Table of Contents
Battery Tech Race
Context: A report by the Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) and the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) highlighted that a planned investment of ₹1,151 crore over the next five years could give India a significant international lead in battery technology development for electric vehicles.
More in News
- e-mobility R&D Roadmap: Identifies 4 key areas: energy storage cells, electric vehicle aggregates, materials recycling, and the charging and refuelling infrastructure.
About Battery
Battery: A battery is an electrical storage device consisting of one or more electrochemical cells. These cells can be dry or liquid, containing electrodes (Cathode and Anode) where charges move during charging and discharging.
- At the time of charging, the charge moves from one electrode to another.
- The electrode from which charges leave is called Cathode (positively charged), and the electrode at which the charges get deposited is called Anode (negatively charged).
- In this movement, the charges are stored in the form of potential energy near the anode.
Key Components of a Battery
- Cathode: Composed of materials like Lithium, Nickel, and Cobalt, which contribute ions for storage.
- Anode: Typically made from Graphite or Silicon, stores ions and releases them during discharge.
- Separator: Keeps cathode and anode materials apart while allowing ion movement.
- Current Collectors: Collect electrons at both the cathode (Aluminum) and anode (Copper) sides.
- Electrolyte: Ensures good conductivity and stability of ions.
Performance Characteristics of Battery Technology
- Energy Density: Measures energy stored per unit volume or mass, critical for EVs and storage applications.
- Power Density: Indicates the energy a battery can release within a given capacity.
- Charging Rate: Describes how quickly a battery can be charged.
- Life Span: Reflects how the battery’s capacity declines overcharge and discharge cycles.
- Cost: Often calculated per kWh, vital for achieving cost parity with internal combustion engines.
- Safety: Focuses on reducing risks associated with flammable components and operational wear.
Chandipura Virus Infection (CHPV)
Context: Chandipura Virus Infection is spreading in Gujarat.
About Chandipura Virus Infection (CHPV)
- Family and Vectors:
- CHPV (Chandipura Virus) is part of the Rhabdoviridae family.
- Transmitted by Phlebotomine sandflies, Phlebotomus papatasi, and Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.
- The virus resides in the insect’s salivary glands and is transmitted through bites.
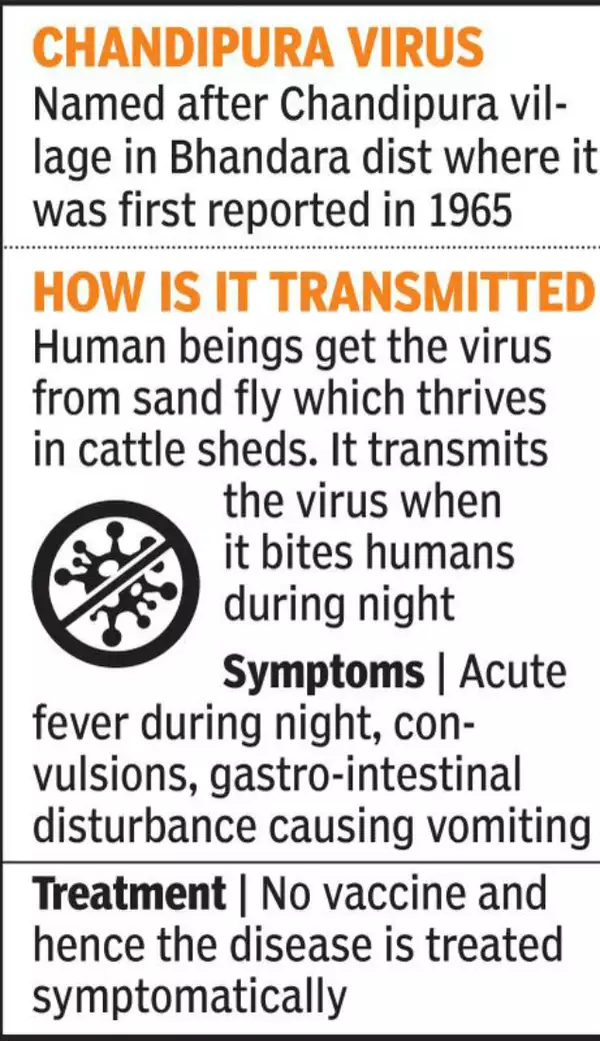
- Transmission to Humans: The virus can infect humans and domestic animals, reaching the central nervous system and potentially causing encephalitis, which is inflammation of the brain.
- Symptoms of CHPV Infection:
- Starts with flu-like symptoms including fever, body ache, and headache.
- Can progress to altered sensorium, seizures, and encephalitis.
- Other reported symptoms include respiratory distress, bleeding tendencies, and anaemia.
- Rapid progression after encephalitis, potentially leading to death within 24-48 hours of hospitalisation.
- Susceptibility: Primarily affects children under 15 years of age.
- Management of Infection:
- No specific antiretroviral therapy or vaccine available.
- Management focuses on symptomatic treatment, especially controlling brain inflammation.
- Regional Impact in India:
- First isolated in 1965 in Maharashtra during a dengue/chikungunya outbreak.
- Significant outbreaks in 2003-04 in Maharashtra, northern Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh with over 300 child fatalities.
- High case fatality rates observed: 78% in Gujarat (2004) and 55% in Andhra Pradesh (2003).
- Endemic to central India, correlated with higher populations of vector sand flies and mosquitoes.
- Environmental and Seasonal Factors:
- Outbreaks often in rural, tribal, and peripheral areas.
- Linked to environmental conditions that favour sandfly proliferation, such as monsoon season and activities like using cow dung in construction, which attracts sandflies.
- Changes in Disease Pattern:
- New patterns in disease manifestation and vector behaviour noted.
- Recent findings include sandflies at higher elevations and new clinical presentations such as brain haemorrhage.
- New outbreak centres are emerging in other tribal areas of Gujarat.
India’s Quantum Future
Context: India trails behind leading nations like China and the United States in quantum science and technology.
About Quantum Technologies
- Quantum technologies exploit phenomena like superposition and entanglement of sub-atomic particles, which behave counter-intuitively at very small scales.
- These properties have been verified experimentally and are now being harnessed for practical applications.
- Quantum computers, which can perform complex calculations much faster than conventional computers, are one of the early applications of these technologies.
About National Quantum Mission
- Launched in 2023 to foster scientific and industrial research in Quantum Technology (QT) and Applications (QTA).
- Aims to establish a vibrant ecosystem for QT-led economic growth and position India as a leader in QTA.
- Objectives of the Mission:
- Develop quantum computers with 50-1000 qubits within eight years using superconducting and photonic technology.
- Implement secure satellite-based quantum communications across ground stations over a 2000 km range within India.
- Establish secure long-distance quantum communications internationally.
- Set up inter-city quantum key distribution networks and multi-node Quantum networks over a 2000 km range.
- Focus Areas:
- Development of high-sensitivity magnetometers, atomic clocks, and atomic systems for precision in timing, communications, and navigation.
- Design and synthesis of quantum materials like superconductors, topological materials, and innovative semiconductor structures.
Challenges for India’s National Quantum Mission
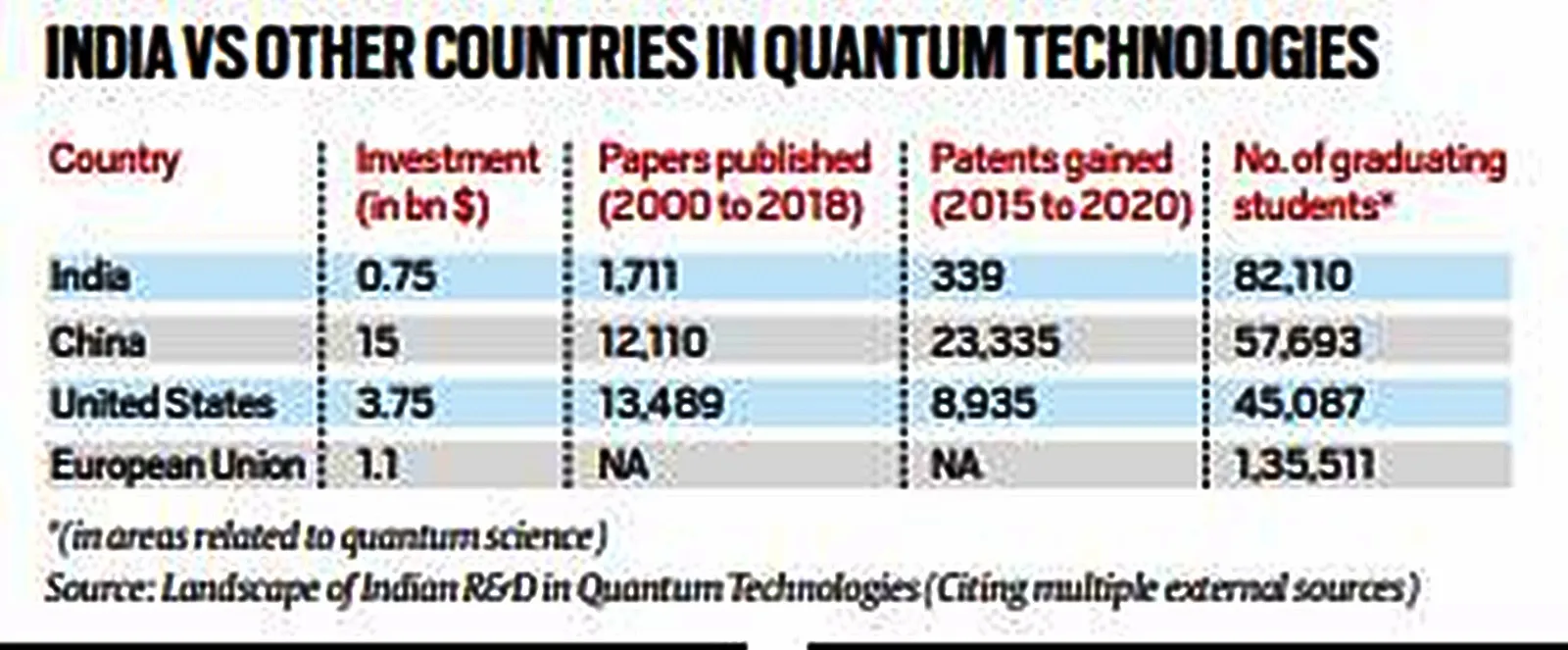
- Significant Funding Gap: Compared to global leaders, India’s funding for quantum technologies is relatively modest.
- While India has allocated ₹6,000 crore (about $0.75 billion), countries like China and the US have invested substantially more ($15 billion and $3.75 billion, respectively).
- Research Output and Patents: India trails significantly in the number of scientific papers and patents in quantum-related technologies.
- Example: Between 2015 and 2020, China and the US registered 23,335 and 8,935 patents respectively, whereas India registered only 339.
- Global Competition: Leading nations have a head start not just in investments but also in the number of researchers working in this sector and the scientific output they generate.
- Resource Allocation: There is a discrepancy in the utilisation and allocation of resources towards quantum technology, which could hinder India’s progress in catching up with or surpassing global standards.
Recommendations
- Increase Investment: To close the gap with leading nations, significantly increasing investment in quantum technologies is crucial. This would involve not just government spending but potentially also encouraging private sector participation and international collaborations.
- Talent Identification and Promotion: The mission should focus on identifying and nurturing young talent in quantum sciences. Creating opportunities for education, training, and research in quantum technologies at universities and research institutions is vital.
- Establish a Dedicated Cadre of Quantum Scientists: Similar to India’s approach with atomic energy and space sciences, there could be merit in raising a separate cadre of quantum scientists. This would help in building a focused and dedicated team working towards quantum advancements.
- Strengthening Patenting and Research Publications: Enhancing the framework and support for patenting innovations and increasing the global dissemination of research through publications can help India boost its standing in the global quantum research community.
- Focus on Niche Areas: While competing globally, focusing on niche areas where India already has expertise, like quantum communications and sensing, could provide strategic advantages and lead to early successes.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















