite imagery.
- Second SSBN – Arighat: The second SSBN, Arighat, was launched in November 2017. It underwent advanced sea trials in 2021-22, but its commissioning into the Indian Navy has been delayed and is now anticipated for 2024.
| Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) |
|
Black Holes
Context:
- Researchers observed a dramatic brightening at the heart of a galaxy.
- This brightening is caused by a supermassive black hole awakening from dormancy and beginning to consume nearby material.
- This marks the first time such a process has been seen as it happens.
| Facts |
|
About Black Hole
- About: Areas in space-time with gravity so intense that nothing, not even light, can escape.
- Formation: Occur when a massive star collapses into itself after its lifecycle, becoming extremely dense and warping surrounding space-time.
- Types:
- Stellar Black Hole: Results from the collapse of a single massive star.
- Intermediate Black Hole: Masses are between 100 and 100,000 solar masses.
- Supermassive Black Hole: Masses range from millions to billions of solar masses, located at the centres of most galaxies, including the Milky Way.
- Supermassive black holes create a violent environment by shredding and consuming any nearby material due to their immense gravity.
- A swirling disc of diffuse material forms around the black hole called an accretion disk.
- This accretion disk heats up to extremely high temperatures and radiates immense energy, sometimes outshining an entire galaxy.
- A bright and compact region powered by a supermassive black hole at the centre of a galaxy is called an active galactic nucleus (AGN).
- AGNs emit vast amounts of energy across the electromagnetic spectrum, from radio waves to gamma rays.
- These AGNs are some of the most luminous objects in the universe.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
- Coral Bleaching (GS 3): The United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) announced that the world’s coral reefs are experiencing a global mass bleaching event due to the combined effects of climate change and an El Niño climate pattern, which have pushed ocean temperatures to record highs.
- 67% of the world’s reefs are impacted by unprecedented heat stress.


 International Polar Bear Day 2026: Impor...
International Polar Bear Day 2026: Impor...
 Recent Defence Expansion in India: Moder...
Recent Defence Expansion in India: Moder...
 What is El Niño Labelling and Why It Ma...
What is El Niño Labelling and Why It Ma...




















