Current Affairs 14th July 2023 for UPSC Prelims Exam
Rafale-M Jet
Context: India’s Defence Ministry has approved the proposed procurement of 26 Rafale-M fighters from France.
More on News
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi is expected to sign a deal for acquisition of 26 Rafale-Marine fighters and a repeat order for building three more Scorpene (Kalveri) class submarines at Mazagon Dockyards Limited (MDL) through the “Make in India” route during his two-day visit to France.
- While the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has granted the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) to procure the 26 fighter jets, the price and other terms of purchase will be negotiated subsequently with the French government, since they will be bought on an Inter-Governmental Agreement (IGA) basis.
- The Rafale is one of the key components of France’s nuclear deterrence.

About Rafale Marine Fighters
- The Rafale Marine fighters are the naval variant of the Rafale fighter jets, 36 of which are operated by the Indian Air Force.
- Rafales Fighter Jets: They are manufactured by France’s Dassault Aviation.
- The Rafales are advanced twin engine, multirole fighter jets.
- They are equipped with latest weapon systems including Meteor-beyond visual range air-to-air missiles, Hammer air to surface smart weapon system, Scalp cruise missiles.
- They are fitted with modern sensors, and radar to detect and track and attack targets.
- The jets can carry exceptionally high payloads.
- Jets have also been equipped with certain India-specific enhancements and can carry out a range of missions.
- Rafale Marine Fighters Jets: The Marine version of the jets will be slightly different, given that they will operate from aircraft carriers on sea.
- These have foldable wings, a longer airframe for landing on carriers, and a tail hook for arrested landing on a carrier.
- The nose and main landing gears on the navy version have been reinforced to satisfy the difficult aircraft carriers landing and catapulting conditions for the aircraft.
- The Rafale M nose gear also incorporates the “jump strut technology” in the shock absorber to give the aircraft an angle of attack during catapulting.
- It can also carry a wider range of weapons, including anti-ship missiles and air to surface missiles and radar meant for maritime operations.
- All the 26 fighters will be single-seater versions with Indian Navy pilots being trained in France as well as on advanced simulators in Goa.
- Significance of the Deal: The Indian Navy has been facing a scarcity of aircraft and submarines for the last few years.
- These jets will be used by the Indian Navy on the INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya, which currently employ the MiG-29. This will be the second such fighter jet purchase from the French aerospace major Dassault Aviation in recent years.
- These jets will add more teeth to the formidable arsenal of Indian Navy.
- It is understood that India and France will sign a defence-industrial road map to push India to scale up its manufacturing of hardware platforms through indigenously developed engines and technologies.
- PM Modi and French President Emmanuel Macron will also unveil a bilateral road map for the Indo-Pacific with specific steps to ensure freedom of navigation and maritime security for sea lanes in the area contested by a rising China.
- Also, the repeat order for three Scorpene class submarines through the government-to-government route will not only add muscle to the Indian Navy to take up the challenge of PLA expansion in the Indian Ocean but also give a new lease of life to submarine manufacturing capacity of MDL after INS Vaghsheer is commissioned in 2024.
- The procurement of additional submarines, with higher indigenous content, will not only help in maintaining required force level and operational readiness of the Indian Navy, but also create significant employment opportunities in the domestic sector.
Current Affairs 13th July 2023 for UPSC Prelims Exam
Link between Diabetes and TB
Context: Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor that increases the incidence and severity of tuberculosis.
More on News
- India has been experiencing the double burden of two debilitating and severe epidemics: type 2 diabetes (diabetes mellitus, DM) and tuberculosis (TB).
- Currently, India has around 74.2 million people living with diabetes while TB affects 2.6 million Indians every year.
- Among people with TB, the prevalence of DM was found to be 25.3% while 24.5% were pre-diabetic, in a 2012 study in tuberculosis units in Chennai.
What is Diabetes Mellitus (DM)?
- Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which the body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin, causing blood sugar (glucose) levels to be abnormally high.
- Cause: During digestion, food is broken down into basic components. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. Glucose is a critically important source of energy for the body’s cells.
- Insulin traveling in the blood signals the cells to take up glucose. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. When levels of glucose in the blood rise (for example, after a meal), the pancreas produces more insulin.
- Diabetes mellitus occurs when the body’s cells resist the normal effect of insulin, which is to drive glucose in the blood into the inside of the cells. This condition is called insulin resistance. As a result, glucose starts to build up in the blood.
- The pancreas responds by making extra insulin to maintain a normal blood sugar.
- Over time, the body’s insulin resistance gets worse. In response the pancreas makes more and more insulin. Finally, the pancreas gets “exhausted“. It cannot keep up with the demand for more and more insulin. As a result, blood glucose levels start to rise.
- DM increases the risk of developing respiratory infections.
- There’s no cure for DM.
- Losing weight, eating well and exercising can help manage the disease.
- If diet and exercise aren’t enough to control blood sugar, diabetes medications or insulin therapy may be recommended.
What Is Tuberculosis?
- Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease that is a major cause of ill health and one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
- TB is caused by the bacillus Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is spread when people who are sick with TB expel bacteria into the air.
How Does DM Increase Risk of TB?
- DM not only increases the risk of TB, it also delays the sputum smear and culture conversion of an individual affected by both diseases.
- DM reduces the number of TB bacteria to below the threshold required to claim they have ‘healed’ will take longer than usual.
- DM impairs cell-mediated immunity; uncontrolled DM affects the cytokine response and alters the defences in the alveolar macrophages.
- The altered functions of small blood vessels in the lung (due to hyperglycaemia) along with poor nutritional status may facilitate the invasion and establishment of TB.
- As people with diabetes have already compromised immune function, the risk of TB infection is high. They will also have a higher bacterial load.
- The coexistence of TB and DM in patients may also modify TB symptoms, radiological findings, treatment, final outcomes, and prognosis.
- Individuals with TB and DM are more likely to have cavitary lesions in lower lung fields.
- In a study, a TB-DM group showed reduced lung functioning after TB treatment completion compared with the TB non-DM group. There was a greater improvement in radiographic scores among people with TB non-DM compared to DM.
- The average number of days taken for smear conversion (from ‘positive’ to ‘negative’) for people with TB and DM (64.5 days) was higher than that for people with TB only (61.5 days).
- DM also increases the likelihood of unfavourable TB treatment outcomes, such as treatment failure, relapse/reinfection, and even death.
- People with DM and TB suffer more severely and must fight harder to survive – illustrating the greater impact of the twin burden of DM and TB not just on patients but also on the healthcare system, their families, and their communities.
- In individuals affected by both diseases, the lungs are severely affected.
- Persistent inflammation has also been seen in people with DM and TB – even after they have completed their TB treatment.
- Experts have reported that TB-related respiratory complications have been a common cause of death among people with TB and DM, but which wasn’t the case with people with TB only.
Why Does DM Make TB Difficult to Cure?
- DM directly affects the outcomes of those affected by both diseases.
- A recent study reported that a higher fraction of unfavourable TB treatment outcomes occurred among people with low body-mass indices and with low glycated haemoglobin levels (better known as HbA1c) compared to people with low BMI and high HbA1c. This indicates that one’s nutritional status is important for favourable TB treatment outcomes.
- In effect, the study extended the evidence of association of undernutrition with TB.
- Another similar study in Pune found that DM is an independent risk factor for early mortality of people with both TB and DM.
- It also showed that the most common cause of deaths were respiratory complications (50%) followed by events related to cardiovascular
Agnipath Scheme
Context: Former Congress chief Rahul Gandhi will take part in a padayatra in Uttarakhand where the party will highlight how the future of the youth has been “jeopardised” by the Agnipath scheme.
About the Agnipath Scheme
- Definition: It is a scheme by the Department of Military Affairs, MoD under which rigorous military training will be imparted to the youth (male and female aspirants) aged between 17.5 to 21 years.
- Aim: The scheme aims at improving battle preparedness through transformative evolution with energetic, fitter, diverse, more trainable & resilient youth, suited to the changing dynamics. The scheme will empower, discipline & skill youth with a military ethos.
- The scheme is a pioneering step towards building a strong and prosperous ‘New India’.
- Features:
- Candidates inducted through this scheme will be called Agniveers.
- The selected candidates will be enrolled as “Agniveers” for a period of four years, on completion of which 25% of Agniveers shall be enrolled in the Armed Forces as a regular cadre.
- Benefits:
- Individuals enrolled under this Scheme will be paid an Agniveer package of Rs. 30,000/- per month with a fixed yearly increment.
- The candidates will be provided Risk & Hardship Allowance.
- Agniveers will be provided non-contributory Life Insurance Cover of Rs 48 lakhs for the duration of their engagement period in the Indian Armed Forces.
- A non-lapsable dedicated ‘Agniveer Corpus Fund’ will be created in the interest-bearing section of the Public Account head.
- Each Agniveer is to contribute 30% of his monthly income to ‘Agniveer Corpus Fund’.
- The Government will provide interest rate equivalent to the Public Provident Fund on the amount accumulated in the fund.
- On completion of the engagement period of four years, Agniveers will be eligible to receive ‘Seva Nidhi’ package, which shall comprise their contribution (into the Agniveer Corpus Fund) and matching contribution from the Government and interest on the accumulated amount. The ‘Seva Nidhi’ will be exempt from Income Tax.
- Arrangements are being made jointly by MoD & Ministry of Education to ensure proper education to the Agniveers.
- In collaboration with Ministry of Finance, arrangements are being made to provide loans at reasonable rates to Agniveers, who wish to start self-employment or any business after service.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Context: The Peruvian government has recently declared a state of national emergency due to a spike in the number of cases of a rare neurological disorder called Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
About Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Definition: Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a rare neurological disorder where the body’s immune system which normally protects it from infections and other foreign bodies mistakenly attacks its own peripheral nerve cells.
- More specifically, the myelin sheath — an insulating layer of fat and protein that surrounds the nerve cells — becomes inflamed.
- The myelin sheath enables signals to pass through the nerve tracts at breakneck speed under normal conditions. If the sheath is inflamed, the nerves can hardly transport stimuli.
- Thus, the peripheral nerves — the nerves that branch out from the brain and the spinal cord — get damaged as a result, and the muscles can become weak or paralyzed.
- Causes: The exact reasons for Guillain-Barré Syndrome are not yet understood.
- Our immune system is highly specialized to recognize foreign substances such as viruses, bacteria and fungi. It produces proteins called antibodies that bind to the surface structures of pathogens while building up an immune response against them.
- In an autoimmune disease like Guillain-Barré Syndrome, the invaders camouflage themselves with a surface that mimics the body’s own structures.
- So, the antibodies also target the body’s own cells and structures as foreign bodies and attach themselves to the surface. This results in a cascade of reactions. The exact nature of these interactions in autoimmune diseases are not yet known.
- However, Guillain-Barré Syndrome often develops shortly after a person gets an infectious disease.
- The syndrome also was linked to the cytomegalovirus, Epstein Barr virus, Zika virus and even the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Occasionally vaccinations can also cause GBS as vaccines tend to have similar weakened or inactive structures akin to the pathogens they protect against. The body’s immune system then triggers an immune response.
- Symptoms: The first symptoms include a tingling sensation in the body’s extremities, weakness in the legs that spreads to the upper body, difficulty in facial movements, unsteady walking or inability to walk, pain and, in severe cases, paralysis.
- Cure: Currently, there is no certain cure for Guillain-Barré Syndrome but there are also two treatments that can help recovery and reduce the severity of the disease:
- Plasma Exchange or Plasmapheresis: The plasma or the liquid part of the blood is removed and separated from the blood cells, inducing new plasma production to make up for the loss. This treatment is aimed at removing the antibodies which are attacking the peripheral nerves.
- Immunoglobin Therapy: In this therapy, the healthy antibodies from blood donors are injected intravenously. The damaged antibodies contributing to GBS are then blocked by the high doses of the immunoglobulins. Apart from this, physical therapy might also be useful in alleviating pain.



 Light Water Reactors (LWRs): India’s S...
Light Water Reactors (LWRs): India’s S...
 Graviton: The Quest to Detect the Quantu...
Graviton: The Quest to Detect the Quantu...
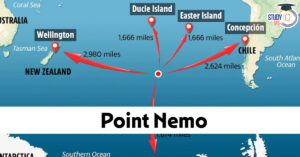 Point Nemo: The Most Remote Place on Ear...
Point Nemo: The Most Remote Place on Ear...

























