Table of Contents
Pompe Disease
Context: Recently, India’s first Pompe disease patient passed away after battling the disease.
About Pompe Disease
- Pompe disease, also known as Glycogen Storage Disease Type II, is a rare, inherited disorder caused by a deficiency in the enzyme acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA).
- GAA enzyme is responsible for breaking down glycogen, a storage form of glucose, within the lysosomes of cells.
- When GAA is deficient, glycogen accumulates in various tissues, particularly muscles, leading to progressive weakness and other complications.
- Prevalence and Diversity: Pompe disease affects individuals of diverse ethnicities and populations, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 40,000 to 1 in 300,000 births.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Impact on Individuals
- Muscle Weakness: Progressive weakness, affecting both skeletal (movement) and smooth muscles (organ function).
- This can significantly impact mobility, daily activities, and respiratory function.
- Motor Skill Delay: Delays in achieving motor milestones like sitting, crawling, and walking.
- The degree of delay can vary, with some individuals never achieving certain milestones.
- Degenerative Bone Impact: Prolonged weakness and reduced mobility can lead to joint contractures and skeletal deformities, impacting bone health and movement further.
- Respiratory Complications: Weakening of respiratory muscles, including the diaphragm, can cause shortness of breath, respiratory infections, and even respiratory failure in severe cases.
- Cardiac Involvement: Pompe disease can affect the heart muscle, leading to complications like heart palpitations, fatigue, chest pain, and even hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (a thickening of the heart muscle walls) in some cases.
- Implications for Daily Living: Patients with Pompe disease may face challenges in performing daily activities due to muscle weakness and respiratory limitations.
- Assistive devices such as wheelchairs and respiratory support equipment may be necessary.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Pompe disease involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Enzyme Assays: These tests measure the activity of GAA enzymes in blood or skin cells, providing insights into the extent of the deficiency.
- Genetic Testing: This analysis identifies mutations in the GAA gene responsible for Pompe disease, confirming the diagnosis.
- Clinical Evaluation: A thorough assessment of patient symptoms and medical history aids in understanding the disease’s impact and guiding treatment decisions.
Treatment
- While there is no cure for Pompe disease, Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) offers a significant treatment option.
- ERT involves the regular administration of the missing GAA enzyme to help break down accumulated glycogen and alleviate symptoms.
- This therapy can improve muscle strength, respiratory function, and overall quality of life for patients with Pompe disease.
Lakadong Turmeric
Context: Recently, Meghalaya’s Lakadong turmeric has been awarded the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
About Lakadong Turmeric
| Property | Description |
| Quality | Considered one of the world’s best varieties |
| Curcumin Content | 6.8% to 7.5% |
| Colour | Darker than other turmeric varieties |
| Cultivation | Grown organically without fertilizers |
| Location | Lakadong area of Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya |
| Significance |
|
Curcumin
| Property | Description |
| Type | Polyphenol |
| Benefits | Inflammatory conditions, metabolic syndrome, pain, eye conditions, kidney health |
| Mechanism | Antioxidants and anti-inflammatory effects |
Geographical Indication (GI) Tag
| Property | Description |
| Purpose | Protects products with specific geographical origin and unique qualities |
| Applications | Agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine, spirits, handicrafts, industrial products |
| Legislation | Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 |
| Validity | 10 years (renewable) |
| Other products that received GI Tag from Meghalaya |
|
GNoME: New Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tool
Context: Researchers at Google DeepMind have made a significant breakthrough by using artificial intelligence (AI) to predict the structures of over 2 million new materials
About Graph Networks for Materials Exploration (GNoME)
- The AI model, called GNoMe (Graphical networks for material exploration), was trained on a massive dataset of existing materials and their properties.
- GNoME can then use this information to generate new material structures with specific desired properties.
- Discovery: GNoME is said to have discovered over 2.2 million new materials including 380,000 materials that it predicts to be stable.
- This breakthrough could have wide-reaching application in sectors such as renewable energy, battery research, semiconductor design and computing efficiency.
Working Of GNoME
- Leveraging Graph Representation: GNoME uses a graph neural network (GNN) representation to mimic the atomic connections within materials.
- This allows the model to identify patterns and relationships between atoms, leading to accurate predictions of new material structures.
- Active Learning for Enhanced Discovery: GNoME employs active learning, a technique that continuously improves the model’s performance by focusing on the most promising candidates for further analysis.
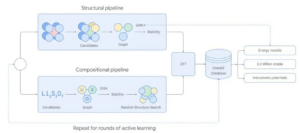
- Two Pipelines for Diverse Exploration: GNoME utilises two pipelines:
- Structural Pipeline: Creates candidates similar to known crystals, ensuring stability and building upon existing knowledge.
- Compositional Pipeline: Explores a wider range of possibilities through a randomised approach based on chemical formulas, potentially uncovering novel and unexpected materials.
- Density Functional Theory: GNoME generates predictions for new materials, which are then analysed using Density Functional Theory to determine their stability. This method helps evaluate the potential of the predicted materials.
Significance
- Significant Accuracy Improvement: GNoME has achieved a remarkable 80% precision rate in predicting material stability, a significant leap from the previous 50%. This translates to nearly 800 years of knowledge based on publicly available data, demonstrating the model’s exceptional capabilities.
- Building upon Existing Research: GNoME was trained on crystal structure data from The Materials Project, contributing to the ongoing collaborative effort in the scientific community to discover innovative materials across various domains.
- Reduced costs: The ability to eliminate unstable materials early saves researchers valuable resources, leading to more efficient use of time and funding.
Reaching the Last Mile Forum
Context: The 2023 Reaching the Last Mile Forum at COP28 secured a staggering $777 million in pledges to tackle the growing threat of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs).
About 2023 Reaching the Last Mile Forum?
- Hosted by: Reaching the Last Mile (under UAE President His Highness Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan patronage) and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Held on: The sidelines of COP28 first ever ‘Health Day‘
- Purpose: Assess climate change’s impact on human health and address neglected tropical diseases (NTDs).
- Key announcement: Expansion of Reaching the Last Mile Fund (RLMF) from $100 million to $500 million.
- Focus: Eliminating lymphatic filariasis and onchocerciasis (river blindness) in sub-Saharan Africa (10-year, multi-donor fund).
| What Are Neglected Tropical Diseases? |
Global Initiatives To Eliminate NTDsWorld Health Organization (WHO) – Global Programme to Eliminate Lymphatic Filariasis (GPELF)
Global Onchocerciasis Control Programme (GOCP)
Reaching the Last Mile Fund (RLMF)
NTD Roadmap 2030
|
Global Carbon Budget Report
Context: The Global Carbon Budget has highlighted that in 2023, worldwide carbon emissions stemming from fossil fuels have surged to unprecedented levels, surpassing the figures recorded in the previous year.
Key Findings Of The Report
- Global Emissions:
- Total fossil CO2 emissions projected to reach 36.8 billion tonnes, up 1.1% from 2022.
- Total CO2 emissions, including land-use changes, expected to hit 40.9 billion tonnes.
- Regional Trends:
- Europe and USA see decreased emissions.
- India (8.2%) and China (4.0%) show notable increases.
- Emissions Sources and CO2 Levels:
- Fossil fuels:
- Coal emissions +1.1%.
- Oil emissions +1.5%.
- Gas emissions +0.5%.
- Land-use change includes deforestation and efforts in reforestation and afforestation.
- Atmospheric CO2 levels projected to average 419.3 parts per million, a 51% rise from pre-industrial levels.
- About half of CO2 absorbed by land and ocean “sinks.”
- Fossil fuels:
- Fires and CO2 Removal Technologies:
- CO2 emissions from fires increased due to extreme wildfire seasons, notably in Canada.
- CO2 removal technologies currently at 0.01 million tonnes CO2, significantly lower than fossil CO2 emissions.
- Paris Agreement Targets and Urgency:
- 5°C warming limit likely exceeded within seven years at the current emission rate.
- Rapid cuts in fossil fuel emissions required to achieve the 2°C warming limit.
- India’s Context:
- UN report commends India for maintaining comparatively low carbon emissions.
- India’s global warming contribution is 5% with 18% of the world population.
- India’s climate pledges:
- Net-zero emissions target by 2070.
- Achieving 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity by 2030 under the Panchamrit Action Plan.
- Fulfilling at least half of its energy requirements through renewable energy by 2030.
Bhungloti
Context: The Tai-Khamyang Buddhist community in Assam expanded their Chala Village Sanctuary(a community-led village sanctuary) by 30 hectares to conserve biodiversity and support local traditions.
About Bhungloti
- Bhungloti is a creeper that in combination with the pith of the roots of a jackfruit tree yields a saffron dye.
- This is used for making the robes which were donated to monks every year on the Buddhist occasion of the Kathina ceremony.
RBI New Updates On Digital Lending
Context: RBI raises the UPI payment limit for healthcare and education from ₹1 lakh to ₹5 lakh.
What Is Digital Lending?
- Digital lending refers to the process of providing loans through online platforms or mobile applications. It leverages technology and automation to streamline the lending process, making it faster, more accessible, and cost-effective for both borrowers and lenders.
- Benefits:
- Streamlined Application: Easier, faster, more open loan process.
- Digitizing Information: Increased transparency, reduced bottlenecks.
- Data Analysis: Accurate decisions, fewer errors, no manual work.
- Loan Options for All: Credit score less important.
- Increased Efficiency: Lower costs, more revenue, faster growth.
| What is Lending Service Providers (LSPs)? |
| Lending Service Providers (LSPs) act as intermediaries, deploying their technology platforms to connect borrowers with lenders. Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) serve as financial institutions, disbursing loans based on the LSP’s assessment. |


 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
 New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
New Phase of Operation Chakra to Combat ...
 Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...
Soyuz Aircraft: History, Design and Sign...





















