Table of Contents
Citizenship (Amendment) Act
Context: The Union Home Ministry notified the Citizenship Amendment Rules, 2024 that would enable the implementation of the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) passed by Parliament in 2019.
Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) Overview
Background
- Legislative Passage: The Citizenship (Amendment) Bill 2019 was approved by India’s Parliament in December 2019, with the Lok Sabha passing it on December 9 and the Rajya Sabha on December 11.
- Amendment to Citizenship Act, 1955: The Bill amends the Citizenship Act, of 1955, to grant eligibility for Indian citizenship to illegal migrants of specified religious communities from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan.
- Pre-Amendment Criteria: Prior to the amendment, Indian citizenship could be obtained through birth in India, descent, registration, naturalisation (prolonged residence), or incorporation of territory.
- The new law introduces religion as a sixth criterion for acquiring citizenship, explicitly excluding Muslims.
What are the Provisions?
- Eligibility for Certain Refugees: The CAA enables refugees from Hindu, Sikh, Jain, Buddhist, Christian, and Parsi communities, arriving from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Pakistan before December 31, 2014, to acquire Indian citizenship even without holding valid passports from these countries or an Indian visa.
- Eligibility for Specified Illegal Migrants: The law specifies that illegal migrants from the mentioned countries and communities, who entered India before December 31, 2014, will be eligible for citizenship and will be recognized as Indian citizens from the date of their entry.
- It also concludes all legal proceedings related to their status as illegal migrants.
- Residency Requirement Relaxation: The residency requirement for eligibility has been relaxed from 11 years to 5 years for these migrants.
- Exclusion of Certain Areas: The amendments do not apply to tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, and Tripura under the Sixth Schedule, as well as states under the “Inner Line” permit like Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Nagaland.
- OCI Registration Amendments: The law has revised provisions concerning OCI cardholders, allowing foreigners of Indian origin or those married to persons of Indian origin to register as OCI for various benefits in India.
- OCI Cancellation Provision: It introduces the provision for cancelling OCI registration if the individual has violated any Indian law as notified by the central government.
Legal Challenge to the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA)
Core Legal Arguments
- Violation of Article 14: The main argument against the CAA is that it violates Article 14 of the Constitution, which guarantees equality before the law, by using religion as a basis for citizenship eligibility.
- Discrimination Against Muslims: Coupled with the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam, discriminates against Muslims by excluding them from the list of “persecuted minorities” eligible for citizenship.
- Legal Scrutiny: The Supreme Court’s assessment will focus on whether the act’s classification is reasonable under Article 14 and if excluding Muslims constitutes discrimination.
- Exclusion of Other Persecuted Groups: Questions have been raised about the exclusion of persecuted groups from non-listed countries, such as Tamil Hindus from Sri Lanka or Rohingya Muslims from Myanmar, and whether the selection of countries was aimed at excluding Muslims.
The CAA and Assam
- The challenge also touches upon Section 6A of the Citizenship Act, 1955, related to the Assam Accord, which is separately under scrutiny by the Supreme Court.
- The Accord, signed in 1985, defines the criteria for determining foreigners in Assam, with a cut-off date of March 24, 1971, for regularisation of certain migrants. The CAA’s provisions create a conflicting timeline with this Accord.
Broader Constitutional and Social Implications
- Secularism at Stake: Beyond the legal technicalities, the challenge raises questions about secularism as a foundational principle of the Indian Constitution, and whether the CAA undermines this by introducing religion as a criterion for citizenship.
Supreme Court Stance
- Court Proceedings: In October 2022, a Supreme Court bench indicated that final hearings would start in December 2022, but the case has not proceeded since then.
- Currently, the case is listed before a bench headed by Justice Pankaj Mithal.
Understanding AI
Context:
- Nvidia has become a leader in producing GPUs essential for building large AI models, with its valuation rapidly reaching $2 trillion, highlighting its significant impact on the AI hardware market.
- Resistance arises from efforts to develop alternative hardware, create smaller ANNs that require fewer resources, and develop new software to reduce dependency on Nvidia’s GPUs.
| Note |
| GPUs, initially designed for video gaming graphics, are crucial for running ANNs due to their ability to perform parallel computing tasks. |
Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI signifies machine-based intelligence, characterised by a machine-software combination without a universally agreed-upon definition. It focuses on applying knowledge to solve problems.
- Example of AI Thinking: Linear Classification
- A basic AI problem involves classifying points on a graph into two groups by drawing a straight line, demonstrating a simple task of differentiation, such as separating images of cats and dogs.
Advanced AI Problem Solving
- Differentiating Between Categories: AI can differentiate between categories like cats and dogs by analysing images for various features (e.g., face shape, paw size) using computational tools and plotting these features on graphs for classification.
- Complex Decision Making: More complex AI applications involve multiple parameters and contextual decision-making, such as determining when a driverless car should brake based on various factors including urgency and potential obstacles.
- Generative AI: Unlike classification models, generative AI like ChatGPT predicts the next word in a sentence, learning from a vast corpus of text without direct classification, involving over 100 billion parameters.
Learning Mechanisms in AI
- Supervised Learning: Involves labelled data where the machine learns from provided examples with defined categories.
- Unsupervised Learning: The machine organises and understands data without labels, identifying patterns or structures on its own.
- Reinforcement Learning: The machine learns through trial and error, using feedback scores to adjust its actions and improve performance.
The Structure of AI: Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
- Structure:
- Network is built with layers of interconnected nodes (artificial neurons).
- Three main types of layers: input, hidden (one or more), and output.
- Each node has a “weight” and a “threshold” associated with it.
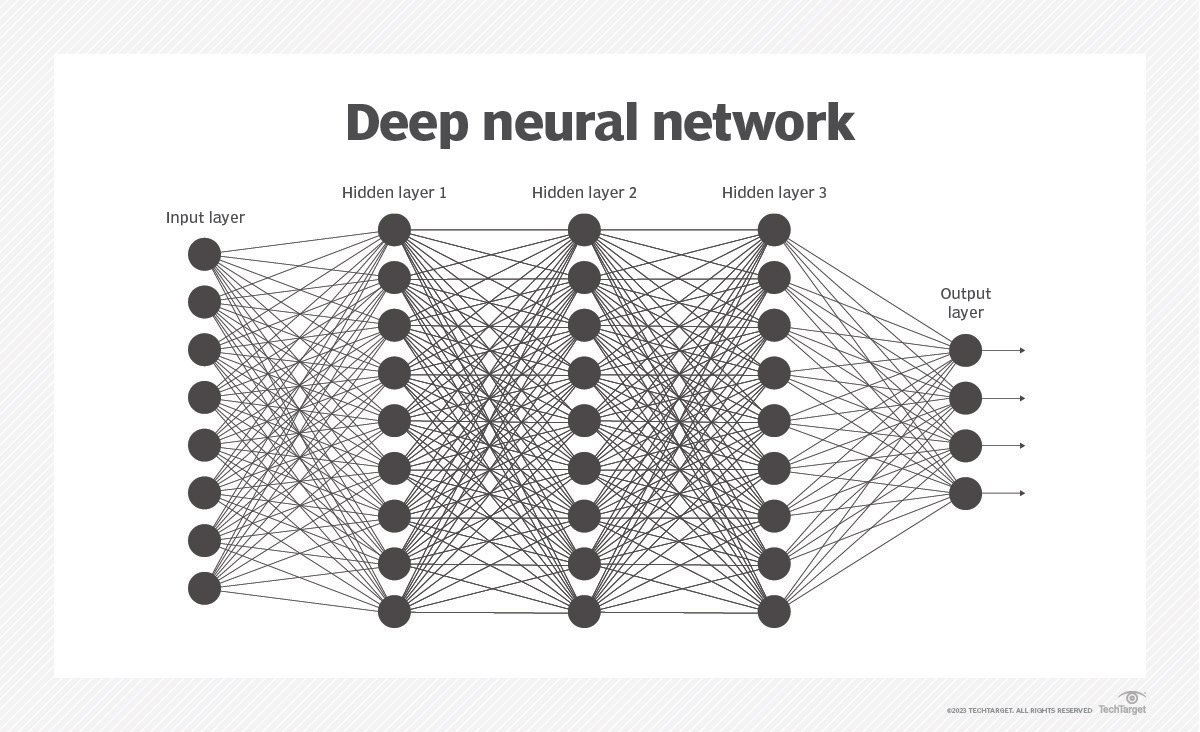
- Function:
- Input data activates nodes based on weight and threshold.
- Activated nodes send data to the next layer.
- Training data helps the network learn and improve accuracy.
- Activation Functions and Weights: Activation functions compute outputs based on inputs from connected nodes, while weights determine the significance of these inputs in the final decision-making process.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
James Webb Telescope
Context: The James Webb Space Telescope discovered the universe’s earliest-known ‘dead’ galaxy, ceasing star formation 700 million years post-Big Bang, challenging our understanding of early cosmic history and galaxy evolution.
About the Telescope
- About: It is an orbiting infrared observatory that will complement and extend the discoveries of the Hubble Space Telescope, with longer wavelength coverage and greatly improved sensitivity.
- Development: Began in 1996 was developed by NASA, with contributions from the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
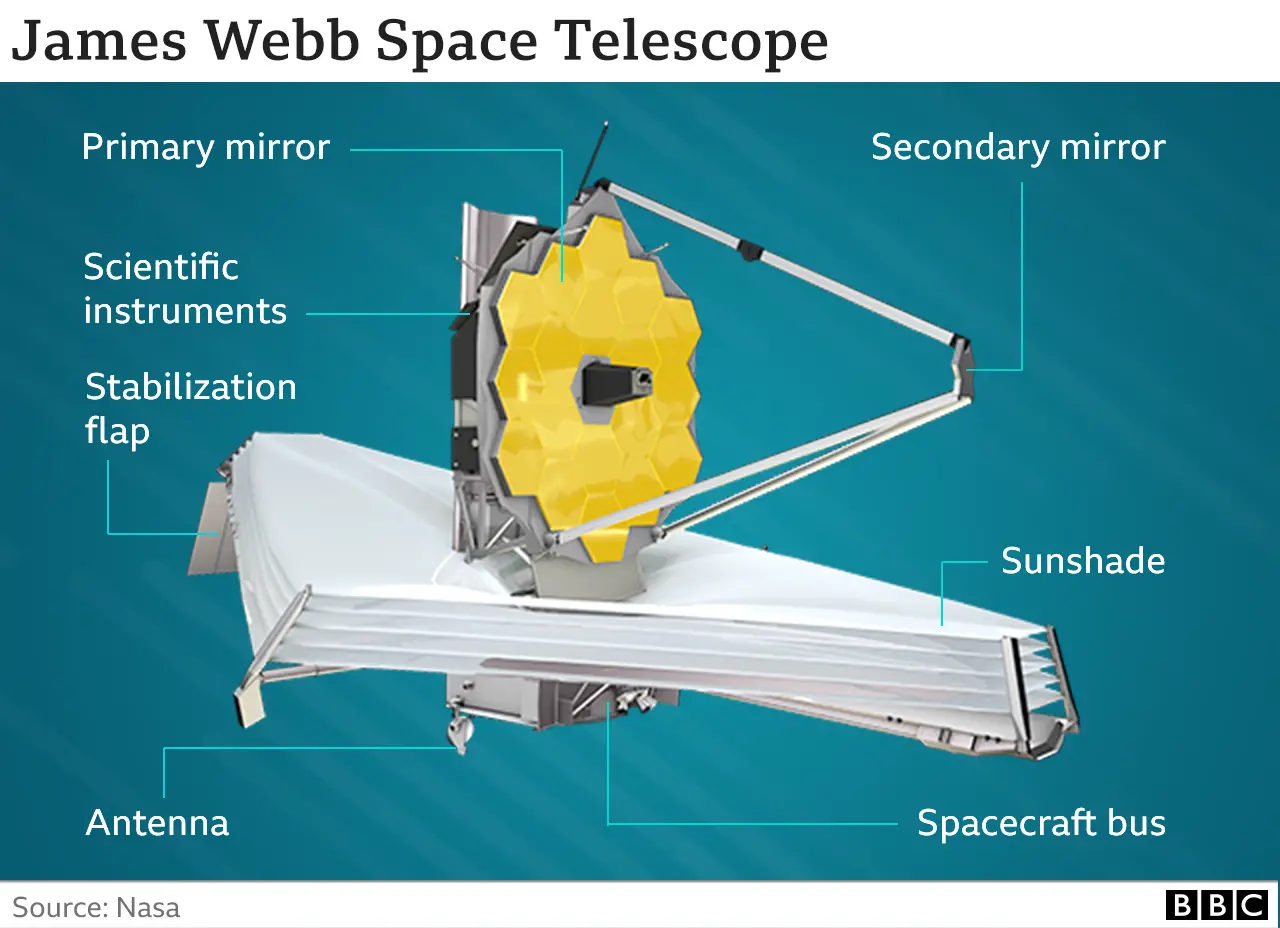
- Launch: Launched in 2021, it has an anticipated mission duration of between 5 to 10 years.
- Location: Positioned at the second Lagrange point (L2), roughly 1.5 million kilometres from Earth, in a direct line away from the Sun.
- Telescope Size: Features a primary mirror that is 6.5 metres in diameter, offering a significantly larger light-collecting area compared to existing space telescopes.
- Wavelength Coverage: Operates across wavelengths from 0.6 to 28 microns, encompassing a broad range of the infrared spectrum.
Mission Objectives
- Exploring Cosmic Dawn: Aims to identify the universe’s earliest galaxies and luminous objects that emerged following the Big Bang.
- Galactic Evolution: Seeks to understand the development of galaxies from their inception to the present day.
- Star Formation: Observes the initial stages of star formation through to the creation of planetary
- Planetary System Analysis: Measures the physical and chemical attributes of various planetary systems, including our Solar System, to assess their potential for supporting life.
| Hubble Space Telescope |
|
Oscars
Context: The 96th Academy Awards took place at the Dolby Theatre in Los Angeles.
About Oscars
- Type: Biggest and most prestigious entertainment awards in the world.
- Aim: To honour the art and artists of the world of cinema from all across the globe.
- Established in: 1929
- Organiser: Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS).
Indian Oscar Award Winner’s Name
| Indian Recipient | Category | Year |
| Bhanu Athaiya | Best Costume Design | 1983 |
| Satyajit Ray | Honorary Award | 1992 |
| Resul Pookutty | Best Sound Mixing | 2009 |
| Gulzar | Best Original Song | 2009 |
| A R Rahman | Best Original Score | 2009 |
| Best Original Song | 2009 | |
| Kartiki Gonsalves | Best Documentary Short | 2023 |
| MM Keeravani and Chandrabose | Best Original Song | 2023 |
Examples, Case Studies and Data Points For Value Edition
- The Democracy Report 2024 by the V-Dem Institute (GS 2): Key findings related to India from the report are:
- India continues to be classified as an electoral autocracy.
- India’s scores for various components of democracy have been falling.
- India was listed among the top 10 standalone autocratizers in 2023.
- The report also highlighted concerns about restrictions on free expression, peaceful assembly, and other rights in India.


 Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO...
Serious Fraud Investigation Office (SFIO...
 Article 142 of Indian Constitution, Sign...
Article 142 of Indian Constitution, Sign...
 Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK): History...
Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir (PoK): History...





















