Current Affairs 11th September 2023 for UPSC Prelims Exam
The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI)
Context: The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) has directed the drugs controllers of the States and Union Territories to keep a strict vigil on the sale and distribution of falsified versions of the liver medication Defitelio and cancer drug, Adcetris (injection).
About The Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI)
- Drug Controller General of India heads the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) department.
- DCGI is responsible for approval of licenses of specified categories of Drugs such as blood and blood products, I. V. Fluids, Vaccine and Sera.
- The Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- CDSCO functions under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare.
- CDSCO aims to safeguard and enhance the public health by assuring the safety, efficacy and quality of drugs, cosmetics and medical devices.
- CDSCO is responsible for:
- approval of New Drugs,
- clinical Trials in the country,
- laying down the standards for Drugs,
- control over the quality of imported Drugs,
- coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organisations and
- providing expert advice with a view of bring about the uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
- CDSCO Head quarter is located in Delhi.
Current Affairs 9th September 2023 for UPSC Prelims Exam
Monkey Pox
Context: Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the monkeypox a global health emergency.
About Monkey Pox
- Definition: Monkeypox, or Mpox, is a viral disease caused by the monkeypox virus.
- Monkeypox virus is an enveloped double-stranded DNA virus of the Orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family, which includes variola, cowpox, vaccinia and other viruses.
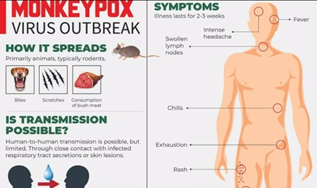
- Symptoms: Common symptoms of mpox are:
- rash
- fever
- sore throat
- headache
- muscle aches
- back pain
- low energy
- swollen lymph nodes.
- Spread: Anyone can get mpox. It spreads from contact with infected:
- persons, through touch, kissing, or sex
- animals, when hunting, skinning, or cooking them
- materials, such as contaminated sheets, clothes or needles
- pregnant persons, who may pass the virus on to their unborn baby.
- Treatment: Getting an mpox vaccine can help prevent infection. Several antivirals, such as tecovirimat, originally developed to treat smallpox have also been used to treat mpox.
- Global Concern:
- In the European region, new cases have been reported from Spain and the U.K.
- The African region has also experienced a surge in cases in Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Nigeria.
- China, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Taiwan, Pakistan and Japan have also reported cases of mpox.
- Incidentally, several cases have a travel history to the Middle East, however, reports from Middle East do not indicate an increase in the number of cases.
- Genomic surveillance of the monkeypox pathogen allows for contact tracing and monitoring of its evolution. There is a noticeable lack of genomic data from developing countries, particularly in Asia.
- Amidst increased globalisation and travel, the need for global public health efforts, cooperation, and resource sharing is needed.
Belt and Road Initiative
Context: Italy has been planning to step out of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
About Belt and Road Initiative
- Definition: The Belt and Road Initiative is a Chinese foreign policy initiative promoted by president Xi Jinping in 2013.
- The BRI is also known as the “One Belt One Road” (OBOR), the “Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road” or just the “New Silk Road”.

- Aim: The BRI aims to connect Asia, Europe and Africa.
- BRI partnerships encompass infrastructure investments in the construction, transport, aviation, telecommunications and energy sectors stretching across many countries in Asia and Africa.
- Countries: China has presented the BRI as an open arrangement in which all countries are welcome to participate.
- To date, 147 countries—accounting for two-thirds of the world’s population and 40% of global GDP—have signed on to projects or indicated an interest in doing so.
- Trade volume between China and countries joining the BRI has surpassed $6 trillion with more than $80 million of Chinese investment in those countries.
- Features: The BRI comprises:
- Silk Road Economic Belt: A trans-continental passage that links China with south east Asia, south Asia, Central Asia, Russia and Europe by land;
- 21st century Maritime Silk Road: A sea route connecting China’s coastal regions with south east and south Asia, the South Pacific, the Middle East and Eastern Africa, all the way to Europe.;
- China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC): The CPEC comprises infrastructure and development projects underway in Pakistan since 2013.
- This economic corridor will connect the north-western Chinese province of Xinjiang with the Pakistani port of Gwadar through a network of roads measuring around 3000 kms (1,800 miles), providing Pakistan its much-needed economic infrastructure, especially power-generation plants.
- The CPEC is a key part of BRI that aims to build a modern-day “Silk Road”.
- Significance of BRI for China:
- Financial Institutions: Promotion of Chinese-led financial institutions like the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Maritime power: Put forward China as a maritime power in the South China Sea and the Indian Ocean and its littoral
- Development of Western Provinces: Develop poorer western provinces of China, especially Xinjiang. Xinjiang has had ethnic tensions and is considered to be vulnerability for China.
- Energy route: Creation of an energy route from the Middle East and Africa. This will act as a proof against any possible prohibition at points like Hormuz and the Malacca strait
- Boost to domestic infrastructure industry: Development of ports, railways, pipelines and highways across Asia and the Indian Ocean will help China utilise its excess capacity in steel, cement and infrastructural engineering
- Trade: BRI will help China to compete with Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) and Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) or any other future mechanisms which seek to establish new trading norms.
- India and BRI: India does not support the BRI, and has declined to join the project.
- The major reason for this is that the BRI passes through Indian territory illegally held by Pakistan.
- The arm of the BRI project that links mainland China to the Arabian Sea runs from Kashgar in China’s Xinjiang Uighur Autonomous Region to Gwadar port in southwestern Baluchistan in Pakistan.
- The project enters Indian territory occupied by Pakistan in Gilgit Baltistan, and traverses the entire length of Pakistan from north to south before reaching the Arabian Sea.
- Italy and BRI: Italy is the only G7 country (the grouping of advanced economies of US, the United Kingdom, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan, with the European Union as a “non-enumerated” member) to sign up for the BRI, which it did in 2019.
- Italy had joined the BRI at a time it was desperate for investment and infrastructure building, having survived three recessions in 10 years.
- Its government at the time did not share warm relations with the EU, and was happy to turn to China for the funds it could pump in.
- However, the Chinese FDI in Italy dropped from $650 million in 2019 to just $33 million in 2021. In fact, China invested far more in non-BRI countries in Europe.
Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs)
Context: The Education Ministry has been persuading the Sates to open Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs) under the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR).
About Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs)
- Definition: It is an initiative by the Ministry of Education. Vidya Samiksha Kendras which are data repositories that will have data from all schemes run by the Ministry. This will include regularly updated data from:
- the PM-POSHAN mid-day meal programmes;
- teacher training data from the National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement portal;
- textbook content from the Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing;
- school dropout and attendance-related data on the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE+);
- Vidya Samiksha Kendras from the National Achievement Survey; and Performance Grading Index which evaluates school education system at the State and Union Territory (UT) level.

- Objectives:
- To monitor the real-time status of various projects/ activities under the ambit of Samagra Shiksha.
- To keep track of enrolled students including learning outcomes, Dropouts, support required by teachers and schools, etc.
- To monitor and track field level academic and non-academic activities at state level and also empower administrators and teachers in the field to take data driven decisions.
- To identify and analyse improvement areas for decision making and implementation that needs urgent attention.
- To improve the academic performance of students and to enhance the accountability of teachers in schools and effective utilisation of the available resources.
- To setup centralized helpdesk for grievance redressal mechanism for stakeholders of School ecosystem.
- To develop Centralized dashboard providing the real-time performance indicators of Schools.
- Increase accountability among all the field level staffs / administrators & monitor the real-time status towards various projects components / activities under the ambit of School Education.
- Implementation:
- Currently, at the Central level, a VSK is housed in the Central Institute of Educational Technology building in NCERT campus, with multinational IT company Ernst and Young (EY) managing its operations.
- It is an open-source platform run on C-Qube software.
- Finance: The Centre has allocated funds ranging from ₹2 crore to ₹5 crore to each State.
- Importance:
- The idea of bringing all data on one platform is to employ analytics for correlation. Currently the NCERT has data from different schemes that cater to 15 lakh schools, 96 lakh teachers, and 26 crore students, but it is irrelevant if it cannot be correlated or analysed.
- For instance, in certain schools, Gujarat has employed biometrics to capture attendance patterns of students and teachers.
- The attendance gets recorded and reported at State level.
- This can be mapped with trends of student dropout data to analyse any correlation between both data sets.
- Another instance would be correlating data from the mid-day meal scheme, or PM-POSHAN, with attendance.
- This will give insight on whether in those demographical areas where mid-day meals are provided regularly, students are more incentivised to attend schools.
- The idea of developing VSKs is also to map the school location layer with the population layer to assess the Gross Access Ratio, which can help plan for new schools, or for industry clusters to understand skilling requirements of the area, and help plan higher educational institutions based on demand and future scenarios.


 Daily Quiz 02 April 2025
Daily Quiz 02 April 2025
 LIGO India Project, Working and Signific...
LIGO India Project, Working and Signific...
 Future Circular Collider (FCC): The Worl...
Future Circular Collider (FCC): The Worl...





















