Table of Contents
Cardiovascular Kidney Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome is an emerging health concern that underscores the interconnectedness of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), kidney disorders, and metabolic abnormalities. For UPSC aspirants, understanding CKM Syndrome is crucial for addressing questions related to public health, preventive medicine, and sustainable healthcare systems.
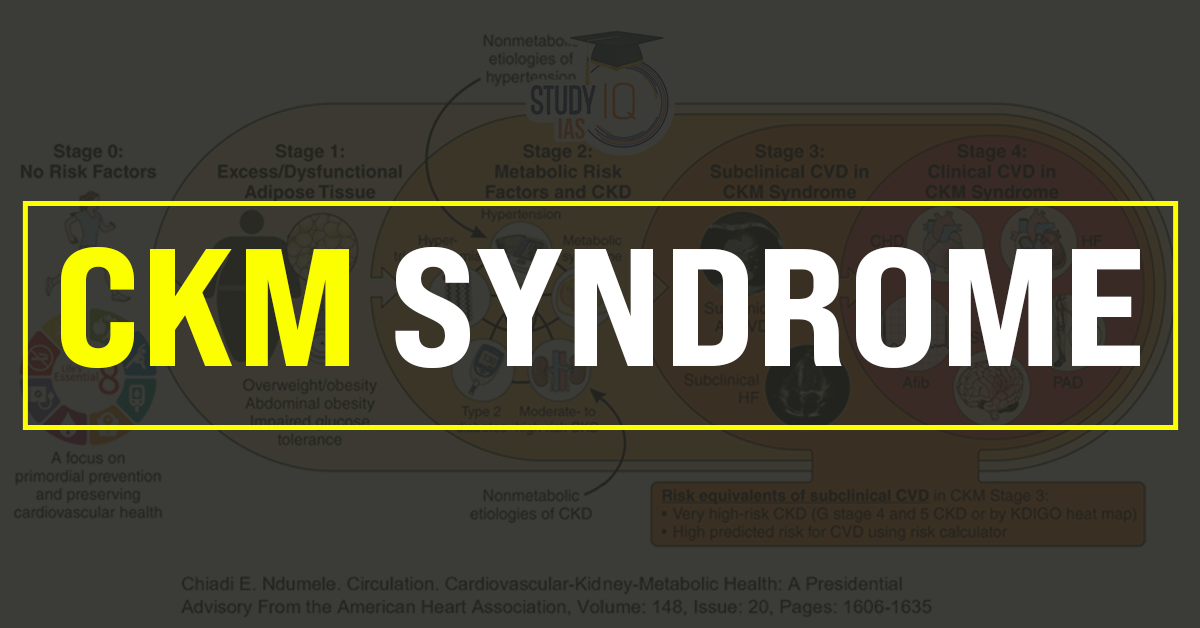
What is CKM Syndrome?
CKM Syndrome refers to a cluster of interrelated health conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, kidney dysfunctions, and metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. The syndrome represents a continuum of pathophysiological interactions where dysfunction in one system exacerbates issues in others.
Key Features of CKM Syndrome
- Interconnected Pathophysiology:
- Cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension and heart failure often lead to kidney damage, termed cardiorenal syndrome.
- Metabolic disorders, including diabetes and obesity, significantly increase the risk of both cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
- Chronic Nature:
- CKM Syndrome is characterized by chronic and progressive conditions requiring long-term management.
- High Prevalence:
- With the rise in lifestyle-related diseases, CKM Syndrome is becoming increasingly common, particularly in low- and middle-income countries like India.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Unhealthy Lifestyle: Sedentary habits, poor diet, and lack of exercise.
- Aging Population: Increased prevalence among older individuals.
- Comorbid Conditions: Diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of cardiovascular or kidney diseases.
Impact on Public Health
- Economic Burden:
- CKM Syndrome imposes a significant financial strain on healthcare systems due to the cost of treatment and long-term management.
- Increased Morbidity and Mortality:
- CKM contributes to premature deaths and reduced quality of life.
- Healthcare Challenges in India:
- Limited access to early diagnostic tools and specialized care in rural areas exacerbates the problem.
Management and Prevention
- Preventive Strategies:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Promoting healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and tobacco cessation.
- Early Screening: Identifying at-risk individuals through routine health check-ups.
- Medical Interventions:
- Use of antihypertensive drugs, glucose-lowering agents, and statins.
- Dialysis and kidney transplantation in severe cases.
- Policy Measures:
- Strengthening healthcare infrastructure to address non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
- Initiatives like the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) in India.
Global Perspective on CKM Syndrome
- World Health Organization (WHO):
- Advocates for integrated healthcare approaches to address CKM Syndrome.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- Goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages.
- Collaborative Research:
- International collaborations to develop cost-effective treatments and preventive measures.
Way Forward
- Awareness Campaigns:
- Educating the population about lifestyle changes to prevent CKM Syndrome.
- Strengthening Healthcare Policies:
- Allocating resources for the early detection and treatment of CKM-related conditions.
- Technological Integration:
- Using AI and big data for predicting and managing CKM risks.
- Promoting Research and Development:
- Encouraging pharmaceutical advancements for affordable and effective CKM drugs.
Conclusion
CKM Syndrome poses a significant public health challenge, especially in developing nations like India. Addressing this requires a multifaceted approach involving policy reforms, lifestyle changes, and technological advancements. For UPSC aspirants, understanding CKM Syndrome is essential for articulating solutions to contemporary healthcare issues in India and globally.

 Algorithmic Sovereignty Should Be India�...
Algorithmic Sovereignty Should Be India�...
 $100 Oil: Why Supply Security Matters Mo...
$100 Oil: Why Supply Security Matters Mo...
 Bridging the Digital Divide: Meaning, Ch...
Bridging the Digital Divide: Meaning, Ch...




















