Table of Contents
National Youth Festival
Context: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi inaugurated the 27th National Youth Festival in Nashik (Maharashtra).
About National Youth Festival
- India hosts the National Youth Festival each year to celebrate National Youth Day from January 12-16.
National Youth Day
- Celebrated on: January 12 (annually).
- Commemorations: The birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.
- Year Of Inception: 1985
- Purpose: To inspire the youth to embody the values, principles, and beliefs of Swami Vivekananda.
- 2024 Theme: “Viksit Bharat@ 2047: Yuva ke liye, yuva ke dwara”
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Borrowings By States
Context: The Supreme Court has decided to examine an original suit from Kerala which accuses the central government of harming the economy of this financially limited state by meddling with its finances.
Constitutional Provisions Related To Borrowings By The States
- Article 293: It deals with the borrowing powers of state governments in India.
- It outlines the conditions and limitations under which states can raise loans.
- Article 293(3) restricts states from raising loans without the Indian Government’s consent if they have outstanding government loans.
- This provision has been actively managed by the Centre, following recommendations from the Finance Commission.
Current Status Of Borrowings Of States
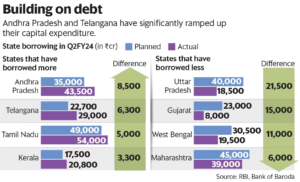
State Borrowing Limits
- Typically, state borrowing limits are capped at 3% of their GSDP.
- For the fiscal year 2024, this translates to Rs 8,59,988 crore, as per the Fifteenth Finance Commission’s suggestions.
- States can access an additional borrowing capacity of 0.5% of GSDP, tied to power sector reform performance.
- For FY24, states may borrow an additional Rs 1.43 lakh crore, subject to the Power Ministry’s endorsement.
States with a High debt-to-GSDP ratio
- Punjab: Around 47 per cent
- Manipur: 40 per cent
- Nagaland: 42 per cent
- Arunachal Pradesh: 53 per cent
Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003 Provisions
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) framework set a target for the Central Government to cap its fiscal deficit at 3% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- It further provides that, the Central Government shall endeavour to limit the General Government Debt to 60 percent of GDP and the Central Government Debt to 40 percent of GDP, by 31st March, 2025.
Yuva Nidhi Scheme of Karnataka
Context: Recently the Karnataka government launched the Yuva Nidhi Scheme which marks the fulfilment of the fifth and final pre-poll promise.
About Yuva Nidhi Scheme
- Purpose: To provide economic security to the youth of Karnataka and reduce their financial dependence on others.
- ₹3,000 monthly for unemployed graduates.
- ₹1,500 monthly for unemployed diploma holders.
- Allowance Distribution Start Date: The government will start distributing allowances in January.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Beneficiaries must be unemployed for at least six months post their graduation or diploma.
- Must be residents of Karnataka.
- Completion of degree or diploma must be in the academic year 2022-2023.
- Not eligible if receiving loans under other state or central schemes, or from banks.
- Ineligibility for those benefiting from other similar unemployment schemes.
- Students pursuing higher education are not eligible.
- Individuals already receiving apprentice salaries or employed in private or government sectors cannot apply.
- Duration: Aid will be provided until the beneficiary secures employment or for up to two years, whichever is earlier.
- Method of Payment: Direct Bank Transfer (DBT) to the bank accounts of eligible beneficiaries.
- Registration Process: Registration on the Seva Sindhu website is required, which can be done online or offline.
Global Pulses Convention
Context: The Global Pulses Convention will be held in New Delhi this year.
About Global Pulses Convention
- Organised By: National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd. (NAFED) and the Global Pulse Confederation (GPC).
- Aim: To facilitate knowledge sharing among experts, stakeholders, and policymakers.
- Previous Editions:
- 2023: Sydney, Australia
- 2022: Dubai
About Global Pulse Confederation (GPC)
- Previous Name: Initially known as CICILS IPTIC.
- Representation: The Global Pulse Confederation (GPC) represents various sectors in the pulse industry including growers, researchers, logistics, traders, exporters, importers, governmental entities, multilateral organisations, processors, canners, and consumers.
- Membership Composition: Comprises 24 national associations and over 600 members from the private sector.
- Headquarters: Dubai.
Pulses Production In India
- Global Standing in Pulses: India is the world’s largest producer (25%), consumer (27%), and importer (14%) of pulses.
- Contribution to Agriculture:
- Pulses occupy about 20% of the total area under food grain cultivation.
- They contribute approximately 7-10% to India’s total foodgrain production.
- Seasonal Production:
- Pulses are cultivated during both the Kharif and Rabi seasons.
- Over 60% of India’s pulse production comes from the Rabi season.
- Leading Producing States: The top states for pulse production are Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Karnataka.
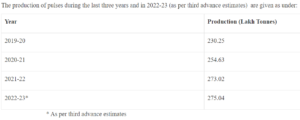
Mauna Kea
Context: An official delegation from the Department of Science and Technology recently visited Mauna Kea to address challenges facing the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) project.
About Mount Kea
- Location: Situated on the island of Hawaii.
- Type: An inactive volcano.
- Peak Altitude: Reaches 4,207.3 metres (13,803 feet) above sea level.
- State Record: The highest point in the state of Hawaii.
- Global Ranking:
- Second-highest island peak in the world.
- Just 38 metres shorter than the neighbouring Mauna Loa.
- Comparison with Mount Everest:
- Considered by some to be the tallest mountain in the world when measured from its underwater base.
- Exceeds Mount Everest in height when measured from base to peak.
- Topographic Isolation: Mauna Kea ranks eighth in the world in terms of topographic isolation.
Retail Inflation Over Last 10 Years
Context: Data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) showed retail inflation in India spiked due to food prices, affecting factory output, with varying impacts across sectors and states.
Key Highlights Of The Findings
- Factory Output Decline: Fell to an eight-month low of 2.4% in November.
- Down from 11.6% a month ago and 7.6% a year ago.
- Reasons: High-base effect and slower growth in manufacturing, mining, and capital goods.
- Retail Inflation Trend: Second consecutive month rise, exceeding 4% for over four years.
- Food Inflation Rate: Jumped to 9.53% in December from 8.70% in November.
- Urban areas saw 10.42% while rural areas had 8.49% in December.
- Core Inflation: Dropped to sub-4% level at 3.9% in December.
- Food and Beverages Inflation: Increased to 8.70% in December.
- Vegetable Inflation: Spiked to 27.64% in December.
- Pulses and Spices Inflation: Rose to around 20% levels.
- Cereal Inflation: High at 9.93%, though slightly lower than November.
- Goods vs Services Inflation: Goods inflation nearly 9.5%, services (miscellaneous) inflation 4.07% in December.
- Clothing and Footwear Inflation: Moderated to 3.61% in December.
- Housing Inflation: Increased to 3.63% in December.
- Fuel and Light Inflation: In negative territory at (-)0.99% in December.
- Rural-Urban Inflation Split: Rural inflation at 5.93%, urban at 5.46% in December.
- State-Specific Inflation Rates: Highest in Gujarat (7.07%), followed by Rajasthan, Haryana, Karnataka, and Maharashtra.
- Industrial Output by Sector:
- Manufacturing growth at 1.2% in November.
- Mining and electricity output growth at 6.8% and 5.8% respectively.
- Primary and infrastructure/construction goods growth at 8.4% and 1.5%.
- Capital Goods Output: Dropped to a 13-month low of (-)1.1% in November.
- Consumer Durables and Nondurables Output: Fell to a five-month low of (-)5.4% and a 13-month low of (-)3.6% respectively in November.
- Cumulative Factory Output: Grew 6.4% during April-November of the financial year.
- Manufacturing Sector Performance: Only six out of 23 sectors registered growth in November.
- Top Performing Sectors: Coke and refined petroleum products, beverages, rubber, and plastic products.
Non-Performing Sectors: Computer, electronics, optical products, electrical equipment, furniture, apparel, and leather.
Kalaram Temple
Context: PM Narendra Modi recently visited Kalaram Temple on the banks of the Godavari in the Panchavati area of Nashik in Maharashtra. The temple is the site of a landmark agitation led by Babasaheb Ambedkar demanding temple entry rights for Dalits more than 90 years ago.
About Kalaram Temple
- Ancient Origins: The original temple, dating back to the Rashtrakuta Period (7th –11th centuries), was dedicated to an unknown deity.
- Historical Event: During early Turkish invasions, the temple’s idol was hidden in the Godavari River by priests for protection.
- Reconstruction: In 1792, Sardar Rangarao Odhekar led the efforts to build the new temple.
- Idol Recovery: Sardar Odhekar, guided by a dream, retrieved a black statue of Lord Ram from the Godavari River and established the temple.
Temple’s Uniqueness and Architecture
- Ramkund: The site where the statues were found was named Ramkund.
- Inner Sanctuary: The sanctum sanctorum contains statues of Lord Ram, goddess Sita, and Lakshmana.
- Main Entrance: Features a black idol of Hanuman.
- Design Feature: The temple allows a direct line of sight from Hanuman’s idol to Lord Ram’s idol.
- Symbolic Steps: The main temple’s 14 steps symbolise the 14 years of Lord Rama’s exile.
- Pillars’ Significance: The 84 pillars in the temple represent the belief in 84 lakh species in the cycle of life, culminating in human birth.
- Sacred Tree: Houses an ancient tree with impressions of Dattatreya’s footprints on stone, honouring the revered monk and yoga lord.
- Statue of Founder: A statue of Sardar Odhekar is present within the temple.
- Architectural Similarity: The design echoes the architectural style of the Trimbakeshwar temple.
- Construction Material: Built with black stone, the temple features four doors, one on each side.
- Surrounding Shrines: Encircled by smaller temples dedicated to deities like Vithal, Ganapathi, and Maru


 UDAN Scheme, Objectives, Funding and Ach...
UDAN Scheme, Objectives, Funding and Ach...
 Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
Indus Water Treaty 1960 Suspended by Ind...
 5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...
5 Years of SVAMITVA Scheme and Its Benef...





















