Table of Contents
Heat Dome
Context
- The entire western United States is currently experiencing an intense heatwave.
- The scorching temperatures and dry conditions are a result of a heat dome centred over California.
About Heat Dome
- Definition: A heat dome is a weather phenomenon where a high-pressure system traps warm air like a lid on a pot, causing extended periods of high temperatures.
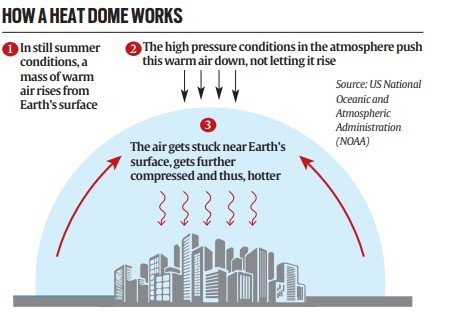
- Mechanism:
- Trapped warm air prevents cloud formation and allows more sunlight to reach the earth, leading to increased warming and drying of the soil.
- Reduced evaporation decreases the likelihood of rain cloud formation.
- The longer the heat dome stays in place, the hotter it gets.
Role of the Jet Stream
- Jet Stream Behaviour:
- The jet stream, an area of fast-moving air high in the atmosphere, typically moves weather systems along the earth’s surface in a wave-like pattern.
- When these waves become larger and more elongated, they slow down or become stationary.
- A stationary jet stream can trap a high-pressure system in place, leading to the formation of a heat dome.
Impact of Climate Change
- There is ongoing debate about how climate change impacts the blocking weather events that cause heat domes.
- Established Facts:
- Rising global temperatures are making heat domes larger and more intense.
- A 2021 study by the World Weather Attribution team found that the searing temperatures during the heat dome in Canada in June 2021 “would have been virtually impossible without the influence of human-caused climate change.”
- A 2023 study in the journal Nature indicated that the intensity of heat domes is increasing faster than the rate of global warming.
EV Policy
Context: The government is expanding the scope of its electric vehicle (EV) policy to include retrospective effects.
About The EV Policy
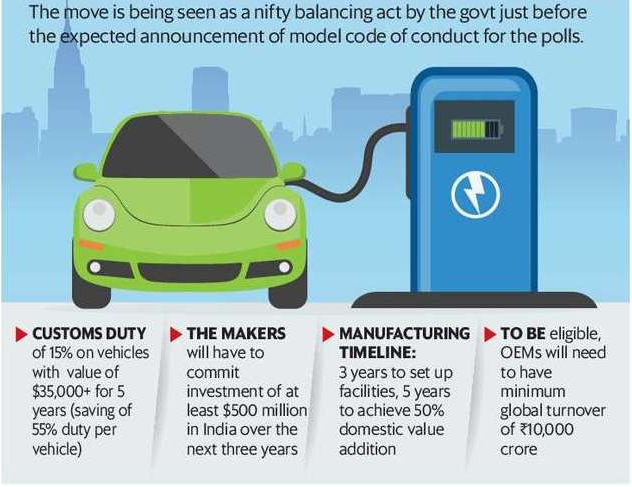
- Import Duty Reduction: The Indian government has slashed the import duties for electric vehicles (EVs) that are imported as completely built units (CBUs) to 15%, down from the existing range of 70% to 100%.
- Objective: To expand the electric vehicle market in India by attracting new players and introducing advanced EV technology to the country.
- It is not intended to undercut the existing market but to complement and enhance it by fostering technological growth and broadening consumer choice.
- Manufacturing Incentive: This reduction in import duties is contingent upon the EV manufacturer committing to set up a local manufacturing unit in India within 3 years of availing the duty reduction.
- Investment and Production: Automakers are required to invest a minimum of ₹4,150 crore (or around $500 million), begin manufacturing locally within 3 years, and achieve at least 25% domestic value addition within that time frame.
- Technology Access and Competition: Providing Indian consumers with access to the latest technology and fostering healthy competition among EV players to achieve higher production volumes, economies of scale, and lower production costs.
- Domestic Value Addition: Mandating that half of the value addition in overall manufacturing be done domestically within five years.
- Limitation: The concessional duty rate applies only to EVs that are priced at $35,000 or more, which includes cost, insurance, and freight charges.
- There is a limitation on the number of vehicles that can be imported at the reduced duty, capped at 8,000 vehicles per year.
- Policy Duration: The duty relief is valid for five years.
Examples, Case Studies and Data
Internal Security (GS 3): The Maharashtra government introduced the Maharashtra Special Public Security Bill, 2024, addressing the rising threat of Naxalism in urban areas.



 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















