Table of Contents
Context: ISRO successfully tested the SE2000 semi-cryogenic engine’s Power Head Test Article (PHTA) for future heavy space launches.
What is a Cryogenic Engine?
Cryogenic engines use cryogenic propellants, which are gases that exist in liquid form at extremely low temperatures. In the case of ISRO’s CE20 engine, the propellants used are liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2), both of which must be stored at very low temperatures—below -183 °C for LOX and –253°C for LH2. Cryogenic engines are known for their high efficiency and ability to generate more thrust compared to other types of rocket engines. This makes them ideal for launching heavy payloads into space.
Overview of the CE20 Cryogenic Engine
Developed indigenously by ISRO’s Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC), the CE20 cryogenic engine is a critical component of the LVM3 launch vehicle, which is designed for launching heavier payloads into geosynchronous orbits. This engine has a thrust capability of 19 tonnes, a remarkable achievement for India, enabling it to compete with global space powers like the US, Russia, China, France, and Japan.
The CE20 engine has already powered several successful space missions, including Chandrayaan-3 and Gaganyaan (India’s upcoming manned mission to space). The engine is being further upgraded to produce a thrust level of 22 tonnes to support more advanced missions and larger payloads.
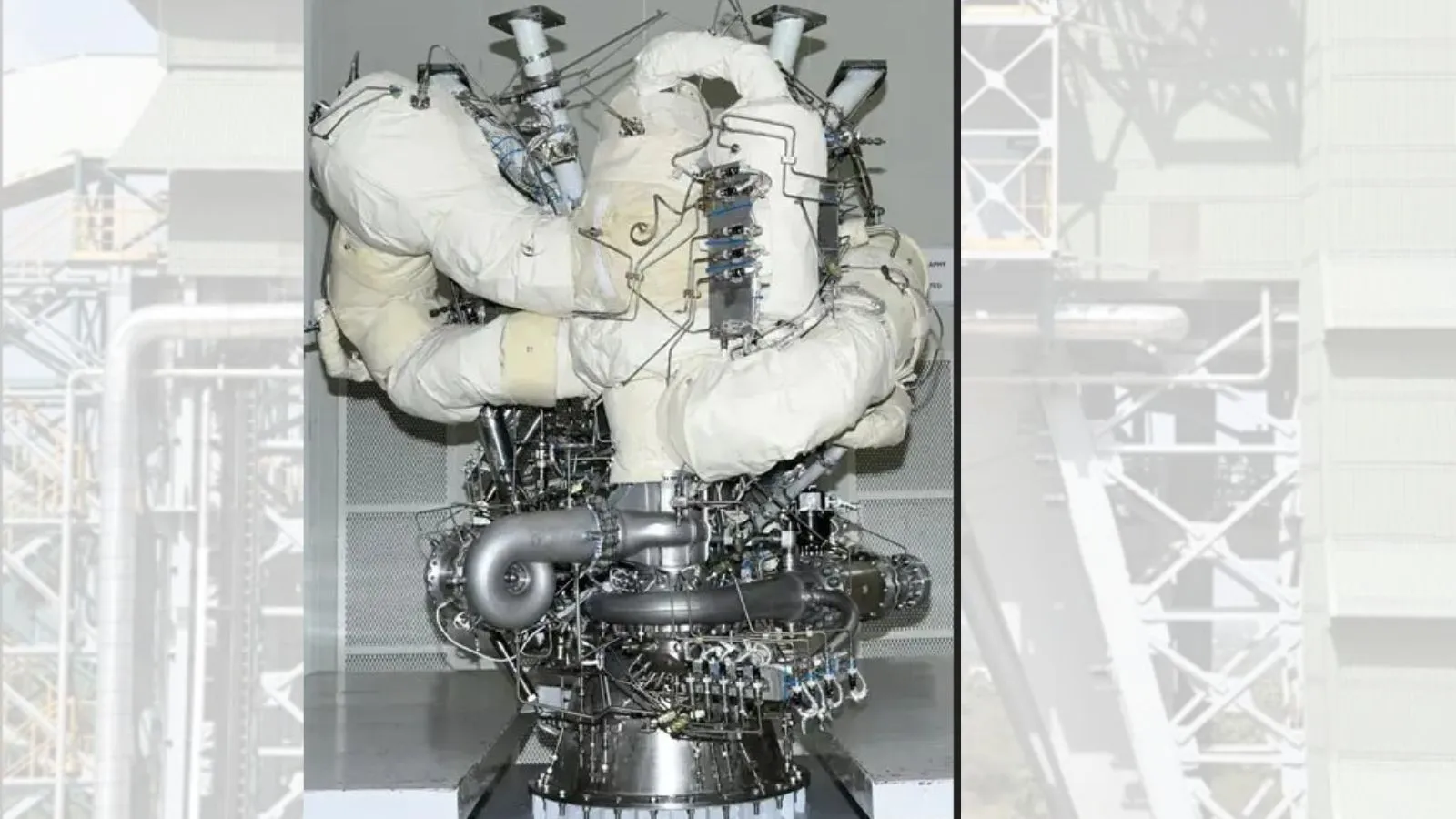
About Power Head Test Article (PHTA)
- ISRO is developing a semi-cryogenic engine that uses a Liquid Oxygen and Kerosene-based propulsion system that offers an enhanced thrust.
- PHTA is the first hardware test for the development of semi-cryogenic engines.
- The test involves performing a hot-firing for an extremely brief duration of not more than 5 seconds.
Why Semi-Cryogenic Engines Matter
- Current cryogenic engines use Liquid Oxygen (LOX) and Liquid Hydrogen (LH2).
- Liquid hydrogen is difficult to handle due to its extreme storage temperature (-253°C) and high inflammability.
- The semi-cryogenic engine uses LOX and Kerosene, which has advantages such as:
- Higher density impulse (more efficiency than cryogenic)
- Less toxic storage
- More cost-effective propulsion
- Easier handling of kerosene compared to liquid hydrogen
Upcoming Developments by ISRO – Upgradation of LVM-3
- ISRO is working on upgrading Launch Vehicle Mk III (LVM3).
- The LVM3 will be equipped with a C32 cryogenic upper stage, replacing the older C25 stage.
- C32 advantage over C25:
- Carries more propellant, extending mission duration.
- Increases payload capacity by 25%.
- Will increase spacecraft launch capacity from 4 tonnes to 5.1 tonnes to Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) without increasing cost.
Importance of the CE20 Cryogenic Engine for ISRO and India
The successful testing of the CE20 cryogenic engine holds profound implications for India’s space ambitions. ISRO’s ability to develop indigenous cryogenic engines places the country among the elite nations in space technology. As of now, only a few countries—the US, Russia, China, France, and Japan—have developed cryogenic propulsion systems capable of supporting heavy payloads.
The CE20 engine boosts India’s capacity to launch heavier payloads, including communication satellites, weather monitoring systems, and interplanetary probes. It also increases India’s ability to conduct interplanetary exploration missions, such as missions to Mars, Venus, and beyond. This self-reliance in cryogenic propulsion reduces the dependency on foreign technology and contributes to India’s space security.
Key Features of the CE20 Engine
- Thrust Capability: The CE20 engine is designed to produce a 19-tonne thrust with a potential upgrade to 22 tonnes in the future for even more powerful launches.
- Innovative Nozzle Protection System: This feature protects the nozzle from issues like flow separation and vibrations, ensuring smooth operation under sea-level conditions.
- Multi-Element Igniter: A critical component that enables the engine to restart in space, an essential capability for missions like Gaganyaan.
- Liquid Oxygen and Liquid Hydrogen Propellants: Using LOX and LH2 as propellants enhances the engine’s efficiency and thrust capabilities.
- Significant Missions: The CE20 has already powered key missions like Chandrayaan-3, positioning ISRO as a leader in lunar exploration.
Future Prospects: Gaganyaan and Beyond
One of the most exciting prospects for the CE20 engine is its role in India’s Gaganyaan mission. India’s first manned spaceflight will rely heavily on the CE20’s capabilities to carry astronauts into space and ensure their safe return. The upgraded thrust capacity of 22 tonnes will be essential for ensuring the mission’s success.
Beyond Gaganyaan, the CE20 engine’s technology will contribute to other high-profile projects, such as interplanetary exploration and the launch of larger communication satellites. It will play a pivotal role in deep-space missions, including potential missions to the Moon, Mars, and Venus, strengthening India’s position in the global space race.
Global Significance and Geopolitical Implications
The successful development of the CE20 engine places India alongside leading spacefaring nations. With this technological breakthrough, India has demonstrated its advanced space capabilities, ensuring that it remains competitive in the growing global space economy. The development of indigenous cryogenic technology also has significant geopolitical implications; it positions India as a leader in space diplomacy, offering technological support and collaboration opportunities to other developing nations.
Conclusion
ISRO’s successful testing of the CE20 cryogenic engine is a monumental achievement for India’s space program. It reflects the nation’s growing capabilities in space technology and propulsion systems, ensuring that India will play a leading role in space exploration in the coming decades. The CE20 engine’s thrust power, advanced restart systems, and cutting-edge innovations like the Nozzle Protection System make it a cornerstone for future missions, including the Gaganyaan mission.
As ISRO continues to develop and refine its cryogenic technologies, the future looks promising for India’s space exploration endeavors, with exciting possibilities for interplanetary missions and global space partnerships.


 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...

























