Table of Contents
Context: India’s growing global interests compelled it to ensure the Taiwan Strait’s status quo remained peaceful to protect trade ties and avert regional conflict with catastrophic economic implications.
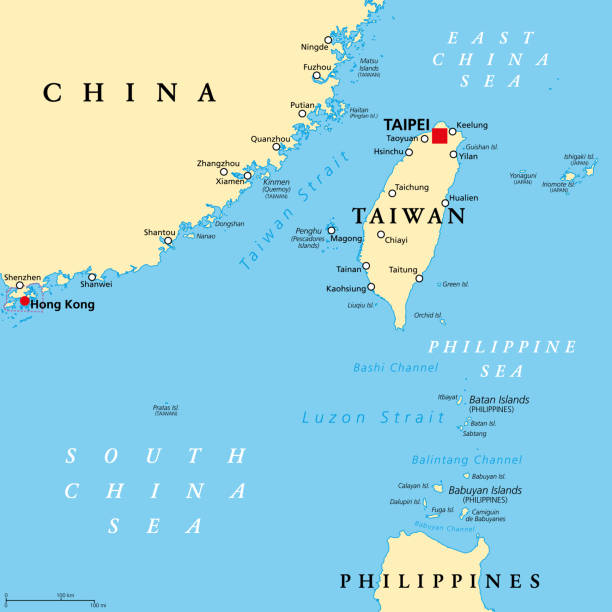
Background of China-Taiwan Conflict
| China-Taiwan Conflict | |
| Historical Control of Taiwan |
|
| Post-War Developments and Civil War |
|
| China’s Claim vs. Taiwan’s Position |
|
| S. Policy and Military Involvement |
|
| Political Shifts and Economic Ties |
|
| Impact of Economic Interdependence |
|
| Ongoing Tensions |
|
India’s Stance on Taiwan
- Preservation of Status Quo: India’s main stance is maintaining the current self-governing status of Taiwan without pushing for independence, due to the increasing economic ties, including trade growth and technological investments such as the Tata partnership with Powerchip for semiconductor manufacturing.
- Economic Implications: Conflict with Taiwan could disastrously disrupt global trade, severely impacting India’s economy and supply chains, potentially costing over 10% of global GDP according to a Bloomberg study.
- Security Risks: A China-U.S. war over Taiwan could escalate tensions on the India-China border, disrupt regional industrial capacity, and risk nuclear escalation. The conflict would be detrimental to India’s pursuit of stability and growth.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
Potential Outcomes of Taiwan Conflict
If China were to emerge victorious in a conflict over Taiwan,
- it could become the dominant regional military power,
- altering security architecture,
- destabilising regional relations, and
- potentially influencing India’s security, especially in the Indian Ocean and in its border regions.
India’s Role and Policy Options
- Deterrent Strategies: India can utilise a variety of policy tools to deter aggression, such as reinforcing international law, countering aggressive narratives, diplomatic communication, economic strategies, support for Taiwanese morale, and possibly military assistance to U.S. forces.
- Grand Strategic Benefits: By enacting these policies, India could not only leverage its position against China but also strengthen its ties with the U.S., enhancing its global leadership, particularly among Global South nations.
- Self-interest and Costs: Adopting these policies serves India’s own interests, even if they might provoke Chinese backlash. The consequences of inaction are seen as significantly more damaging than the costs of potential retaliation.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 Africa’s Nuclear Energy Market Status ...
Africa’s Nuclear Energy Market Status ...





















