Table of Contents
UN – Global Growth
Context: The United Nations has raised its 2024 global economic growth forecast to 2.7%, up from its earlier prediction of 2.4% in January.
More In News
- This improved outlook is driven by stronger performance in the U.S. and emerging markets like India.
- While matching the 2023 growth rate, this figure remains below the pre-pandemic level of 3%.
- The UN also anticipates further growth in 2025, projecting a rate of 2.8%.
Projections For India
- India’s Growth: India’s GDP is expected to grow by 6.9% in 2024 and 6.6% in 2025.
- The revision is primarily due to strong public investment and resilient private consumption, despite subdued external demand impacting merchandise export growth.
- Pharmaceuticals and chemicals exports are expected to expand significantly.
- Inflation: Consumer price inflation in India is projected to decrease from 5.6% in 2023 to 4.5% in 2024, remaining within the central bank’s target range.
- Labour Market: Labour market indicators have improved due to robust growth and increased labour force participation.
- Fiscal Deficit: The government remains committed to gradually reducing the fiscal deficit while increasing capital investment.
| Facts |
|
South Asia’s Outlook
- Regional Growth: South Asia’s GDP is projected to grow by 5.8% in 2024 and 5.7% in 2025, driven by India’s strong performance and a slight recovery in Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- Challenges: Tight financial conditions, fiscal and external imbalances, potential energy price increases, and geopolitical tensions pose risks to the region’s economic outlook.
Global Economic Outlook
- Global Growth: The world economy is now forecast to grow by 2.7% in 2024 and 2.8% in 2025, mainly due to a better outlook in the U.S. and large emerging economies like Brazil, India, and Russia.
- Trade Recovery: Global trade is expected to recover in 2024, with China’s foreign trade growing faster than expected in the first two months of 2024, driven by exports to emerging markets.
- Challenges: Persistent geopolitical tensions, disruptions in the Red Sea, and escalating freight costs continue to pose challenges to global trade.
Other Notable Developments
- China’s Growth: China’s growth is projected to moderate to 4.8% in 2024, facing challenges from the property sector.
- Overall Outlook: While the global economic outlook has improved since January, challenges such as higher interest rates, debt sustainability, geopolitical tensions, and climate risks persist.
Orcas
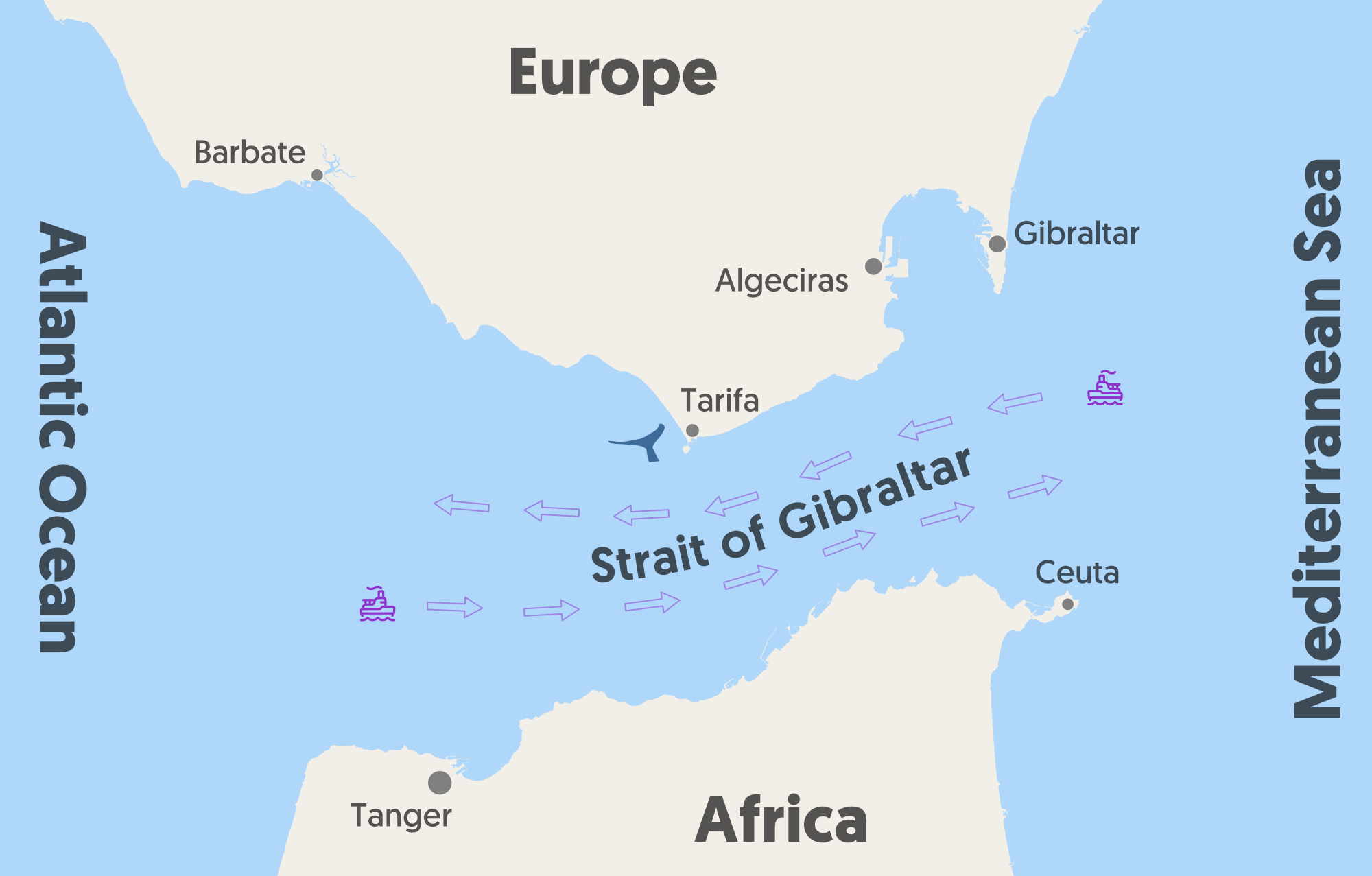
Context: Recently, two people were rescued after a group of orcas, also known as killer whales, sank their 15-metre-long sailing yacht in the Strait of Gibraltar, 22.5 kilometres off the coast of Morocco.
Previous Incidents
- November 2023 Incident: Orcas attacked the rudder of a yacht for nearly 45 minutes, forcing the crew to abandon the boat, which eventually sank near the Tanger Med port, 45 km northeast of Tangier, Morocco.
Frequency of Interactions
- Since 2020, over 700 interactions between orcas and boats have been recorded near the Strait of Gibraltar, with some boats sustaining significant damage.
- The frequency of these interactions has made it a multinational issue involving scientists and officials from Spain, Portugal, and Morocco.
Possible Explanations for Orca Behavior
- Playful Behaviour: Some scientists believe the orcas are simply playing or engaging in a fad behaviour, possibly initiated by a few individuals and then imitated by others.
- Traumatic Experience: Another theory suggests that one or two orcas experienced a traumatic event, such as getting entangled in fishing lines, which triggered a change in their behaviour. This behaviour is then being copied by other orcas in the area.
Concerns and Future Implications
- Researchers are worried that continued attacks on boats could endanger mariners and become a conservation issue for orcas.
- While orcas are not typically aggressive towards humans in the wild, the increased interactions raise concerns about potential harm to both humans and the animals themselves.
| About Orcas |
Southern Resident Killer Whales
|
| Strait Of Gibraltar |
A narrow waterway separating Europe from Africa, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean.
|
Deda Method
- Deda is a traditional method used for preserving seeds, making them look like boulders from a distance.
- Seeds are preserved in leaves and packed almost airtight.
- Packaged seeds are woven with Siali leaf (Bauhinia vahlii), locally known as ‘addakulu’, to create the deda.
- Three-Layer Protection:
- First Layer: Wood ash is spread inside the Siali leaves.
- Second Layer: The ash is covered with lemon leaves to form a casing.
- Third Layer: Seeds are preserved inside the casing and sealed.
- Protection and Longevity:
- This method protects seeds from pests and worms.
- Stored seeds can be used for cultivation for up to five years.
- Cultural Practice:
- Widely practised by the Muria tribes in Chhattisgarh.
- This method is a traditional practice handed down by ancestors in the forests of Chhattisgarh.
- Tribal Settlements: The Murias have settled along the banks of the Godavari and Sabari rivers in the Godavari valley in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
Synchrotron
- A synchrotron is a type of circular particle accelerator where particles move in a loop.
- Operation:
- It accelerates charged particles (typically electrons) through sequences of magnets until they reach nearly the speed of light.
- These high-speed electrons produce very bright light known as synchrotron light.
- Synchrotron Light:
- This intense light, mainly in the X-ray region, is millions of times brighter than conventional light sources and 10 billion times brighter than sunlight.
- The light is directed down beamlines to experimental workstations for research purposes.
- Research Applications:
- Scientists use synchrotron light to study minute matter such as atoms and molecules.
- They analyse how samples scatter, diffract, absorb, or re-emit the light to uncover details about their structure or chemical composition.
- Global Presence:
- There are approximately 70 synchrotrons worldwide, each varying in use and capability, with some focusing on applied sciences and others on fundamental research.
Examples, Data and Case Studies
Global Warming (GS 3): Venezuela has lost its final glacier, La Corona, making it the first country in the Andes without any glacier


 New Window of Opportunity for India amid...
New Window of Opportunity for India amid...
 Cetacean Morbillivirus: Meaning, Feature...
Cetacean Morbillivirus: Meaning, Feature...
 Transforming a Waste-Ridden Urban India:...
Transforming a Waste-Ridden Urban India:...

























