Table of Contents
Motion of Confidence
Context: Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal moved a motion of confidence in the legislative assembly.
About Motion of Confidence
- A Motion of Confidence is a supportive motion introduced by a government in legislative bodies to allow elected representatives to express their trust in the government.
- This motion can only be introduced in Lok sabha and legislative assembly.
- This motion is subject to a vote within the parliament or assembly to determine its acceptance or rejection.
- Governments may introduce a Motion of Confidence as an alternative to a Motion of No Confidence initiated by the opposition.
- If a Motion of Confidence fails in a parliamentary democracy, the government typically must either resign or seek the dissolution of parliament to prompt a General Election.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA)
Context: The Uttar Pradesh government invoked the Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA), banning strikes by government employees in all State government departments, corporations, and authorities for a period of six months.
About Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA)
- The Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA) of 1968 was established by the Indian Parliament to ensure the continuity of key services critical to daily life.
- The Act prohibits employees from striking in vital sectors and does not accept bandhs or curfews as valid reasons for absenteeism.
- Essential Services covered by the Act:
- Public Services: Sanitation, water supply, hospitals, national defence.
- Production and Distribution: Petroleum, coal, electricity, steel, fertiliser.
- Finance: Banking services.
- Communication and Transportation: All related services.
- Food Distribution: Government initiatives related to acquisition and distribution of food grains.
- Enforcement by State and Central Government:
- State Governments: State governments, acting alone or collaborating with other state governments, can enforce their respective acts in specified territories.
- Can enforce the act for services affecting their state(s).
- Central Government: Can enforce the act for nationwide disruptions, especially railways.
- State Governments: State governments, acting alone or collaborating with other state governments, can enforce their respective acts in specified territories.
- Actions against Employees:
- Disciplinary Action: Dismissal from work.
- Legal Action: Imprisonment up to 1 year, fine, or both.
- Arrest: Without warrant by a police officer.
- Related Information:
- Each state has its own ESMA with slight variations.
- Initiating the Act depends on the scope of the strike (state or national).
FEMA and PMLA
Context: The Enforcement Directorate (ED) has not found any violation under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) during its inquiry into Paytm Payments Bank Limited (PPBL) transactions.
Prevention of Money-Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA)
- The PMLA, 2002, is an Indian parliamentary act designed to prevent money laundering and enable the seizure of property linked to money laundering.
- Section 3 of the act defines money laundering as the process of disguising illegal proceeds (crime-derived) as legal funds.
- It involves various stages like placement, layering, and integration to obscure the source of illegal proceeds.
PMLA Provisions:
- The act criminalises money laundering activities and allows for the confiscation of assets associated with money laundering.
- Enforced By: Enforcement Directorate (ED) under the Ministry of Finance.
- Role of ED in relation to PMLA, 2002: The ED has been given responsibility to enforce the provisions of the PMLA by conducting investigation
- to trace the assets derived from proceeds of crime,
- to provisionally attach the property, and
- to ensure prosecution of offenders and confiscation of property by the Special Court.
- Bail provisions under the PMLA, 2002 –
- The PMLA has considerably onerous conditions for bail.
- In complete contrast to criminal law, which functions on the presumption of innocence of the accused person, the PMLA requires an accused to prove that they are not guilty (reversal of presumption of innocence), to receive bail.
- Recent Amendments to PMLA: In 2023, the Government of India amended the PMLA rules, incorporating some of the FATF (Financial Action Task Force) recommendations.
- These amendments included:
- Defining ‘group’ entities for implementing group-wide anti-money laundering policies,
- Defining ‘politically exposed persons’, tightening the definition of beneficial ownership by reducing the threshold from 25% to 10%, and
- Introducing additional documentation requirements for companies, partnerships, and trusts.
- Cryptocurrency exchanges that deal with virtual digital assets must now also comply with the KYC norms under PMLA.
- These amendments included:
Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)
- What it does?:
- Deals with cross-border trade and payments in India.
- Defines rules for foreign exchange transactions.
- Introduced: 1999, replacing Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA).
- Head office: Enforcement Directorate, Delhi.
- Main objectives:
- Facilitate external trade and payments.
- Maintain order in the foreign exchange market.
- Ensure authorised persons handle foreign exchange transactions.
- Encourage specific types of transactions.
- Allow the Reserve Bank of India to regulate capital account transactions.
- Applies to:
- Indian citizens and NRIs.
- Overseas companies owned 60%+ by NRIs.
- Indian companies’ foreign branches/subsidiaries.
- Exports and imports of goods and services.
- Financial services outside India.
- Cross-border sales, purchases, and exchanges.
Chabahar Port
Context: India urged Central Asian Countries to use Chabahar port to enhance connectivity and trade with India and other countries.
About Chabahar Port
Location:
- Southeastern Iran, Gulf of Oman.
- Sistan-Baluchistan province, near the energy-rich southern coast.
- Only Iranian port with direct ocean access.
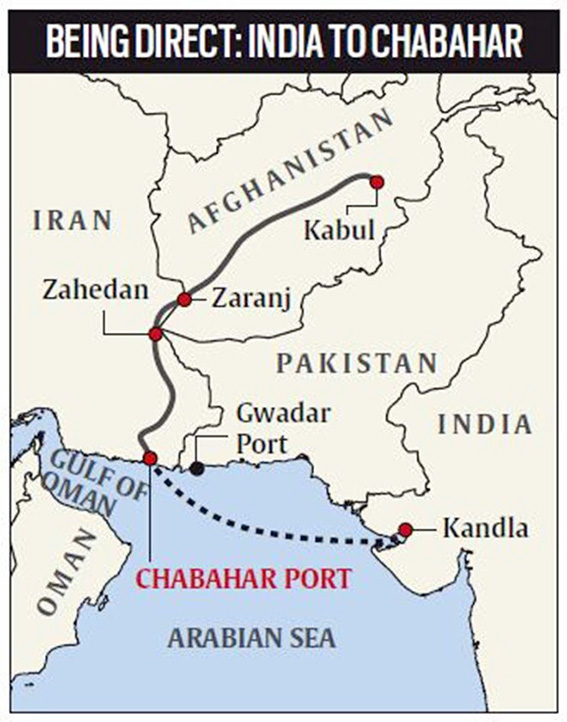
Significance:
- Golden Gate for Trade: Connects India, Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asia.
- India’s Bypass Route: Avoids Pakistan for transporting goods to Afghanistan.
- International North-South Transport Corridor: Boosts trade with Russia and beyond.
- Countering China: Offers alternative to Chinese presence in the Arabian Sea.
- Iranian Gateway: Crucial role in project’s success.
Cash Reserve Ratio
Context: State Bank of India (SBI) was in talks with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to reduce the cash reserve ratio (CRR) requirement on green deposits.
About Cash Reserve Ratio
What is it?
- A portion of a bank’s deposits that must be kept with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) as cash reserves.
- Banks cannot lend or invest this money; it doesn’t earn interest.
- Applies to scheduled commercial banks, not regional rural banks or NBFCs.
Key Objectives:
- Control inflation: Higher CRR means less money for banks to lend, reducing inflation.
- Maintain liquidity: Ensures banks have enough cash to meet customer withdrawals.
- Set a base rate for loans: CRR influences the minimum interest rate banks can offer loans.
- Boost the economy: Lowering CRR increases money supply, stimulating economic activity.
How is it calculated?
- As a percentage of a bank’s Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL).
- NDTL includes savings, current, and fixed deposit balances.
- Currently, CRR is 4.50%, meaning banks must keep Rs 4.50 for every Rs 100 deposited.
Additional Notes:
- RBI sets and can change the CRR percentage.
- CRR is one tool used by central banks to manage monetary policy.
CARTOSAT-2
Context: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) announced the completion of de-orbiting of Cartosat-2.
About CARTOSAT
- Purpose: Remote sensing satellite for mapping (launched 2005)
- Image Resolution: Coarse, medium, and high resolution
- Last Satellite (Generation II): Launched January 2007
- Orbit: Polar, sun-synchronous, 14.78 orbits per day
- Sensors: Panchromatic and multispectral cameras
- Applications:
- Urban planning
- Coastal land use and regulation
- Road network and water distribution monitoring
- Land use maps
- Geographical and land information systems
Open AI- Sora
Context: Open AI unveiled a new generative artificial intelligence called Sora.
About Sora
What is it?
- OpenAI’s advanced AI model that generates videos from text descriptions.
- Creates high-quality videos with complex scenes, multiple characters, and accurate details.
- Understands physical world objects, props, and emotions for lifelike characters.
Limitations and Safety:
- Still under development and struggles with complex prompts.
- Current model limitations include physics simulation and cause-and-effect understanding.
- OpenAI focuses on safety before public release, collaborating with experts to prevent misinformation and harmful content.
- Tools like detection classifiers (e.g., Sora video classifier) will identify AI-generated videos.
Current Status and Future:
- Not publicly available yet; OpenAI prioritises safety and responsible usage.
- Feedback from artists, designers, and filmmakers helps improve the model for creative professionals.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















