Table of Contents
Bitcoin, the world’s largest cryptocurrency, has recently broken through the $89,000 mark, sparking widespread interest and excitement among investors. This surge comes after years of stagnation, raising the question: Is the “crypto winter” finally over?
Bitcoin’s Surge Past $89,000
Bitcoin’s recent surge past $89,000 is fueled by a combination of factors, including optimism surrounding Donald Trump’s election as U.S. president and speculation about pro-crypto policies. His campaign promises, such as turning the U.S. into a global hub for digital assets, have sparked renewed interest in the cryptocurrency market. Additionally, the potential easing of regulatory pressures from the SEC, coupled with growing institutional interest, including Bitcoin ETFs, has contributed to the rally. The Federal Reserve’s rate cut and historical trends following U.S. presidential elections also play a significant role in Bitcoin’s price surge. While the market remains volatile, the outlook for Bitcoin remains positive, with the possibility of reaching $100,000.
What Is Bitcoin?
- What is It?: Bitcoin is a digital currency that exists only in electronic form, unlike physical currencies such as dollars or euros.
- Introduced by: Satoshi Nakamoto, as a payment system that is powered by mathematical algorithms.
- Creation and Access: The creation of Bitcoin is a communal process, open to anyone, where the currency is produced through a technique called mining, which requires computational resources contributed by a distributed network of processors.
Key Features of Bitcoin
- Usable For Transactions: Similar to traditional forms of money that can be transacted digitally, Bitcoin can be used for electronic purchases.
- Decentralised: A key feature of Bitcoin is its decentralised nature, meaning no single entity or institution has governance over the Bitcoin network.
- The decentralised aspect of Bitcoin is a comfort to some users who prefer not to have their funds under the control of any banks or central institutions.
- Anonymity: Users are not directly identified in transactions, but the transactions themselves are publicly viewable.
- Low fees: Transaction fees are generally lower than traditional bank transfer fees.
We’re now on WhatsApp. Click to Join
|
Note |
| Satoshi: The smallest unit- one hundred millionth of a Bitcoin. |
About Bitcoin Halving
- A bitcoin halving (sometimes ‘halvening’) is an event where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, i.e. miners receive 50% fewer bitcoins for verifying transactions.
- Bitcoin halvings are scheduled to occur once every every four years until the maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins has been generated by the network.
- Bitcoin halvings are important events for traders because they reduce the number of new bitcoins being generated by the network.
- This limits the supply of new coins, so prices could rise if demand remains strong.
About Cryptocurrencies
- Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual form of currency secured by cryptography, making it challenging to counterfeit.
- It operates independently of any governmental or institutional control, classifying it as a decentralised currency.
- Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Stellar and Litecoin.
Working of Cryptocurrencies
- Cryptocurrencies function through a technology called blockchain, a public digital ledger that records all transactions across a global network of computers.
- Computers in the network verify and add transactions to the blockchain, ensuring security and transparency.
- To engage with cryptocurrencies, users must have a digital wallet, which safeguards their public and private keys necessary for conducting transactions.
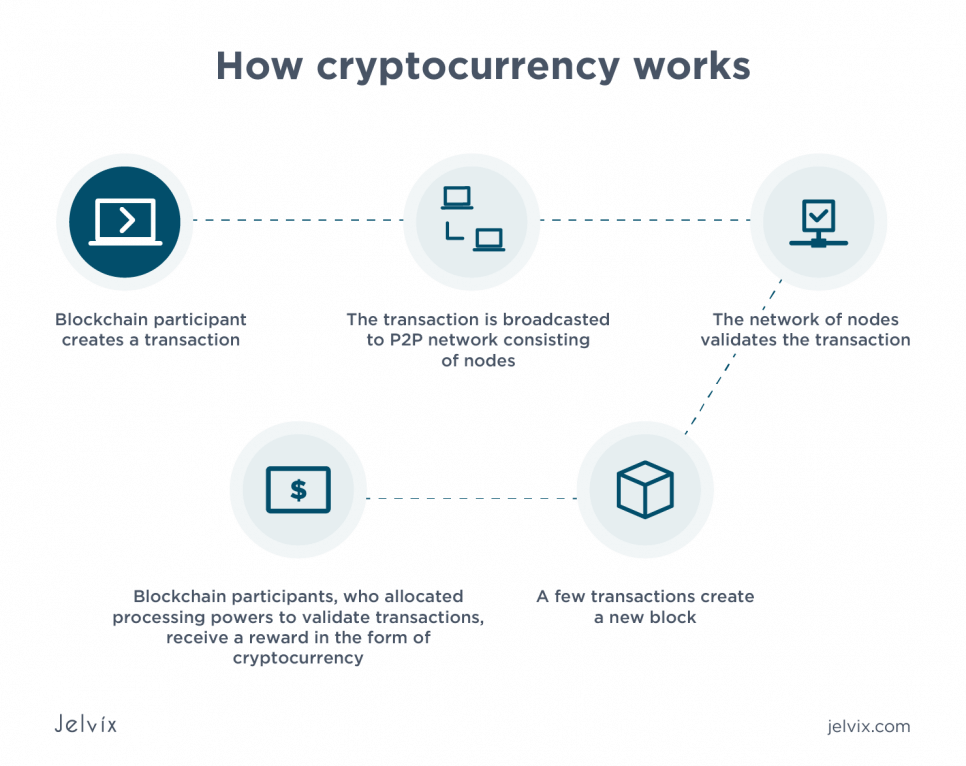
- Public and private keys in the wallet are essential for sending, receiving, and verifying the authenticity of cryptocurrency transactions.
- Cryptocurrency can be obtained through mining, a process where individuals use computational power to solve complex puzzles, securing transactions on the blockchain and earning cryptocurrency as a reward.


 SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0: Transforming I...
 BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
BHIM 3.0 Launched by NPCI: Key Features,...
 150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...
150th Summit of Inter-Parliamentary Unio...





















