Table of Contents
Context: The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovery of microRNAs (miRNAs) and their role in regulating gene expression. This research, conducted using the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans).
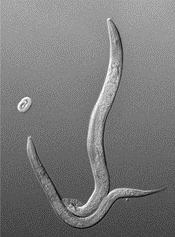
About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. Elegans)
- It is a 1-mm long, transparent nematode commonly used in scientific research.
- It inhabits soil and feeds on microbes, making it easily cultivated in laboratories.
- The adult worm has 959 cells and 302 neurons, providing a simple model for studying development and neuroscience.
- It is widely used in genetic and developmental biology due to its straightforward anatomy and short lifespan.
- It was the first multicellular organism to have its full genome sequenced and neural wiring mapped.
Why is it important for researchers?
- Simpler Anatomy: Elegans lack both respiratory and circulatory systems
- Large-scale production: It can be produced in large numbers within a short period of time. It grows quickly, reaching adulthood in 3-5 days after hatching from eggs.
- Transparency: Its transparency allows scientists to track cell development under a microscope.
- Self- fertilisation: It is hermaphrodite, and can produce both eggs and sperm.
Four Researches based on C. Elegans that led to Nobel Prize
Genetic Regulation & Programmed Cell Death (2002)
- Sydney Brenner, H. Robert Horvitz and John Sulston discovered how genes regulate organ development and programmed cell death.
- Their work revealed the genetic mechanisms that control cell death during development.
RNA Interference (2006)
- Andrew Fire and Craig Mello discovered how double-stranded RNA silences specific genes through RNA interference.
- This mechanism prevents certain genes from producing proteins.
- Their research opened doors for therapies targeting gene expression in diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders.
Green Fluorescent Protein (2008)
- Osamu Shimomura, Martin Chalfie and Roger Tsien developed the Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) to track proteins in living organisms.
- GFP enabled scientists to visualize cellular processes in real time.
- It helped to study molecular interactions within living cells.
MicroRNAs (2024)
- Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun discovered microRNAs (miRNAs) that regulate gene expression by silencing specific genes.
- miRNAs control various biological processes, including development and disease regulation.
- Their research opened new possibilities for diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches in genetic diseases.
| MicroRNA (MiRNA) |
|


 Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
 Ozempic Drug Could Reverse Liver Disease...
Ozempic Drug Could Reverse Liver Disease...
 India secures Hawkeye 360 Technology dea...
India secures Hawkeye 360 Technology dea...





















