Table of Contents
Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra, one of the largest rivers in the world, plays a very important role in Asia as an international river. Many rivers in India which are treated as feminine, the Brahmaputra is regarded as a masculine river. Stretching approximately 2900 kilometers, it originates from the Yarlung Tsangpo River in southwest Tibet which begins at the Angsi Glacier. Flowing through the Himalayas, the river becomes the Dihang River in Arunachal Pradesh before widening and gaining strength as it reaches Assam. Its average depth is 38 meters with a maximum depth of 120 meters, and an impressive average water flow of 19300 cubic meters per second, though it is prone to flooding due to melting Himalayan snow. The river’s course is subject to change, draining various regions, including the Patkai-Bum hills, the northern slopes of the Meghalaya hills, the Assam plains, the northern part of Bangladesh, the Himalayas east of the Indo-Nepal border, the southern-central Tibetan plateau above the Ganges basin, and the southeastern part of Tibet. The highest point in the Brahmaputra basin is Kanchenjunga.
| Brahmaputra River overview: |
|
Brahmaputra River Length
The Brahmaputra river spans around 2900 km. The river’s highest depth is 120 metres, and its average depth is 38 metres.
Origin of Brahmaputra River
- The Brahmaputra River starts in the Kailash hills in the Himalayas at a height of 5300 meters.
- It flows through Bangladesh and Assam enters India through Arunachal Pradesh and finally joins the Bay of Bengal.
- The river’s catchment area in Tibet is 293000 square feet.
Brahmaputra River Map
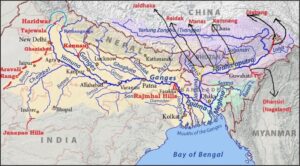
Brahmaputra River System
The river system is surrounded by the Himalayas to the north, Patkai hills to the east, Assam hills to the south, and more Himalayas to the west. Snow is found in the Himalayan regions of Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh, which are part of the Brahmaputra basin. These regions have 55.48% of India’s forest cover making them very green. Majuli, an island in Assam, is the world’s largest and oldest inhabited riverine island, recognized by UNESCO. The Brahmaputra river system has a hydropower potential of 66065 MW. The river gets a lot of sediment from about 20 tributaries on its north bank and 13 on its south bank as it flows from Kobo to Dhubri in Assam.
The South-West monsoon brings most of the rain to this area, with 85% of the yearly total falling from May to September.
| Sub-Names of Brahmaputra rivers |
|
Brahmaputra River Tributaries
Manas River
One of the most important rivers that feeds into the Brahmaputra is the Manas River. It begins in Bhutan, flows through Assam and southern Bhutan, and joins the Brahmaputra near Jogighopa. The Manas River is 376 kilometers long and has steep, mountainous forests in its upper parts, while it flows through plains closer to where it meets the Brahmaputra.
Raidak River
Another river that joins the Brahmaputra in its lower part is the Raidak River. It starts in the Himalayas in Bhutan, flows through Bhutan, India, and Bangladesh, and meets the Brahmaputra in the Kurigram area of Bangladesh. The Raidak River is 370 kilometers long and has several smaller rivers flowing into it from Bhutan.
Sankosh River
That river flows into the Brahmaputra, starting in Bhutan and ending in Assam, India. In Bhutan, it is called Puna Tsang, and its two main smaller rivers are Mo Chhu and Pho Chhu.
Kameng River
Another important river that flows into the Brahmaputra is the Jia Bhorali River, also called the Kameng River. It starts in the Tawang district of Arunachal Pradesh from a glacial lake near the Gori Chen Mountain. The river flows through Arunachal Pradesh, the Sonitpur district in Assam, and Tezpur before joining the Brahmaputra.
Dhansiri River
It begins in Nagaland’s Laisang Peak and runs through the districts of Dimapur and Golaghat before entering the Brahmaputra approximately five kilometres from the Kaziranga Wildlife Sanctuary.
Dihing River
Before joining the Brahmaputra in Dihingmukh, it runs through the Assamese districts of Tinsukia, Dibrugarh, and Arunachal Pradesh, starting in the eastern Himalayas’ Patkai mountain range. Numerous oxbow lakes can be found along Dihing’s route.
Lohit River
Another significant tributary of the Brahmaputra is the Lohit River. Its source is in the Zayal Chu range in eastern Tibet, and it runs through Arunachal Pradesh for two kilometres before it enters the plains of Assam. At this point it combines with the Siang and forms the Brahmaputra at the head of the valley. Due to the river’s turbulence, it was given the name Lohit.
Tista River
Another tributary of the Brahmaputra is the Tista or Teesta River, which rises in Cholomo Lake in Sikkim and flows across the Himalayan Mountains before entering Bangladesh and joining the Brahmaputra there.
Subansiri River
A river that rises in China’s Himalayas and runs into Tibet and India. It enters the Brahmaputra in the Lakhimpur district of Assam and is 442 kilometres long.
Bhogdoi River
The Bhogdoi River is another river that flows into the Brahmaputra. It starts in the Naga Hills, goes through the city of Jorhat in Assam, and then joins a smaller river before merging with the main Brahmaputra. These two rivers together are called Gelabill, and it was once known as Desoi.
Brahmaputra River flows through which States?
| Brahmaputra Flows through these states |
|
Other Indian Geography Topics
Other Fundamental Geography Topics


 Daily Quiz 14 April 2025
Daily Quiz 14 April 2025
 UPSC Syllabus 2025, Check UPSC CSE Sylla...
UPSC Syllabus 2025, Check UPSC CSE Sylla...
 EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...
EU Plans to Slash General Data Protectio...





















