Table of Contents
Context: In India, researchers collaborated to develop NexCAR19, an affordable CAR-T cell therapy.
About Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy
- CAR T-cell therapy is a form of cancer treatment that modifies T cells, a critical component of the immune response.
- These T cells are extracted from the patient’s own blood.
- In a laboratory, the T cells are genetically altered by introducing DNA to carry a special protein known as a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR).
- This CAR enables the T cells to detect and attach to specific antigens found on the surface of cancer cells.
- After the genetic engineering process, the modified T cells are reintroduced into the patient’s body.
- Once administered, the CAR T cells proliferate and hone in on the cancer cells, recognizing and killing them based on the presence of the target antigen.
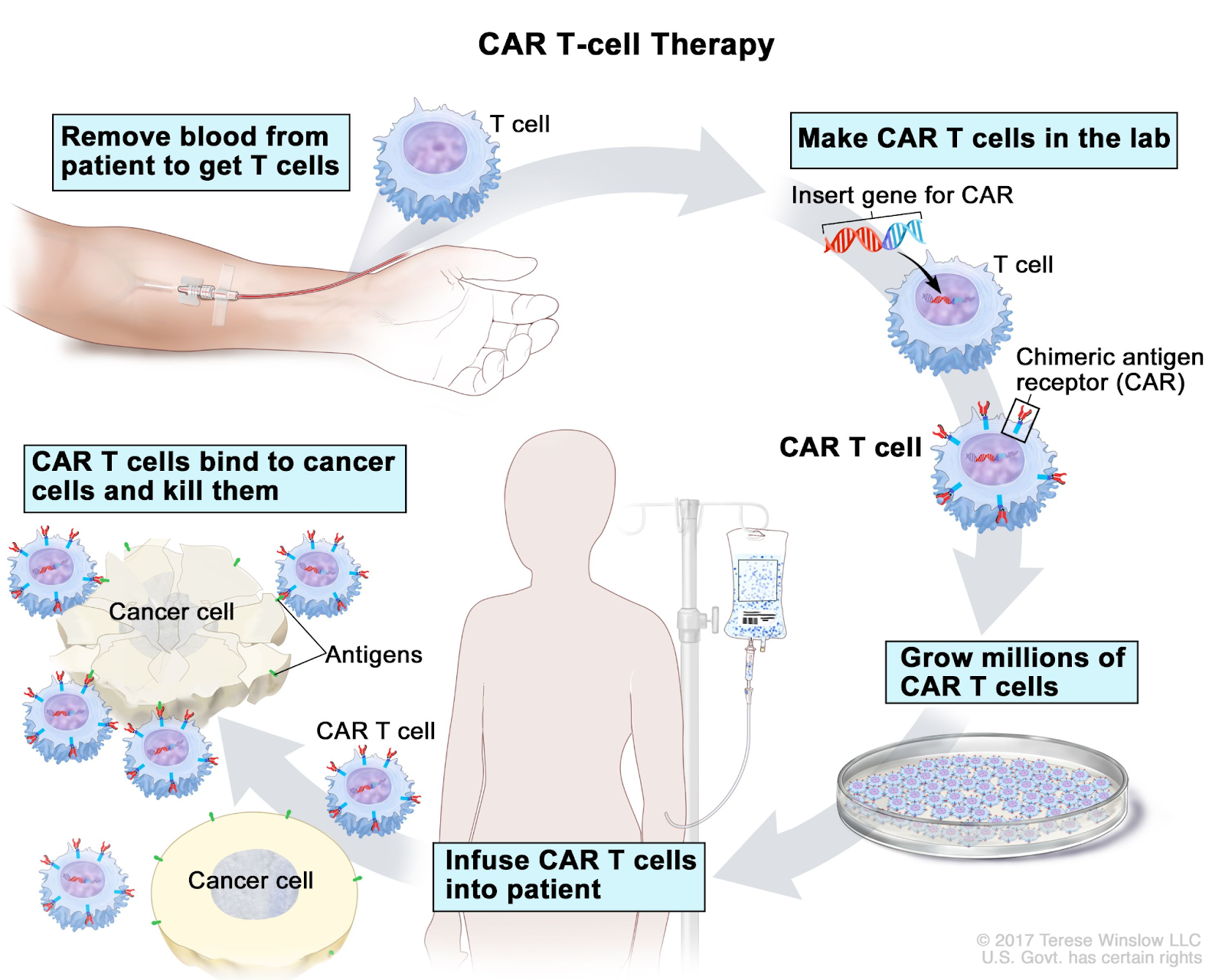
How CAR-T Cells are Made?
- T-cells are collected from patients through a process called leukapheresis and genetically modified to proteins called chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) on their surface that target cancer cells.
- The modified T-cells are expanded in the lab and infused back into the patient post-chemotherapy.
- The CAR comprises several components that enable it to identify cancer cell antigens and stimulate an immune response.
- Each CAR spans across the cell membrane, with a portion extending outside the cell and a portion inside.
- The exterior segment is made of fragments of laboratory-generated antibodies selected for their affinity to bind to the targeted antigen.
- The internal segment of CAR consists of two components responsible for transmitting signalling once the receptor interacts with an antigen.
- The FDA has approved six CAR-T cell therapies till now, and four of them target CD19, a protein produced on the surface of leukaemia and lymphoma cells. NexCAR19 is similar in this aspect.
- A key difference between the CAR-T cell therapies developed in the U.S. and NexCAR19 lies in the composition of antibody fragments.
- While those developed in the US originate from murine (mice) sources, NexCAR19 has human proteins added to the mouse antibody, resulting in a ‘humanised’ CAR.
- This modification might have contributed to its reduced toxicity.
Clinical Trial and Approval for NexCAR19
- The first patient was treated at Tata Memorial Hospital on June 4, 2021.
- In October 2023, CDSCO approved NexCAR19 as the first CAR-T cell therapy to treat relapsed or refractory B-lymphomas and B-ALL.
Risks of CAR-T Therapy
- Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) – the most common side effect, an inflammatory response triggering immune system hyperactivity.
- Neurotoxicity – not observed in NexCAR19 trials, potentially due to humanised antibody fragments.
- Infections and low blood cell counts are other side effects.
Access and Affordability of NexCAR19
- NexCAR19 is priced at ₹40-45 lakh, which is still high for many Indians.
- The cost can be further reduced by:
- Increased production scale.
- Lower hospitalisation cost due to reduced side effects of NexCAR19.
What are the Major Forms of Cancer Treatment?
- The three major forms of treatment for any cancer are:
- surgery (removing cancer),
- radiotherapy (delivering ionising radiation to the tumour), and
- systemic therapy (administering medicines that act on the tumour).
- Surgery and radiotherapy have been refined significantly over time – whereas advances in systemic therapy have been unparalleled.
What are T Cells?
- T cells, also known as T lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that play a central role in the immune response.
- Significance: T cells play a crucial role in the adaptive immune response, which is the part of the immune system that is capable of recognizing and responding to specific pathogens or abnormal cells.
- Production: T cells are produced in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus gland.
- Important types of T cells:
- Helper T cells: These cells play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response.
- Cytotoxic T cells: These cells play a key role in destroying cells that are infected with viruses or cancer cells.
- T regulatory cells (Tregs): These cells play a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance and preventing autoimmunity.
Current Applications of CAR T-cell Therapy
- As of today, CAR T-cell therapy has been approved for leukaemias (cancers arising from the cells that produce white blood cells) and lymphomas (arising from the lymphatic system).
- CAR T-cell therapy is also presently used among patients with cancers that have returned after initially successful treatment or who haven’t responded to previous combinations of chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Efficacy
Its response rate is variable. In certain kinds of leukaemias and lymphomas, the efficacy is as high as 90%, whereas, in other types of cancers, it is significantly lower.
Side effects
The potential side effects are also significant and associated with
- Cytokine release syndrome (a widespread activation of the immune system and collateral damage to the body’s normal cells) and
- Neurological symptoms (severe confusion, seizures, and speech impairment).
Other challenges associated
- Preparation: The difficulty of preparing CAR T-cell therapies has been a major hindrance to their widespread use.
- Affordability: Critics argue that developing CAR T-cell therapy in India may not be cost-effective as it will still be unaffordable for most people.

 Hydrogen For Net-Zero Economy, Governmen...
Hydrogen For Net-Zero Economy, Governmen...
 Mantis Shrimp - Latest Research News and...
Mantis Shrimp - Latest Research News and...
 Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...
Places in News for UPSC 2025 for Prelims...





















