Table of Contents
Context: The Indian Government has secured a 9,000 sq. km block in Zambia to explore copper and cobalt.
About Copper Ore
- Copper is a good conductor of electricity and is ductile (able to be drawn out into a thin wire).
- It is used by the automobile and defence industries and in the electrical industry for making wires, electric motors, transformers, and generators.
Copper Reserves & Production
- Highest Reserve Worldwide: Chile, DR Congo, Peru and China.
- Highest Production Worldwide: Chile, Australia, Peru, Russia
| Challenges with BIS Certification |
|
Copper Ore Distribution in India
- India has low-grade copper ore reserves in India
- Total Reserves around 46 million tonnes.
- States with Highest Reserves: Rajasthan (50%), Madhya Pradesh (24%), Jharkhand (19%)
Production wise
- 1st – Madhya Pradesh (Important Mines- Malanjkhand & Balaghat)
- 2nd- Rajasthan (Khetri- Singhana belt in Jhunjhunu district)
- 3rd Jharkhand (Singhbhum)
Domestic Copper Production Decline
- 2023-24 production: 78 million tonnes (mt) (↓ 8% from 2018-19).
- Hindustan Copper Ltd (HCL) – India’s sole domestic copper miner – reported a 6% decline in ore production from April 2023 to January 2024 (year-on-year).
- Imports doubled: India’s copper concentrate imports: ₹26,000 crore in 2023-24 (compared to 2018-19).
1. Chilpi Series
It covers parts of Madhya Pradesh’s Balaghat and Chhindwara districts. Quartzite, copper-pyrite, mica schist, and marble comprise the series. The copper from this series is used at the Malanjkhand Copper Plant.
2. Ghatsila
This copper smelting plant is located in Jharkhand. It is a refinery that uses electrolysis. It produces brass sheets. It also obtains gold, silver, and nickel from copper processing.
3. Khetri
It is an integrated copper mining and ore refining plant in Rajasthan’s Jhunjhunu District. It was founded in 1967. It also gets copper ore from Madhya Pradesh’s Malanjkhand copper mines. There is also a sulfuric acid plant and a fertiliser plant.
4. Malanjkhand
Malanjkhand is an open cast copper mine in Madhya Pradesh’s Balaghat District. In Malanjkhand, a copper plant has been established. The copper ore is also sent to Rajasthan’s Khetri Copper Plant.
5. Rakha Initiative
The Rakha Copper Plant is located in the Rakha District of Jharkhand’s Singhbhum. It obtains copper ore from the Rakha mines.
6. Tajola
The Tajola Copper Plant is located in the Maharashtra town of Raigadh. Copper cathodes were imported for the plant. It produces copper rods.
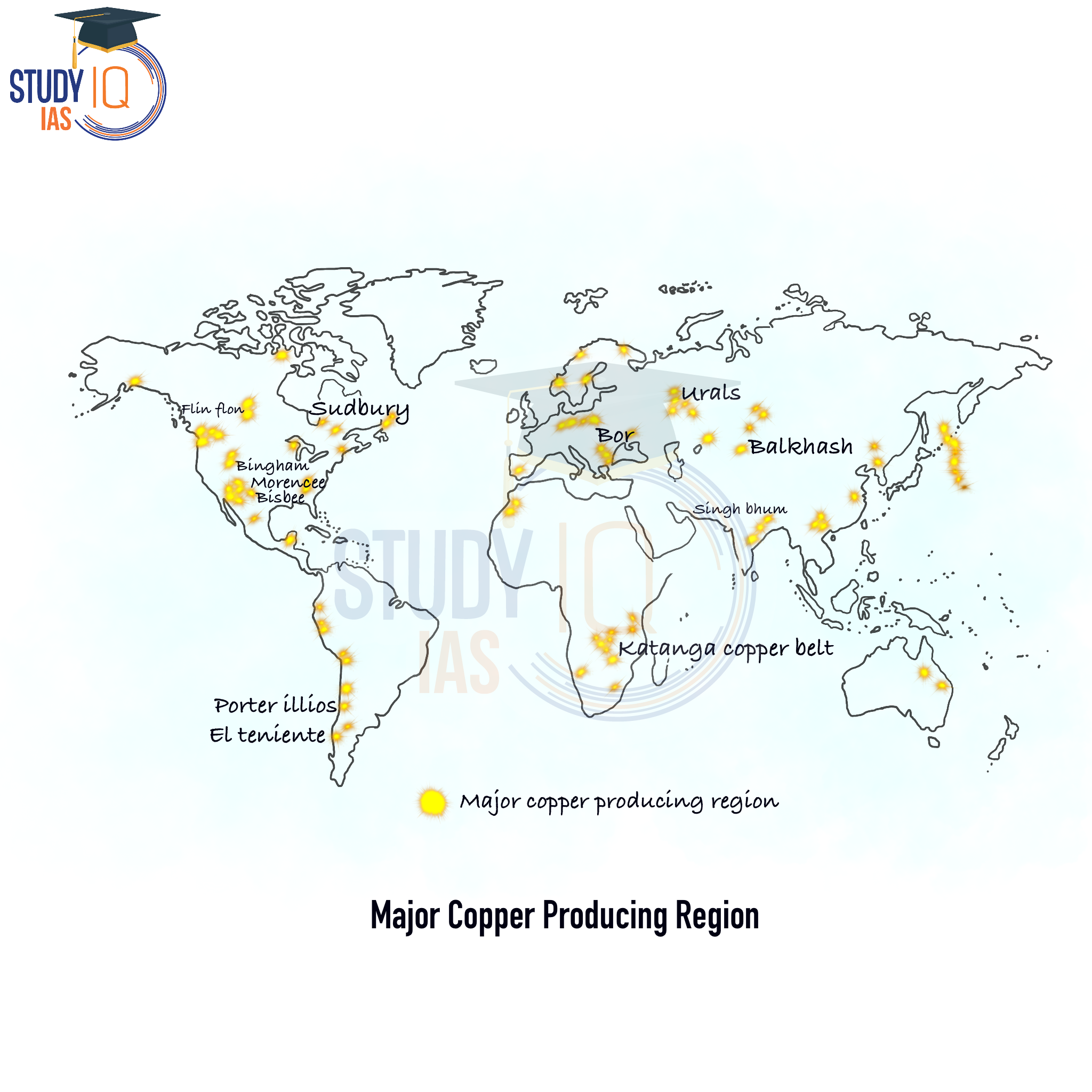
Copper Ore Distribution in the World
Chile is the world’s largest copper producer, followed by Peru. Other copper-producing countries include the USA, Canada, and Australia.
| Country | Areas |
| Chile | Copper Mountain of Chuquicamata, El Teniente, Rio Blanco, Braden |
| Peru | Moquegua region |
| USA | Arizona, Globe, Miami, Nevada, New Mexico |
| Canada | Sudbury, Lynn Lake, Sheridon |
| Sweden | Falun Mine |
| Germany | Mansfield |
| CIS | Degtyarsk, Kazakhstan |
| Australia | Mt Isa, Mt. Morgan |
India produces about 2% of the world’s copper and does not have enough copper ore to meet its needs. The country’s demand for copper and its alloys is met through local production, recycling scrap, and imports. India also imports copper concentrates for its smelters. In the copper production process, copper concentrate is turned into copper anodes, which are then refined into copper cathodes. This refined copper is used to make rods, sheets, wires, and other products.
Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL) is the only major company in India that handles all stages of copper production, from mining to refining. Private companies like Hindalco Industries and Vedanta Limited also produce copper, mainly relying on imported concentrates.
The largest copper reserves are in Rajasthan, which holds over half of India’s total copper resources, followed by Jharkhand and Madhya Pradesh. The Khetri Mine in Rajasthan is one of the largest copper mines in India, with additional reserves found in states like Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra.
Africa’s Rising Share in Mineral Production
- Africa is becoming a major producer of critical minerals:
- Cobalt: 70% of global production (mostly from DRC).
- Copper: 16% of global production.
- DRC: Expected to be the world’s second-largest copper producer by 2030.
- Zambia’s Role: 7th largest copper producer globally.
Uses of Copper Ore
- Copper is great for wiring because it conducts electricity well.
- Copper pipes are used for water and heating because they last long and don’t rust.
- Copper is found in circuit boards and connectors.
- Copper is used in roofs and gutters because it’s strong and looks nice.
- Copper is mixed with other metals to make bronze and brass.
- Copper is used in car electrical systems, radiators, and brakes.
- Copper is important in solar panels, wind turbines, and electric cars.
- Many coins are made from copper or copper alloys.
- Copper kills germs and is used in some medical tools.
Copper Ore Properties
- Copper ore is found in a variety of mineral forms, such as sulfides, oxides, and carbonates. The copper content in copper ore can vary from less than 1% to over 50%.
- Copper ore has a moderate hardness ranging from 3 to 4 on the Mohs scale.
- The specific gravity of copper ore ranges from 2.5 to 3.5, depending on the type and mineral content.
- Copper ore is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
- Copper ore is not highly reactive but can react with strong acids and oxidizing agents.
- Copper ore can range in colour from metallic red to black, depending on the type and mineral content.
- Copper ore is soft and malleable and can be easily bent or shaped without breaking. It also has high ductility, meaning it can be easily drawn into wires or sheets.
| UPSC PYQ |
| Q. About three-fourths of the world’s cobalt, a metal required for the manufacture of batteries for electric motor vehicles, is produced by? (2023)
(a) Argentina (b) Botswana (c) The Democratic Republic of the Congo (d) Kazakhstan Answer: C
|
Copper Ore UPSC
India is unlucky in terms of copper reserves and production. Her total in-situ reserves are estimated to be around 712.5 million tonnes, which equates to 9.4 million tonnes of metal content. India is a poor country in terms of copper reserves and production. India has low-grade copper ore (less than 1% metal content) compared to the international average of 2.5 per cent.
Major copper ore deposits can be found in the districts of Singhbhum (Jharkhand), Balaghat (Madhya Pradesh), and Jhunjhunu and Alwar (Jharkhand) (Rajasthan). India is a poor country in terms of copper reserves and production. India has low-grade copper ore (less than 1% metal content) compared to the international average of 2.5 per cent.
| Related Articles | |
| Types of Resources | Chromium Ore |
| Manganese Ore | Mineral Resources |
| Iron Ore |
Minerals |


 Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2026 for Prelims...
 Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...
Lake Natron: Location, Features, Wildlif...
 Erra Matti Dibbalu Added to UNESCO Tenta...
Erra Matti Dibbalu Added to UNESCO Tenta...

























