Table of Contents
Preventive Detention
Context: The Supreme Court in a recent judgement reiterated that in cases of preventive detention, the detaining authority must furnish to the detenu copies of all documents which are relied upon by it. Failure to do so would vitiate the detention.
What is Preventive Detention ?
- When a person is detained/taken into custody without any trial & conviction by a court.
- It is only a precautionary measure and is based on suspicion.
- Purpose:
- Not to punish a person for a past offence but to prevent him from committing an offence in the near future.
- To protect state security & maintain Public Order.
Rights available to a Detainee under Article-22
- Period of detention: No Preventive detention law shall authorise detention for more than 3 months.
- To detain an individual beyond the period of three months authorisation is needed by an Advisory Board.
- Advisory Board Consists of a judge of a high court, among other members.
- Rights of detenu:
- The grounds of detention should be communicated to the detenu.
- Exception: Facts considered to be against the public interest need not be disclosed.
- He should be afforded an opportunity to make representation against the detention order.
- The grounds of detention should be communicated to the detenu.
| Who has the power to make laws related to Preventive Detention? |
|
| Did You Know |
|
Shabd Glossary Platform
Context: Recently the Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT) has launched a website named Shabd which offers technical terms in all 22 official Indian languages for various educational subjects.
About Shabd Glossary Platform
- It is a data server that provides a central repository for technical terms in Indian languages
- Features:
- The platform hosts glossaries from the Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology and other institutions and agencies.
- Users can search for terms by language, subject, dictionary type, or language pairs.
- Users can also provide feedback on existing equivalents prepared by the CSTT.
- It currently hosts 450 dictionaries comprising 3 million words.
Commission for Scientific and Technical Terminology (CSTT)
- Established: 1960 (HQ – New Delhi)
- It was established under clause (4) of Article 344 of the Constitution of India.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Education (Department of Higher Education)
- Objective: To evolve and define scientific and technical terms in Hindi and all Indian languages.
- Functions:
- Preparation and Publication of Bilingual and Trilingual Glossaries involving English/Hindi and other Indian Languages.
- Prepares university-level textbooks, monographs and journals.
- Identifies and publishes pan-Indian terms.
- Organises workshops, seminars, conferences, orientation, and training programs to popularise the standard terminology of Hindi and other Indian languages.
Hydrogen Trains
Context: The Indian Railways plans to conduct field trials of the country’s first hydrogen fuelled train by January 2025. The first prototype of the train is expected by December this year.
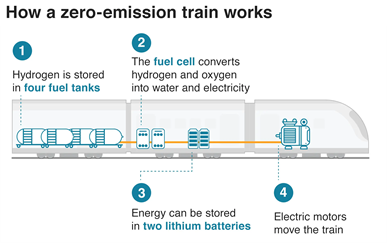
What are Hydrogen Trains ?
- Hydrogen trains use fuel cells to combine hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity, which powers the train’s motors.
- Environment Friendly: As they don’t release harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter released by Diesel Engines.
- Indian Railway has set a target of becoming Net Zero Carbon Emitter by 2030.
| Hydrogen for Heritage Project |
| Under this project Indian Railways plan to run 35 hydrogen trains by retrofitting existing diesel electric multiple units (DEMUs) with hydrogen fuel cells. |
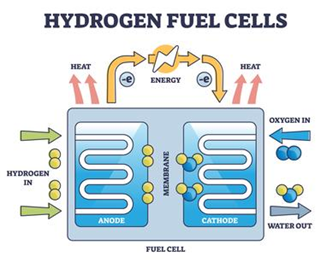
How a Hydrogen Fuel Cell Works ?
- A hydrogen fuel cell works by converting hydrogen’s chemical energy into electricity through an electrochemical reaction with oxygen.
- Procedure:
- Hydrogen and oxygen input: Hydrogen is fed into the anode, and oxygen is fed into the cathode.
- Hydrogen separation: At the anode, a catalyst splits hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons. This process is called oxidation.
- Proton and electron separation: The positively charged protons pass through the membrane to the cathode, while the negatively charged electrons take a different route.
- Electron circuit: The electrons pass through an external circuit to generate electricity.
- Proton and electron recombination: The electrons and protons meet at the cathode, where they combine with oxygen to create water and heat as byproducts.


 Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, Constitutio...
Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha, Constitutio...
 Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS): Com...
Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS): Com...
 Foundation Day of Indian States and UTs,...
Foundation Day of Indian States and UTs,...





















