Table of Contents
New Alzheimer’s Drug
Context: Donanemab developed by Eli Lilly represents a potentially significant advancement in Alzheimer’s treatment.
About Donanemab
- Donanemab is a monoclonal antibody therapy developed by Eli Lilly that targets amyloid beta protein depositions in the brain, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.
- How does it work? Donanemab works by clearing amyloid beta plaques in the brain, slowing cognitive decline in early Alzheimer’s patients.
- How effective is it? Donanemab is designed for patients in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease, such as those with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia.
- It significantly slows the progression of the disease, allowing patients to retain their functions longer.
- The phase 3 study of 1,736 participants, where 860 received donanemab every four weeks until amyloid plaques were cleared, showed a 1% slowdown in cognitive decline at 76 weeks.
- What are the risks? The main adverse effects reported were swelling or bleeding in the brain; 24% of participants experienced brain swelling and 19.7% had brain bleeds.
- There were three treatment-related deaths during the study.
- Most amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) events were non-serious and resolved after discontinuation of therapy.
- Why is this breakthrough important? With an estimated 5.3 million people currently living with dementia in India and a projected increase to 14 million by 2050, an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s is crucial.
- How does it compare to other Alzheimer’s drugs? Donanemab differs from the two previously approved therapies (aducanumab and lecanemab) because of limited dosing protocol.
- Treatment with donanemab is discontinued once a predetermined level of amyloid plaque clearance is achieved.
- This approach is based on the hypothesis that continued treatment beyond the point of significant plaque reduction might not provide additional benefits and could increase risks.
- This dosing strategy is distinct from other drugs that may require ongoing treatment without a specific endpoint based on plaque levels.
- Why was approval delayed? The FDA requested further data on the therapy’s limited dosing protocol and potential implications.
- Additionally, there was increased scrutiny following concerns about the approval process for the first Alzheimer’s drug, aducanumab.
- Aducanumab faced scrutiny and controversy over its approval due to mixed clinical trial results and concerns about its efficacy.
- Lecanemab, similar to donanemab, has been met with cautious optimism but still presents challenges concerning side effects and the degree of clinical benefit.
- Additionally, there was increased scrutiny following concerns about the approval process for the first Alzheimer’s drug, aducanumab.
Heavy Metal Contaminants
Context: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have created a new remediation technique to eliminate heavy metal pollutants like arsenic from groundwater.
More In News
- According to the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), their three-step, patent-pending method not only removes heavy metals but also disposes of them in an environmentally friendly and sustainable way.
- This approach prevents the usual practice of depositing untreated, heavy metal-laden sludge in landfills, which could lead to recontamination of groundwater.
About Heavy Metals
- Heavy metals are metallic elements with a high density relative to water.
- Sources and Release: These metals are naturally found in the Earth’s crust and are released into the environment through industrial processes, mining, and the burning of fossil fuels.
- Indestructibility: Heavy metals cannot be broken down through biological degradation.
- Essential vs. Toxic: Depending on the type and concentration, heavy metals can be either essential or toxic to living organisms.
- Essential Heavy Metals: Certain heavy metals like copper, zinc, and iron are vital as micronutrients for various biochemical and physiological functions, such as oxygen transport in haemoglobin (iron) and enzymatic reactions (zinc).
- Toxic Heavy Metals: Other heavy metals, including lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic, and chromium, are toxic even at low concentrations and can cause health issues like:
- Cancer
- Neurological damage
- Kidney and liver damage
- Reproductive and developmental problems
- Sources of Heavy Metals:
- Natural sources include weathering of rocks and soils, volcanic eruptions, and forest fires.
- Human activities include mining, industrial wastewater, agricultural runoff, and urban stormwater runoff.
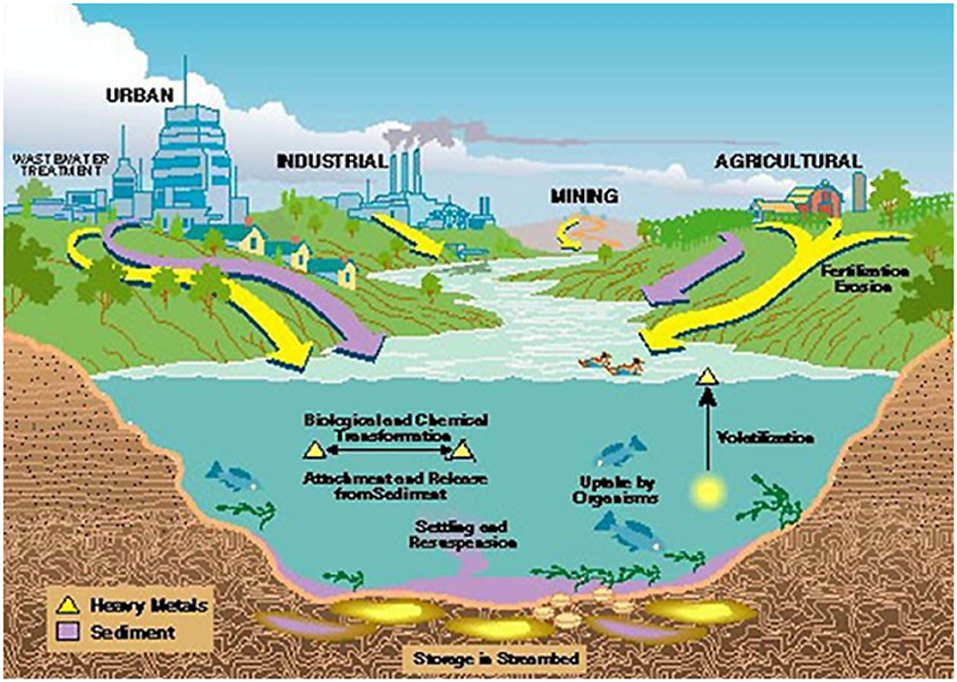
- Entry of Heavy Metals into the Human Body:
- Through drinking contaminated water.
- Consuming contaminated fish.
- Inhalation of volatilized heavy metals from wetlands.
- Skin contact with contaminated water.
Consequences Of Heavy Metal Contamination
- Bioaccumulation: Defined as the net accumulation of pollutants in an organism from all sources including water, air, and food.
- Biomagnification: The process where a chemical accumulates in an organism due to exposure from water and food, leading to concentrations higher than expected from equilibrium.
- Impact on Biological Functions: Some heavy metals affect biological activities and growth, while others may accumulate in specific organs.
- Health Risks: Accumulation of heavy metals can cause severe diseases, including various cancers, skin diseases, and nervous system disorders.
- Free Radical Production: Metal toxicity can lead to the production of free radicals, which can damage DNA.
- Environmental Persistence: Heavy metals are not easily degradable in nature and tend to accumulate in the bodies of animals and humans to toxic levels.
- Developmental and Health Effects: Exposure to heavy metals has been linked to developmental retardation, kidney damage, various types of cancers, and in extreme cases, death.
| About Arsenic Contamination |
Health Impacts of Chronic Arsenic Poisoning:
|
Examples, Data and Case Studies
- Success of Montreal Protocol (GS 3): Scientists (using the data from Advanced Global Atmospheric Gases Experiment and US National Atmospheric and Oceanic Administration) have declared the international efforts to protect the ozone layer a “huge global success,” with damaging gases declining faster than expected.
- The Montreal Protocol is an international agreement made in 1987 to stop the production and import of ozone depleting substances such as chlorofluorocarbons and reduce their concentration in the atmosphere to help protect the earth’s ozone layer.


 Pariksha pe Charcha 2025, Overview, Even...
Pariksha pe Charcha 2025, Overview, Even...
 National Policy on Framework on Agricult...
National Policy on Framework on Agricult...
 How Scientists used Scotch tape to Creat...
How Scientists used Scotch tape to Creat...




















