Table of Contents
Context: Carbon farming offers climate solutions and economic benefits but faces challenges, especially in developing countries like India, where tailored strategies are needed for widespread adoption.
Carbon Farming
- Carbon farming involves regenerative agricultural practices that aim to improve ecosystem health, enhance agricultural productivity, and mitigate climate change by increasing carbon storage and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
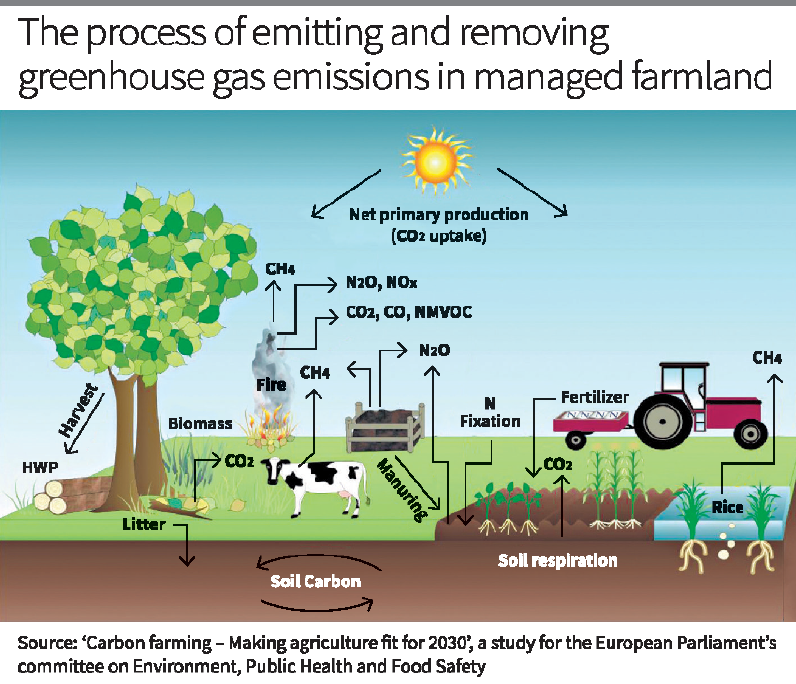
- Techniques include:
- Rotational grazing
- Agroforestry (e.g., silvopasture and alley cropping)
- Conservation agriculture (zero tillage, crop rotation, cover cropping, crop residue management)
- Integrated nutrient management (using organic fertilizers)
- Agro-ecological approaches (crop diversification and intercropping)
- Livestock management (optimising feed, managing waste to reduce methane emissions)
Challenges of Carbon Farming
- The effectiveness of carbon farming is influenced by various factors such as geographical location, soil type, crop selection, water availability, biodiversity, and farm scale.
- Water scarcity in arid regions hinders plant growth and sequestration.
- Financial burdens on farmers, especially in developing countries like India, where small-scale farmers may struggle with the initial costs of sustainable practices.
- Limited policy support and community engagement are crucial for widespread adoption.
Global Initiatives
Several international efforts highlight the growing importance of carbon farming:
- Voluntary carbon markets in countries like the U.S., Australia, New Zealand, and Canada.
- Chicago Climate Exchange and Carbon Farming Initiative in Australia promote carbon mitigation in agriculture.
- Kenya’s Agricultural Carbon Project is supported by the World Bank.
- ‘4 per 1000’ initiative was launched during the COP21 in Paris to enhance carbon sinks.
Opportunities in India
India presents a significant potential for carbon farming due to its large agricultural base and the need for climate-resilient practices.
- Economic potential: Agro-ecological practices could generate significant value, with an estimated potential of $63 billion from approximately 170 million hectares of arable land.
- Carbon credit systems: These can provide additional income to farmers through environmental services, with agricultural soils potentially absorbing 3-8 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually over 20-30 years.
- Regional Suitability: The Indo-Gangetic plains and the Deccan Plateau are favourable for carbon farming, whereas the Himalayan region and coastal areas face specific challenges such as mountainous terrain and salinization, respectively.


 Micrometeoroids: Tiny Space Particles, M...
Micrometeoroids: Tiny Space Particles, M...
 India Needs a National Insolvency Tribun...
India Needs a National Insolvency Tribun...
 Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...
Unlocking the Potential of India–Afric...

























